Credit: Osei-Safo 2020 (CC-BY 2.0)
The discovery of new drugs is vital to achieving the eradication of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) in Africa and around the world. Now, researchers reporting in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases have identified traditional Ghanaian medicines which work in the lab against schistosomiasis, onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis, three diseases endemic to Ghana.
The major intervention for NTDs in Ghana is currently mass drug administration of a few repeatedly recycled drugs, which can lead to reduced efficacy and the emergence of drug resistance. Chronic infections of schistosomiasis, onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis can be fatal. Schistosomiasis is caused by the blood flukes Schistosome haematobium and S. mansoni. Onchocerciasis, or river blindness, is caused by the parasitic worm Onchocerca volvulus. Lymphatic filariasis, also called elephantiasis, is caused by the parasitic filarial worm Wuchereria bancrofti.
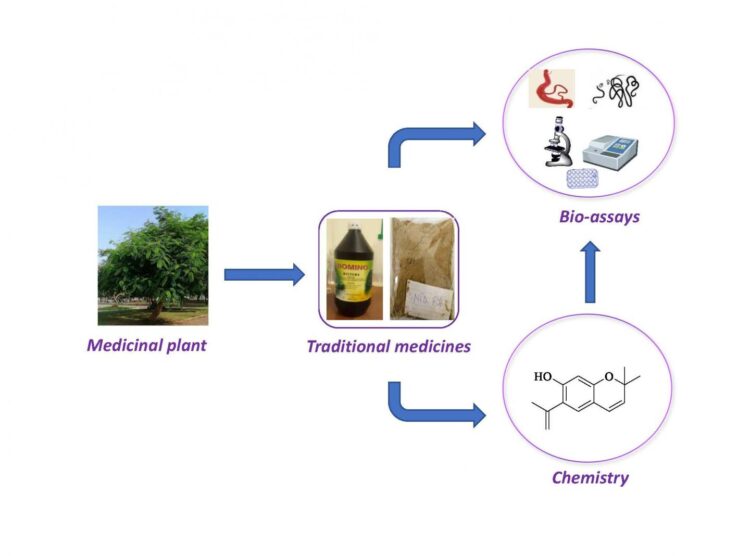
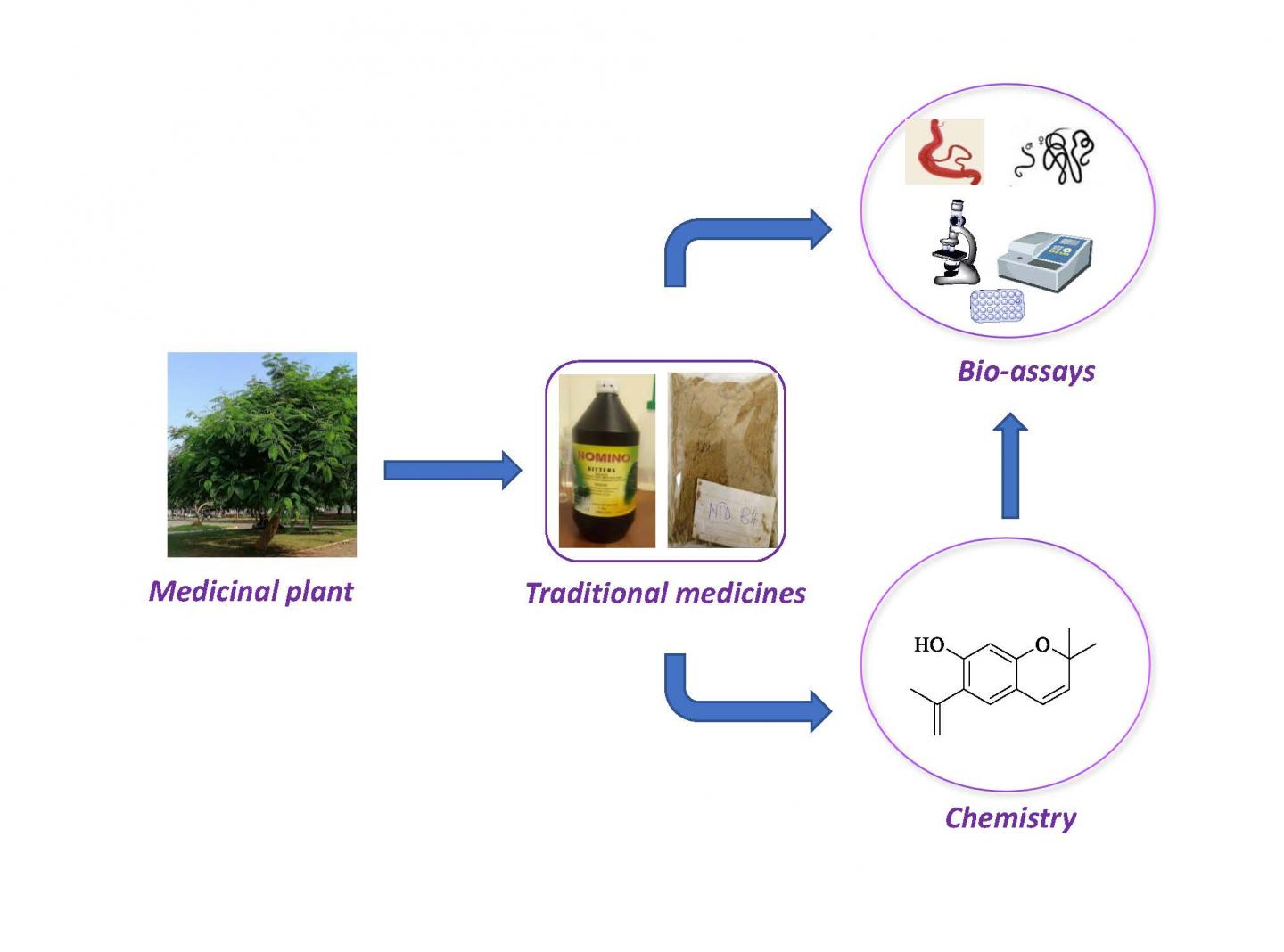
In the new work, Dorcas Osei-Safo of the University of Ghana, and colleagues obtained–from the Ghana Federation of Traditional Medicines Practitioners Association–15 traditional medicines used for treating NTDs in local communities. The medicines were available in aqueous herbal preparations or dried powdered herbs. In all cases, crude extracts were prepared from the herbs and screened in the laboratory for their ability to treat various NTDs.
Two extracts, NTD-B4-DCM and NTD-B7-DCM, displayed high activity against S. mansoni adult worms, decreasing the movement of the worms by 78.4% and 84.3% respectively. A different extract, NTD-B2-DCM, was the most active against adult Onchocera onchengi worms, killing 100% of males and more than 60% of females. Eight of 26 crude extracts tested, including NTD-B4-DCM and NTD-B2-DCM, also exhibited good activity against trypanosomes–parasites that cause other human diseases but weren’t the original targets of the traditional medicines.
“By embracing indigenous knowledge systems which have evolved over centuries, we can potentially unlock a wealth of untapped research and shape it by conducting sound scientific investigations to produce safe, efficacious and good quality remedies,” the researchers say.
###
Peer-reviewed; Experimental study; Cells
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases:
http://journals.
Citation: Twumasi EB, Akazue PI, Kyeremeh K, Gwira TM, Keiser J, Cho-Ngwa F, et al. (2020) Antischistosomal, antionchocercal and antitrypanosomal potentials of some Ghanaian traditional medicines and their constituents. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 14(12): e0008919. https:/
Funding: DOS, KK, RKA, AF, LEA, RAO are grant recipients of the Worldwide Universities Network Research Development Fund 2017 from the Worldwide Universities Network (UK) and grant number 18-191 RG/CHE/AF/AC_G – FR 3240303659 from The World Academy of Sciences. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Media Contact
Dorcas Osei-Safo
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.