Credit: Marine Life Science & Technology
Co-culture: stimulate the metabolic potential and explore the molecular diversity of natural products from microorganisms
Announcing a new publication for Marine Life Science & Technology journal. In this review article the authors Xiao-Yue Peng, Jin-Tao Wu, Chang?Lun Shao, Zhi-Yong Li, Min Chen and Chang-Yun Wang from the Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao, China and Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China consider the metabolic potential and molecular diversity of natural products from microorganisms.
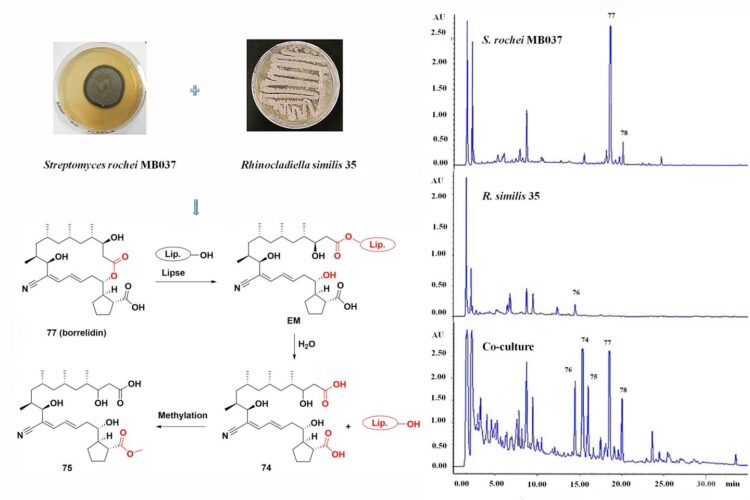
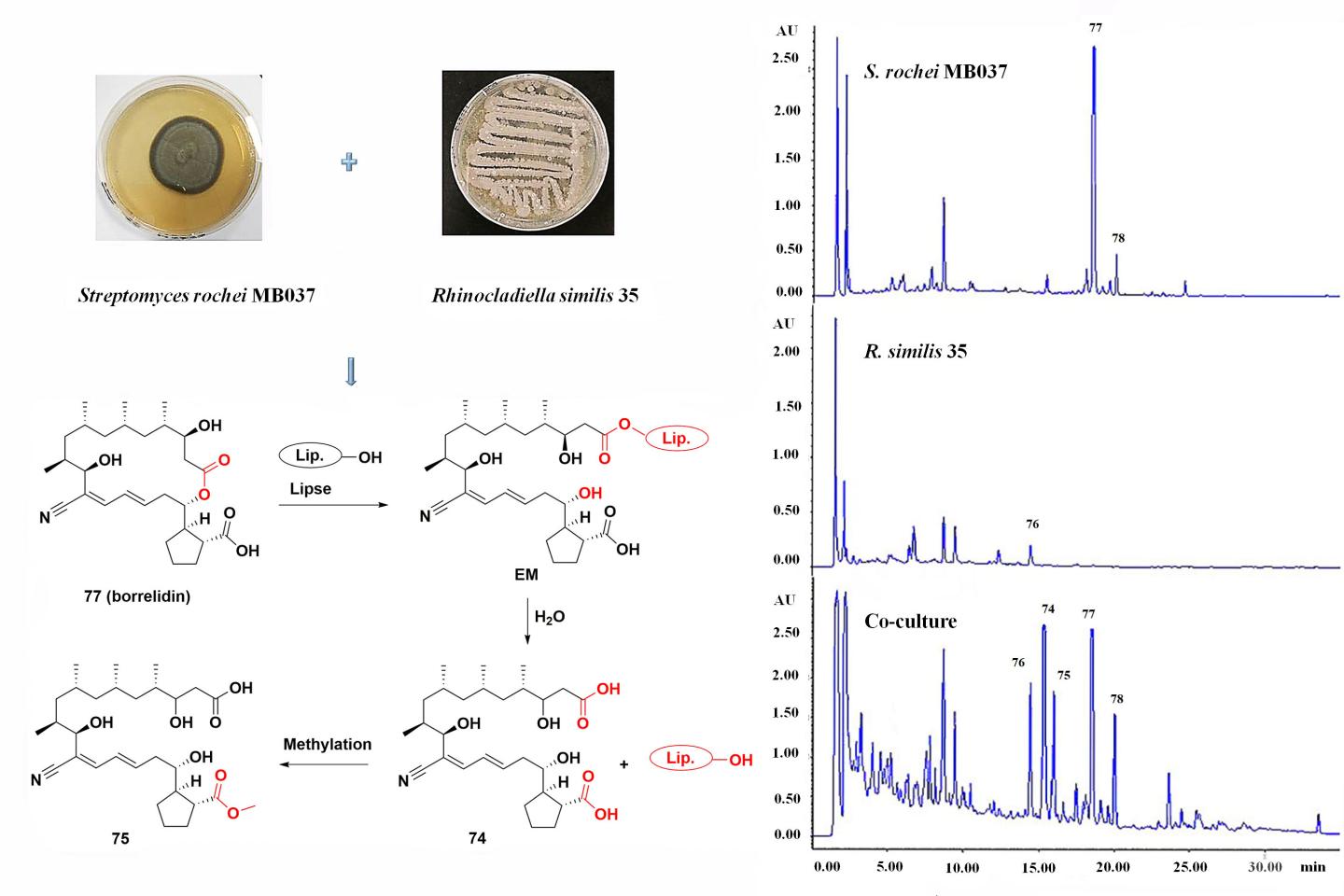
Microbial secondary metabolites have long been considered as potential sources of lead compounds for medicinal use due to their rich chemical diversity and extensive biological activities. However, many biosynthetic gene clusters remain silent under traditional laboratory culture conditions, resulting in repeated isolation of a large number of known compounds. Co-culture strategy simulates the complex ecological environment of microbial life by using an ecology-driven method to activate silent gene clusters of microorganisms and tap their metabolic potential to obtain novel bioactive secondary metabolites.
In this article the authors review representative studies from 2017 to 2020 on the discovery of novel bioactive natural products from co-cultured microorganisms. A series of natural products with diverse and novel structures have been discovered successfully by co-culture strategies, including fungus-fungus, fungus-bacterium, and bacterium-bacterium co-culture approaches. These novel compounds exhibited various bioactivities including extensive antimicrobial activities and potential cytotoxic activities, especially when it came to disparate marine-derived species and cross-species of marine strains and terrestrial strains.
The authors conclude that co-culture can be an effective strategy to tap the metabolic potential of microorganisms, particularly for marine-derived species, thus providing diverse molecules for the discovery of lead compounds and drug candidates.
###
Article reference: Xiao-Yue Peng, Jin-Tao Wu, Chang-Lun Shao, Zhi-Yong Li, Min Chen and Chang-Yun Wang, Co-culture: stimulate the metabolic potential and explore the molecular diversity of natural products from microorganisms, Marine Life Science & Technology, 2020, ISSN 2662-1746, https:/
Keywords: Co-culture, Microorganisms, Secondary metabolites, Chemical diversity
Marine Life Science & Technology (MLST) provides a platform that introduces new discoveries and theories associated with marine organisms, bioresources, and biotechnology. The journal is intended for marine scientists, biological oceanographers, conservation biologists, marine technologists, policy makers and legislators. Accordingly, we publish original research papers across a broad range of marine life sciences and technologies with an emphasis on synergistic interactions of multiple disciplines. Both theoretical and practical papers are welcome, including laboratory and field experimental studies relevant to marine life science and technology. Focused reviews, viewpoints, comments, and short communications are also accepted. As the journal’s aim is to foster multidisciplinary approaches to marine sciences, authors are encouraged to emphasise the relevance of their work in relation across the journals key-disciplines.
For more information, please visit https:/
Editorial Board: https:/
MLST is available on SpringerLink (https:/
Submissions to MLST may be made using ScholarOne ManuscriptsTM (https:/
Abstracted and indexed in:
Astrophysics Data System (ADS)
CNKI
Dimensions
EBSCO Discovery Service
Google Scholar
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China
Meta
Naver
OCLC WorldCat Discovery Service
ProQuest-ExLibris Primo
ProQuest-ExLibris Summon
TD Net Discovery Service
ISSN 2662-1746
Media Contact
Morgan Lyons
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.