Credit: Photo: Pengbo Liang/University of Freiburg
What would it be like to produce fertilizer in your own basement? Leguminous plants, like peas, beans, and various species of clover, obtain the organic nitrogen they need for their growth from symbiotic soil bacteria via specialized structures in their roots. A team led by the cell biologist Prof. Dr. Thomas Ott from the University of Freiburg’s Faculty of Biology has now detected a factor in the root cells that the plants need for the initial contact with these so-called root-associated bacteria, which live in the soil. They discovered a protein found only in legumes called symbiotic formin 1 (SYFO1) and demonstrated the essential role it plays in symbiosis. Together with the molecular biologist Prof. Dr. Robert Grosse University of Freiburg’s Faculty of Medicine and the evolutionary biologist Dr. Pierre-Marc Delaux from the Laboratoire de Recherche en Sciences Végétales (LRSV) in Toulouse/France, the team published their results in the journal Current Biology.
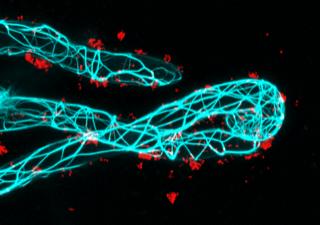
When a root nodule bacterium encounters the roots of a leguminous plant in the soil, the SYFO1 protein causes the tiny hairs of the root to change the direction of their growth. They thus wrap themselves around the potential symbiotic partner. Thanks to these bacterial helpers, legumes do not need any nitrogenous fertilizer, in contrast to other plants. “If we understood precisely how the symbiosis comes into being, we could give crop plants back this special property they have lost in the course of evolution,” says Ott. Both he and Grosse are members of the Cluster of Excellence CIBSS – Centre for Integrative Biological Signalling Studies. Ott’s research at CIBSS involves studying the spatial organization of the signaling paths that enable the symbiotic relationship with symbiotic bacteria in the first place. Grosse, on the other hand, focuses in his work in Freiburg on the cytoskeleton of animal cells. “In our collaboration, which was made possible by CIBSS, we were able to contribute our expertise in different areas of specialization in the best possible way,” says Ott.
The team demonstrated in the legume Medicago truncatula (barrel medic) that the root hairs of plants in which the gene for SYFO1 has been switched off are practically no longer capable of wrapping themselves around the bacteria. In further studies, the researchers discovered that the protein binds to actin, a component of the cytoskeleton, and at the same time to the cell wall outside the cells, thus changing the direction of its growth: Instead of growing straight, the tiny hairs now change their direction and form a loop around the bacterium.
“SYFO1 constitutes a special innovative step in the evolution of the plants,” explains Ott. “While formin proteins are present in many forms in cells and interact with actin, this special type only responds to symbiotic signals from the bacteria.”
###
CIBSS – Centre for Integrative Biological Signalling Studies
https:/
Media Contact
Prof. Dr. Thomas Ott
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




