These reactions should not discourage patients from getting the vaccine, say researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital
Credit: Massachusetts General Hospital
BOSTON – As the speed and scale of vaccinations against the SARS-CoV-2 virus ramps up globally, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) are calling for greater awareness and communication around a delayed injection-site reaction that can occur in some patients who have received the Moderna mRNA-1273 vaccine.
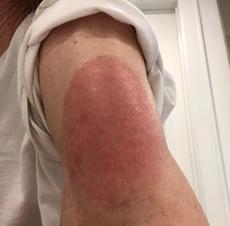
In a letter to the editor published online in The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), the authors note Phase 3 clinical data from the Moderna vaccine trial did show delayed skin hypersensitivity in a small number of the more than 30,000 trial participants. However, the authors say the large, red, sometimes raised, itchy or painful skin reactions were never fully characterized or explained, and they warn clinicians may not be prepared to recognize them and guide patients on treatment options and completion of the second dose of the vaccine.
“Whether you’ve experienced a rash at the injection site right away or this delayed skin reaction, neither condition should prevent you from getting the second dose of the vaccine,” says Kimberly Blumenthal, MD, MSc, lead author of the letter and co-director of the Clinical Epidemiology Program in the division of Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology at MGH. “Our immediate goal is to make physicians and other care providers aware of this possible delayed reaction, so they are not alarmed, but instead well-informed and equipped to advise their patients accordingly.”
In the letter, Blumenthal and her co-authors also note their own clinical observations of the delayed, large, local reactions to the Moderna vaccine, and report on a series of 12 patients with the reactions. In that group, symptom onset ranged from four days after the first dose up to 11 days post-vaccination, with a median onset of symptoms on day eight. Photographs show the varied size and severity of the reactions. Most patients were treated with ice and antihistamines, although some required corticosteroids and one was erroneously treated with antibiotics.
“Delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity could be confused – by clinicians and patients alike – with a skin infection,” says letter co-author Erica Shenoy, MD, PhD, associate chief of the MGH Infection Control Unit. “These types of reactions, however, are not infectious and thus should not be treated with antibiotics.”
On average, symptoms cleared up after nearly a week for the group of 12 reported in the letter. Half of the patients went on to experience a reaction after the second dose – at or around 48 hours post-vaccination. No patient experienced a dose two reaction that was more severe than their dose one reaction.
The authors also say samples taken from skin biopsies confirmed their suspicion of a delayed allergic immune response that is commonly seen in drug reactions.
“For most people who are experiencing this, we believe it’s tied to the body’s immune system going to work,” says Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, director of Global Health Dermatology at MGH and co-author of the NEJM letter. “Overall, this data is reassuring and should not discourage people from getting the vaccine.”
###
To learn more about potentially allergic reactions after COVID-19 vaccination, MGH Allergy is collecting all immediate and delayed reactions in a designated registry.
Additional co-authors of the NEJM letter were Aleena Banerji, MD, Ruth Foreman, MD, PhD, Dean Hashimoto, MD, Lacey Robinson, MD, MPH, Rebecca Saff, MD, and Anna Wolfson, MD, all from MGH; Lily Li, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital; and Sara Anvari, MD, MSc, Baylor College of Medicine, Texas Children’s Hospital.
About the Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital, founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The Mass General Research Institute conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the nation, with annual research operations of more than $1 billion and comprises more than 9,500 researchers working across more than 30 institutes, centers and departments. In August 2020, Mass General was named #6 in the U.S. News & World Report list of “America’s Best Hospitals.”
Media Contact
Julie Cunningham
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




