Quantitative control over localization of key proteins in mesenchymal stem cells
Credit: Tokyo Metropolitan University
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have been quantifying how different batches of mesenchymal stem cells respond to the mechanical stiffness of their environments. They focused on how certain proteins were “localized” in cell nuclei and found key trends in how this changed with stiffness. Their findings explain inconsistencies between previous findings and may guide how scientists control the state of stem cells for research and medical treatments.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are important “progenitor” cells that can transform into muscle, cartilage, bone or fat cells. In 2006, pioneering work by Engler and coworkers showed that they could control what cell type mesenchymal stem cells transformed (or “differentiated”) into by simply placing them on surfaces with a different mechanical stiffness, or elastic modulus. Ever since, scientists have been trying to identify exactly how this occurs. The trouble is, despite the phenomenon being robust and reproducible, it turns out that they are very sensitive to the exact environment into which they are placed, even which batch they came from. The stakes are high: reliable control over MSC states would mean more research and even potential biomedical applications.
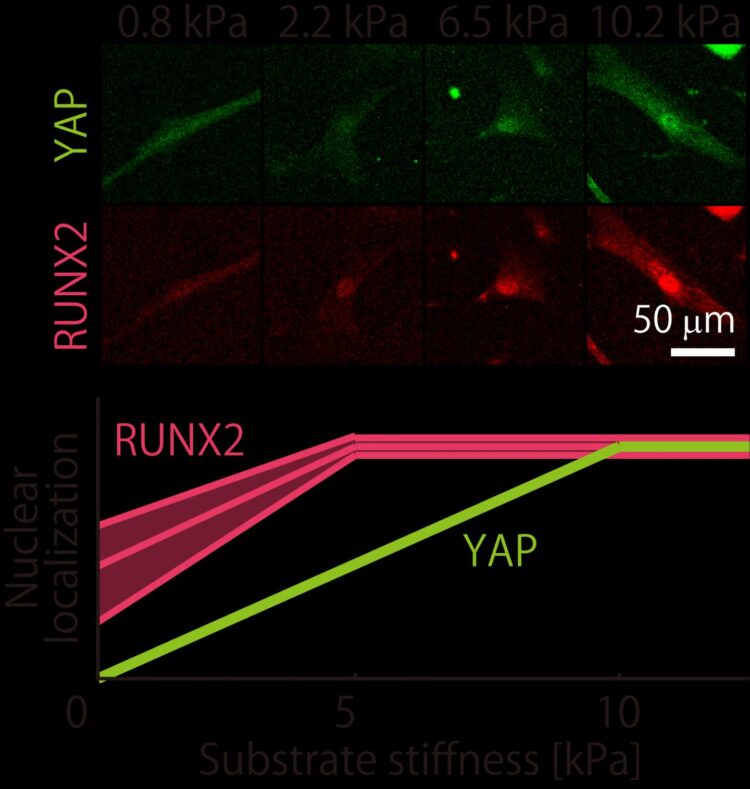
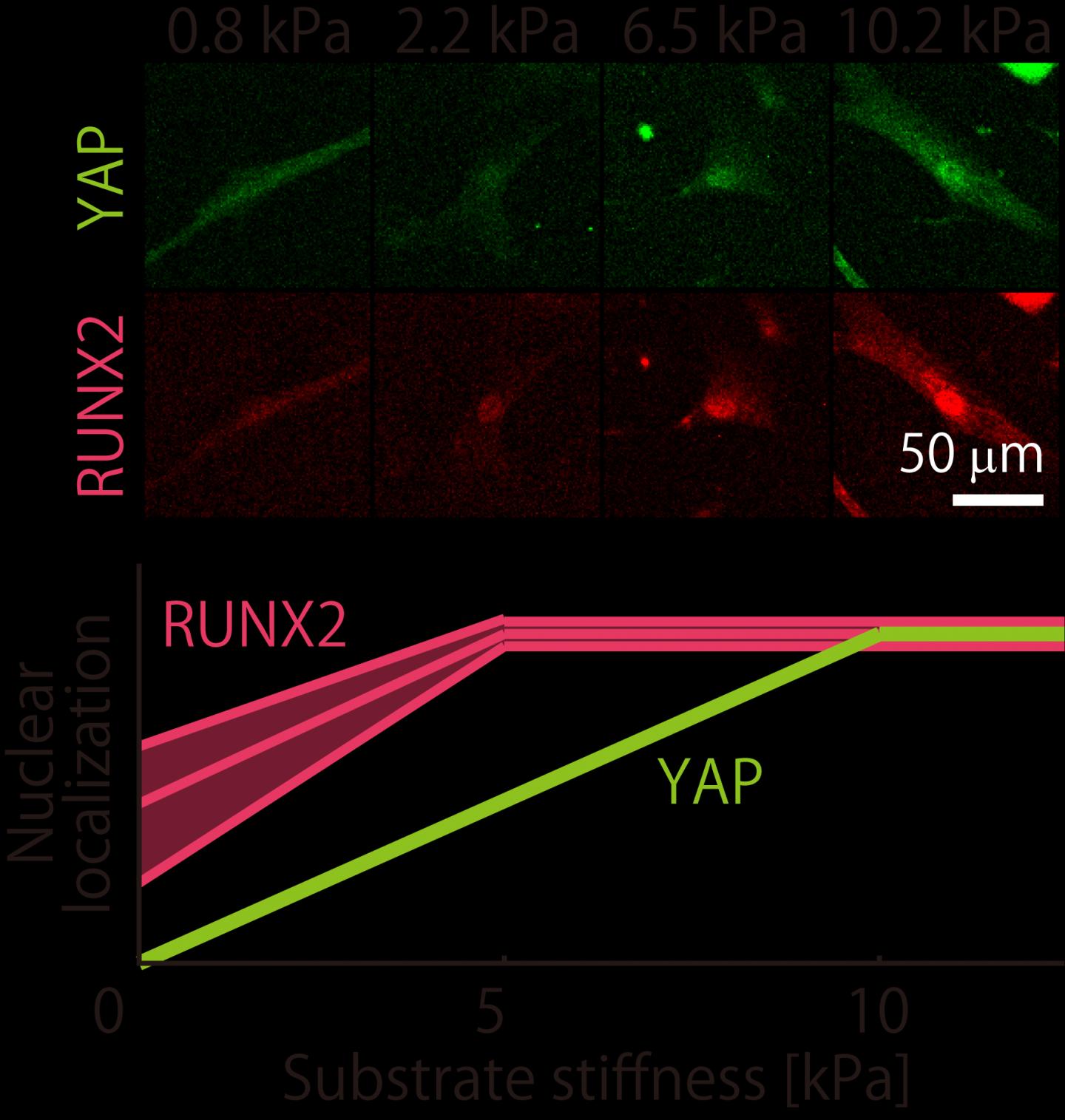
This search inspired a team led by Associate Professor Hiromi Miyoshi of Tokyo Metropolitan University to look at how different batches of MSCs respond to different environments. They focused on two proteins present in MSCs, the YAP protein, which helps cells respond to mechanical environments, and RUNX2, a key player in helping MSCs turn into osteoblasts which eventually become bone. They looked at how different MSC batches have different distributions of YAP and RUNX2 inside their cells. For their “stiff” environments, they chose a specially designed gelatin substrate which had significantly better reproducibility than popular collagen alternatives.
From the beginning, they found that their batches were quite distinct. In basic experiments looking at how they turned into bone-making or fat-making cells, they found that the batches produced very different levels of calcium and fat deposits. But when it came to their mechanoresponsive behavior, it turned out they were not as wildly distinct as initially thought. Firstly, the team found that the proportion of YAP found in the nuclei of cells (or “localization”) turns out to vary in a consistent manner between batches, plateauing at the same stiffness. For RUNX2, though the localization varied differently, they still plateaued at a specific stiffness value (a different one to YAP). Even then, the trend in RUNX2 localization was linear up to the plateau.
With this kind of information, anyone could make a gel of a specific stiffness and actively control the level of YAP/RUNX2 in the nucleus of mesenchymal stem cells. By doing so, they could tune when and how their cells differentiate. The team hope this new level of control over cell fate will help accelerate research into MSCs and potentially lead to therapeutic applications.
###
This work was supported by a JSPS KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid of Scientific Research (JP19J13048) and AMED under grant number 18gm5810012h9904.
Media Contact
Go Totsukawa
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.