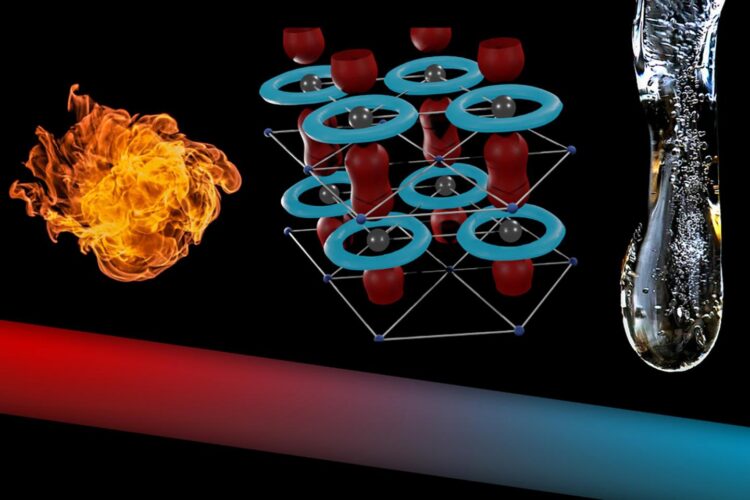
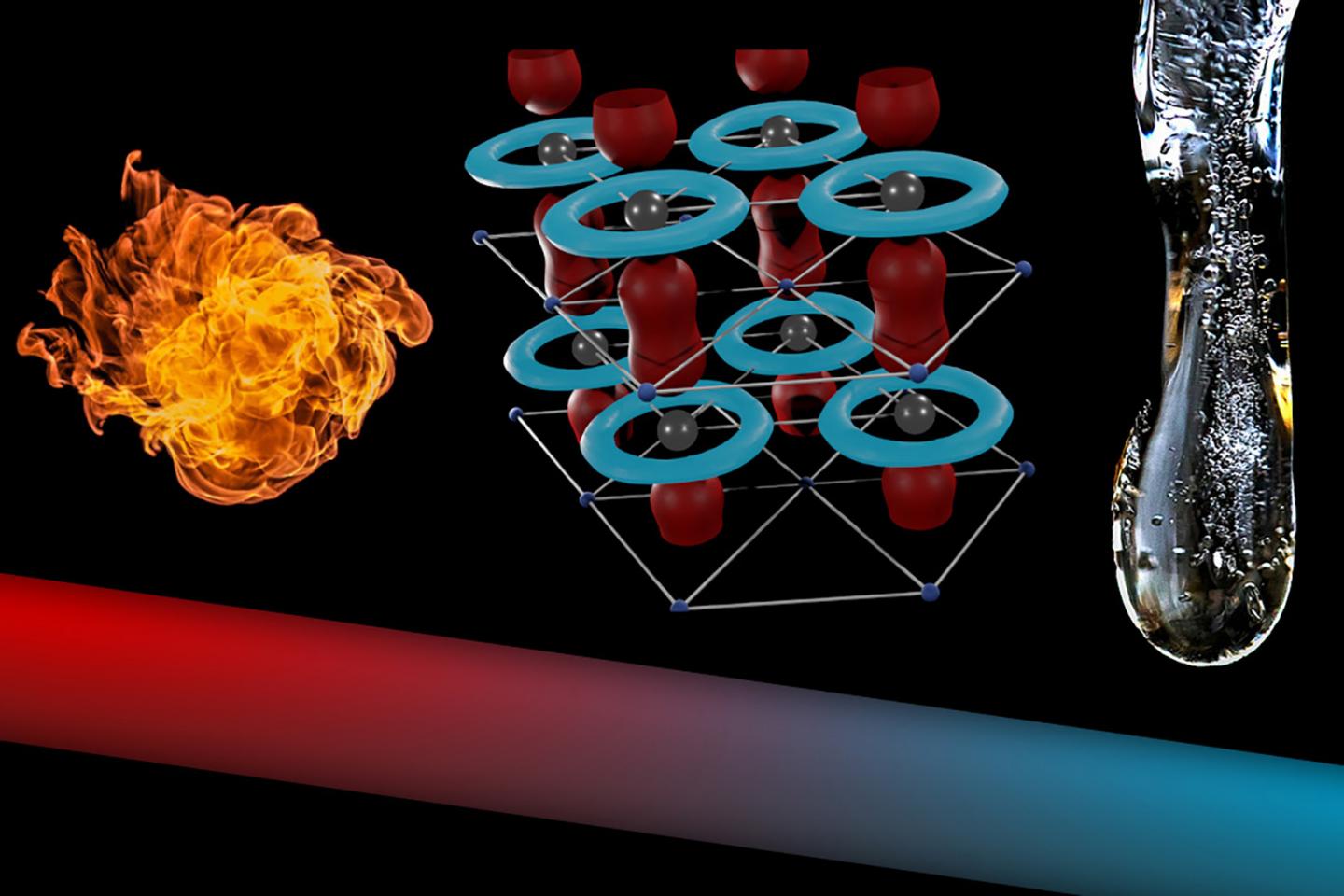
How can we remove heat from computer chips as fast as possible? At TU Wien, a metal compound has now been identified that is particularly well suited for this purpose.
Credit: TU Wien
A thermos bottle has the task of preserving the temperature – but sometimes you want to achieve the opposite: Computer chips generate heat that must be dissipated as quickly as possible so that the chip is not destroyed. This requires special materials with particularly good heat conduction properties.
In collaboration with groups from China and the United States, a research team from TU Wien therefore set out to find the optimal heat conductor. They finally found what they were looking for in a very specific form of tantalum nitride – no other known metallic material has a higher thermal conductivity. In order to be able to identify this record-breaking material, they first had to analyse which processes play a role in heat conduction in such materials at the atomic level. The results have now been published in the scientific journal Physical Review Letters.
Electrons and lattice vibrations
“Basically, there are two mechanisms by which heat propagates in a material,” explains Prof. Georg Madsen from the Institute of Materials Chemistry at TU Wien. “Firstly, through the electrons that travel through the material, taking energy with them. This is the main mechanism in good electrical conductors. And secondly through the phonons, which are collective lattice vibrations in the material.” The atoms move, causing other atoms to wobble. At higher temperatures, heat conduction through propagation of these vibrations is usually the decisive effect.
But neither the electrons nor the lattice vibrations can propagate completely unhindered through the material. There are various processes that slow down this propagation of thermal energy. Electrons and lattice vibrations can interact with each other, they can scatter, they can be stopped by irregularities in the material.
In some cases, heat conduction can even be dramatically limited by the fact that different isotopes of an element are built into the material – i.e. similar atoms with different numbers of neutrons. In that case, the atoms do not have exactly the same mass, and this affects the collective vibrational behaviour of the atoms in the material.
“Some of these effects can be suppressed – but usually not all at the same time,” says Georg Madsen. “It’s like playing Whack-A-Mole: You solve one problem, and at the same time a new one arises somewhere else.”
Tantalum nitride, the all-rounder
Despite our everyday experience of burning our hands on a hot metal plate, metals typically have a mediocre thermal conductivity. The metal with the highest known thermal conductivity is silver – with only a fraction of the conductivity of the record holding material diamond. But diamonds are expensive and very difficult to process.
With elaborate theoretical analyses and computer simulations, the team finally succeeded in identifying a suitable material: The hexagonal θ-phase of tantalum nitride. Tantalum is particularly favourable because there are hardly any different isotopes. Almost 99.99% of the naturally occurring tantalum is the isotope tantalum 181, other variants hardly occur.
“The combination with nitrogen and the special atomic scale geometry make the phase metallic, and it suppresses interactions of the heat carrying vibrations with other vibrations and with the conducting electrons. It is exactly those interactions that inhibit heat conduction in other materials,” says Georg Madsen. “These interactions are not possible in this material because they would violate the law of energy conservation.”
Therefore, this form of tantalum nitride combines several important advantages, making it a record-breaking material with a thermal conductivity several times higher than silver and comparable to diamond.
“For the chip industry, tantalum nitride is a highly promising material,” Madsen is convinced. “Chips are getting smaller and more powerful, so conducting heat is becoming a bigger and bigger problem. No other material solves this problem better than the θ-phase tantalum nitride.”
###
Contact
Prof. Georg Madsen
Institut für Materialchemie
Technische Universität Wien
+43 1 58801 165306
[email protected]
Media Contact
Florian Aigner
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.