Credit: Xingang Wang/Lippman lab, CSHL/2021
Both people and tomatoes come in different shapes and sizes. That is because every individual has a unique set of genetic variations–mutations–that affect how genes act and function. Added together, millions of small genetic variations make it hard to predict how a particular mutation will impact any individual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor and Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator Zach Lippman showed how genetic variations in tomatoes can influence the way a specific mutation affects the plant. He is working toward being able to predict the effects of mutations on different tomato varieties.
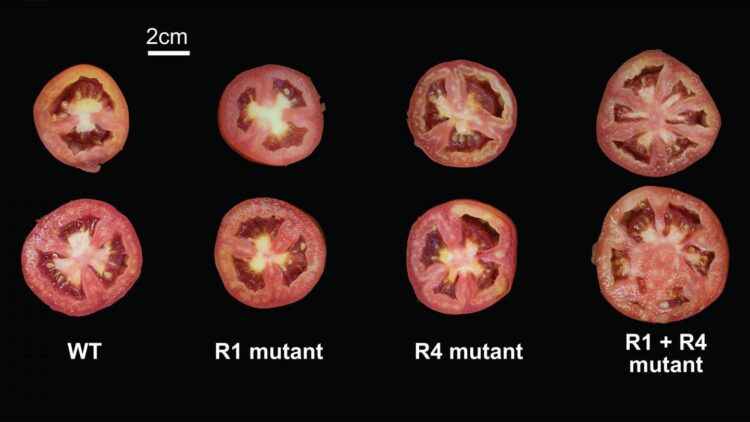
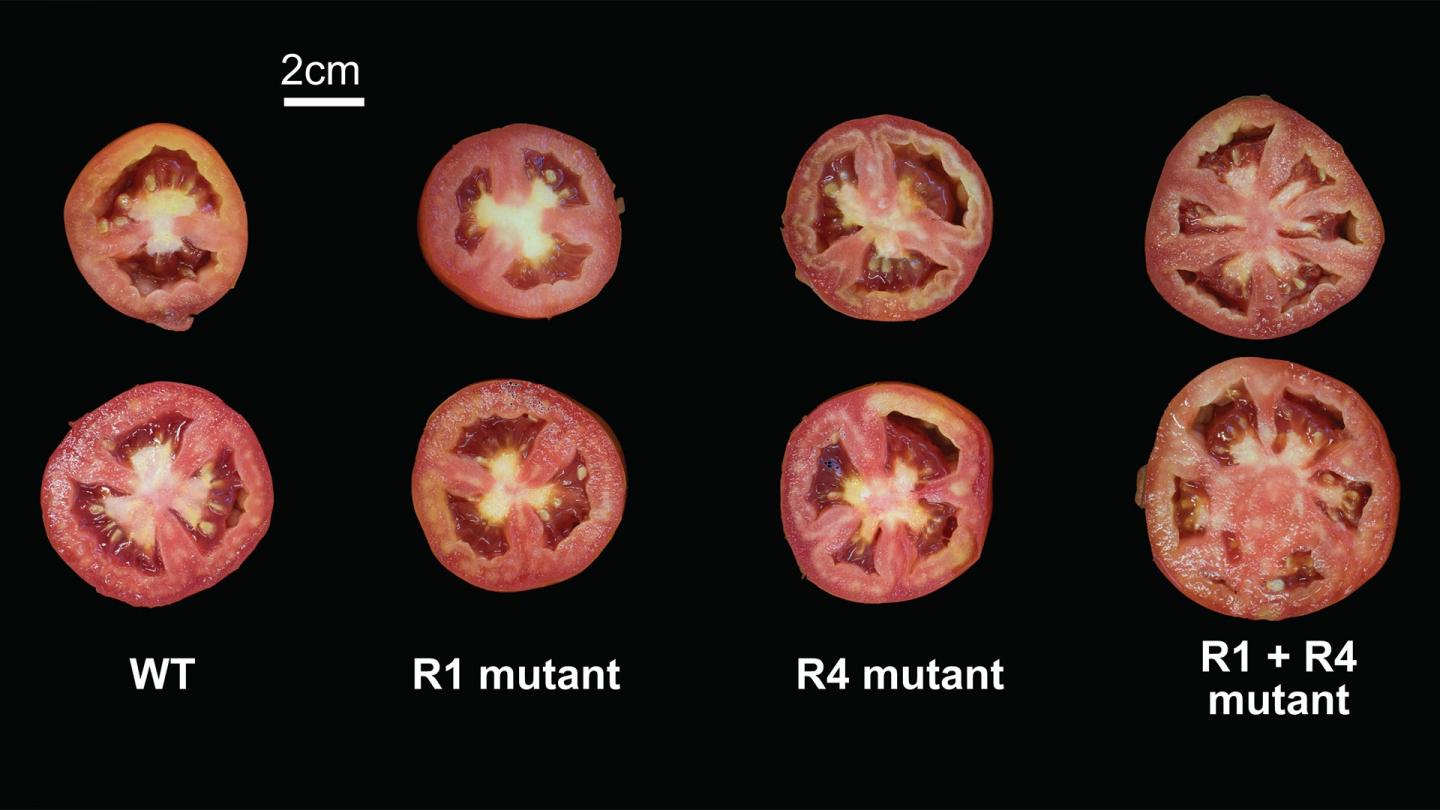
In this study, Lippman and his team used CRISPR, a highly accurate and targeted gene-editing tool, on two tomato genes that control fruit size, SlCV3 and SlWUS. They generated over 60 tomato mutants by removing little pieces of DNA in the promoter regions, areas near the genes that control their expression. In some cases, individual mutations increased the size of the tomatoes by a little bit. Some pairs of mutations did not change fruit size at all. A few synergistic combinations caused a dramatic, unpredicted increase in fruit size. Lippman says:
“The real Holy Grail in all this for crop breeding is predictability. If I mutate this sequence, I’m going to get this effect. Because there is this sea of other variants that nature has accumulated nearby the mutation that you’re engineering, as well as scattered throughout the genome, many of which could be influencing the specific mutation that you’re creating.”
This range of interactions for any two mutations models the consequences of a single mutation occurring in different genetic backgrounds. The effect is comparable to those found in some human diseases, where some people might have certain pre-existing mutations that protect them from disease-causing mutations.
Lippman and his team will continue quantifying how individual and combined mutations affect certain crop traits. So far, they have measured interactions between two individual mutations, but genomes have millions of variations. Lippman hopes to study enough measurable interactions to make breeding more predictable and efficient.
###
Media Contact
Sara Roncero-Menendez
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.