Researchers from Nara Institute of Science and Technology identify antioxidant properties of a ginger-derived compound that may help fight inflammatory diseases
Credit: Daisuke Ori
Ikoma, Japan – Many natural compounds have various anti-inflammatory and other beneficial properties that humans have been utilizing for medicinal purposes for hundreds of years. However, the specific molecular mechanisms behind these health-promoting effects are not always clear. One such compound is 1′-acetoxychavicol acetate, or ACA, which comes from the tropical ginger Alpinia plant. Now, researchers from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) have identified how ACA can help in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
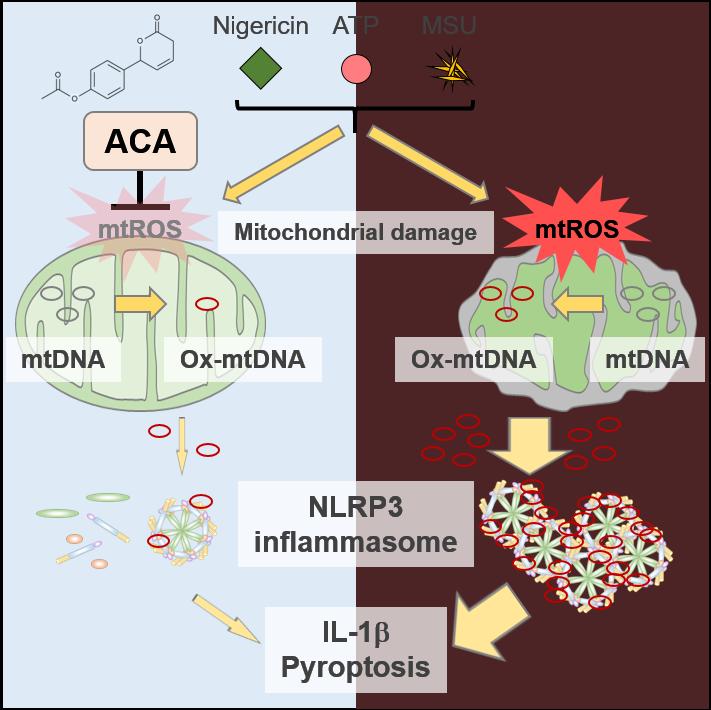
In a report published in International Immunology, they found that ACA attenuates mitochondrial damage through decreasing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS), blocking activation of a crucial protein complex known as the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. Many inflammatory diseases, like inflammatory bowel disease, display improper and chronic activation of this complex.
Previous work has suggested that the NLRP3 inflammasome plays a significant role in promoting inflammation by secreting a molecule called IL-1?. This acts as a messenger that recruits various immune cells to the site of injury or infection. Additional studies described how production of ROS can help trigger activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Because other groups showed that ACA can reduce ROS production in certain immune cells, the NAIST researchers became curious how this compound would impact the NLRP3 inflammasome and its functions.
“Many disease pathogeneses involve dysregulation of the inflammasome,” says Daisuke Ori, co-lead author on the study. “Blood cells from people suffering from rheumatoid arthritis or other autoimmune disorders frequently have increased levels of inflammasome-derived IL-1?. Therefore, targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome with a compound like ACA may be a promising therapeutic strategy.”
The researchers grew immune cells in culture that were obtained from mouse bone marrow, and also used a mouse model of colitis. ACA was added to the growing cells and the live mice were given the compound in their food. The researchers then examined the effects on ROS production, secretion of IL-1?, and other markers of inflammation.
“Cells treated with ACA had significantly reduced IL-1? production, as well as lower levels of ROS,” explains Taro Kawai, senior author. “ACA could also inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the colitis mouse model.” These in vivo results are promising, as they suggest ACA has the potential to treat or prevent the development of inflammatory diseases. “Interestingly, we did not observe high levels of immune cell death when using ACA, which means that it may be relatively safe,” continues Ori.
This work provides novel evidence for a specific molecular mechanism governing the previously observed anti-inflammatory properties of ACA. Furthermore, it highlights the potential of ACA for therapeutic use in diseases mediated by IL-1? molecules, or associated with cytokine storm occurrence, as seen in patients suffering from severe COVID-19.
###
Resource
Title: 1?-acetoxychavicol acetate inhibits NLRP3-dependent inflammasome activation via mitochondrial ROS suppression
Authors: Sophia P. M. Sok, Daisuke Ori, Ayana Wada, Haruna Okude, Takumi Kawasaki, Masatoshi Momota, Noor Hasima Nagoor & Taro Kawai
Journal: International Immunology
DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxab016
Information about the Molecular Immunobiology Laboratory can be found at the following website:
https:/
Media Contact
Takahito Shikano
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




