The article by Dr. Alberto Boretti and colleagues is published in Coronaviruses, 2020
Credit: Dr. Alberto Boretti, Dr. Bimal Banik, Dr. Stefania Castelletto, Bentham Science Publishers
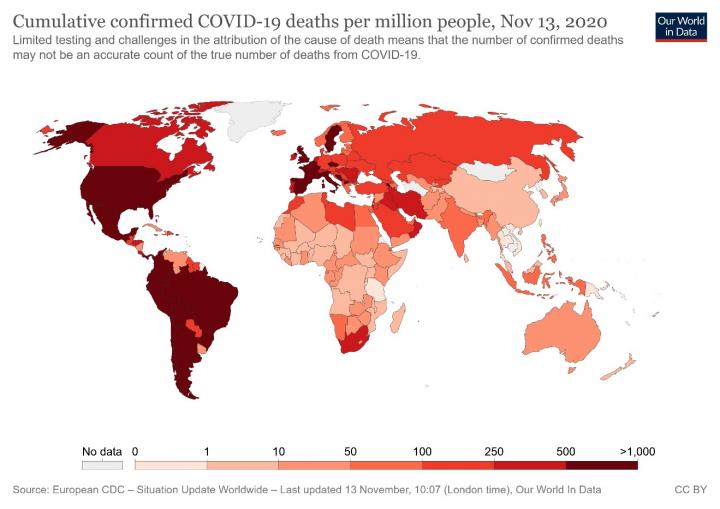
The recent serious outbreak of Covid19 has affected (November 13, 2020) 53,796,098 people worldwide, resulting in 37,555,669 recovered, 1,310,250 deaths (Figure 1), and a large number of open cases. It has required urgent medical treatments for numerous patients. No clinically active vaccines or antiviral agents are available for Covid19. According to several studies, Chloroquine (CQ) and Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) have shown promises as Covid19 antiviral especially when administered with Azithromycin (AZM). However, there is significant controversy. Many countries are limiting the use of CQ/HCQ, while others are accepting this therapeutical option (Figure 2). The work [1] is addressing the open question if Chloroquine (CQ) and Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) are helpful in Covid19 infection by analyzing the latest published literature on the subject while applying the scientific method.
Both papers in favor, or against, this therapeutical option are reviewed [1]. Bias by a conflict of interest is also taken into account. The rationale behind this use is clear. CQ/HCQ is effective against Covid19 in-vitro and in-vivo laboratory studies. Therapy in Covid19 infected patients with CQ/HCQ is supported by evidence of trials and field experiences from multiple sources. The relevant works are reviewed. The presence or absence of conflict of interest is weighed against the conclusions. CQ/HCQ has been used with success in mild cases or medium severity cases. No randomized controlled trial has however been conducted to support the safety and efficacy of CQ/HCQ and AZM for Covid19. Prophylaxis with CQ/HCQ is more controversial, but generally not having side effects, and supported by pre-clinical studies. The mechanism of action against Covid19 is unclear. More research is needed to understand the mechanisms of actions CQ/HCQ have against Covid19 infection, and this requires investigations with nanoscale imaging of viral infection of host cells. Most of the published works indicate CQ/HCQ is likely effective against Covid19 infection, almost 100% in prophylaxis and mild to medium severity cases, and 60% in late infection cases. The percentage of positive works is larger if works conducted under a probable conflict of interest are excluded from the list. The result is consistent with the updated analysis provided in [2], [3], that suggests high efficacy of CQ/HCQ in early treatments and lower efficacy and controversial results only for late treatment. Statistically, 100% of early treatment studies are positive, late treatment studies are mixed with 70% positive effects, 78% of pre-exposure prophylaxis studies are positive, and 100% of post-exposure prophylaxis studies also report positive effects [2], [3].
###
References
[1] Boretti, A., Banik, B., and Castelletto S., 2020. Mechanism of action of Chloroquine/Hydroxychloroquine for Covid19 infection, Coronaviruses.
[2] https:/
[3] https:/
For more information on the research, please visit: https:/
Authors:
Alberto Boretti1,*, Bimal K. Banik1, Stefania Castelletto2
1Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University, ?Al-Khobar 31952, Saudi Arabia; 2RMIT University, Bundoora 3083 VIC, Australia
Media Contact
Faizan ul Haq
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




