Nanoparticles could cross the blood-brain barrier to deliver drugs to the brain
Credit: Jean-Michel Rabanel
Researchers from the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) have shown that nanoparticles could be used to deliver drugs to the brain to treat neurodegenerative diseases.
The blood-brain barrier is the main obstacle in treating neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer and Parkinson. According to a recent study conducted by Jean-Michel Rabanel, a postdoctoral researcher under the supervision of Professor Charles Ramassamy, nanoparticles with specific properties could cross this barrier and be captured by neuronal cells. Researchers are confident that these results will open important prospects for releasing drugs directly to the brain. This breakthrough finding would enable improved treatment for neurodegenerative diseases affecting more than 565,000 Canadians, including 141,000 Quebecers.
“The blood-brain barrier filters out harmful substances to prevent them from freely reaching the brain. But this same barrier also blocks the passage of drugs,” explains the pharmacologist Charles Ramassamy. Typically, high doses are required to get a small amount of the drug into the brain. What remains in the bloodstream has significant side effects. Often, this discomfort leads the patient to stop the treatment. ?The use of nanoparticles, which encapsulate the drugs, would result in fewer collateral side effects while increasing brain efficiency.?
Efficient on an animal model
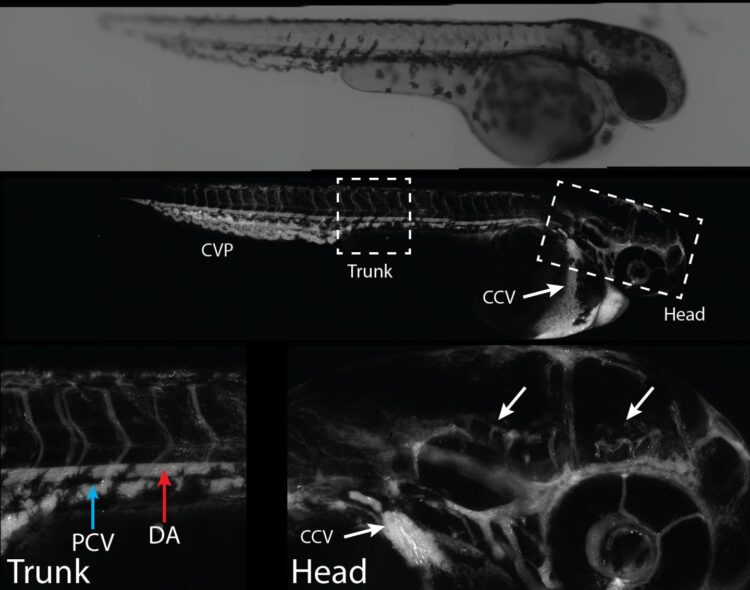
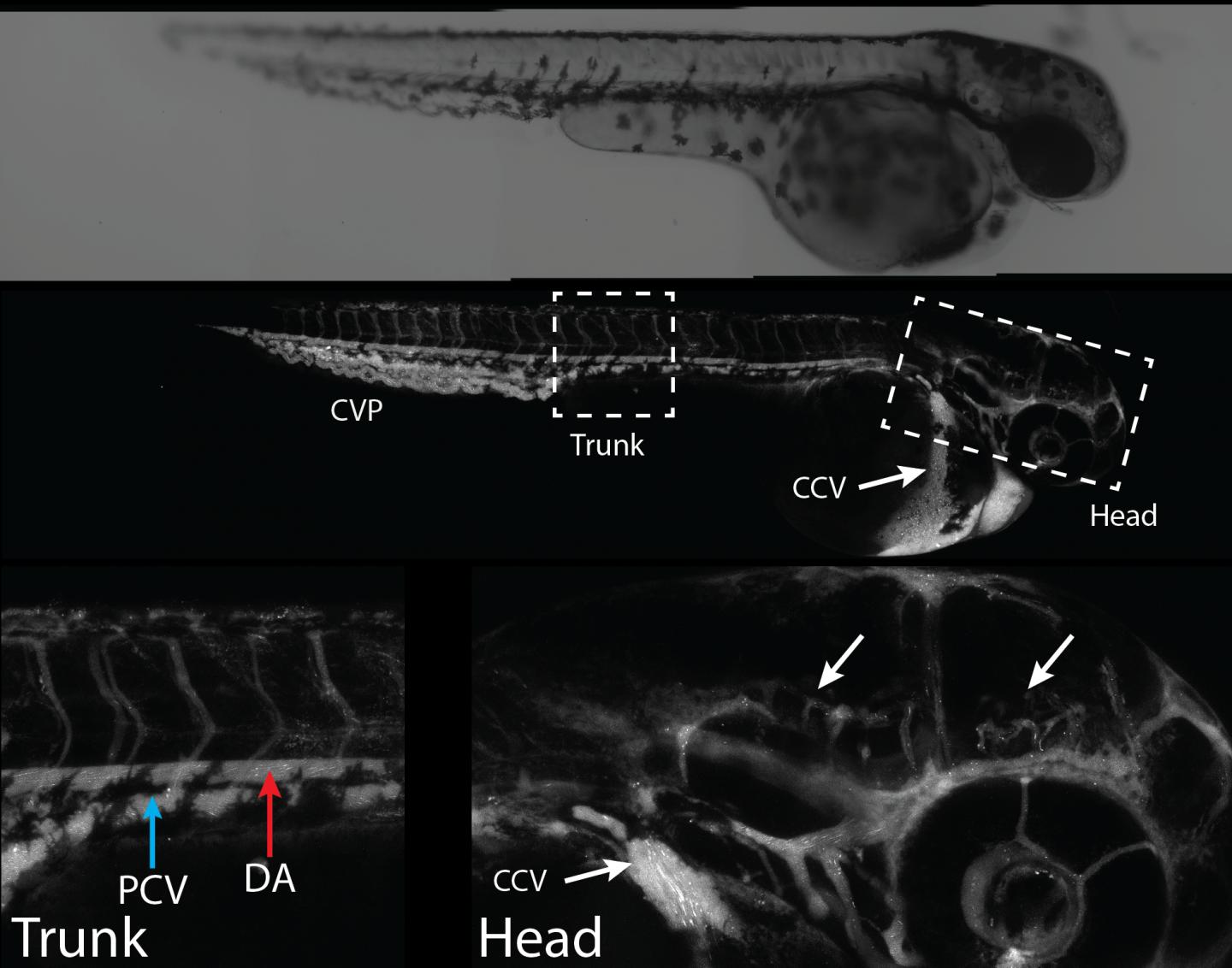
To prove the effectiveness of this method, the research team first tested it on cultured cells, then on zebrafish. “This species offers several advantages. Its blood-brain barrier is similar to that of humans and its transparent skin makes it possible to see nanoparticles’ distribution almost in real time,” says Professor Ramassamy, Chairholder of the Louise and André Charron Research Chair on Alzheimer’s disease, from the Fondation Armand-Frappier.
Using in vivo tests, researchers were able to observe the crossing of the blood-brain barrier. They also confirmed the absence of toxicity in the library of selected nanoparticles. “We made the particles with polylactic acid (PLA), a biocompatible material that is easily eliminated by the body. A layer of polyethylene glycol (PEG) covers these nanoparticles and makes them invisible to the immune system, so they can longer circulate in the bloodstream,” he explains. After several years of research on effective and safe nanoparticles, the research team will continue laboratory testing, targeting the delivery of active ingredients to other animal models with ultimate clinical applications.
###
About this study
The article “Transport of PEGylated-PLA nanoparticles across a blood brain barrier model, entry into neuronal cells and in vivo brain bioavailability” was published in September 2020 in the renowned Journal of Controllled Release. The research team received financial support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the Fonds de recherche du Québec – Nature et technologies (FRQNT), the Fonds de recherche du Québec – Santé (FRQS), the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) and the Fondation Armand-Frappier (Louise and André Charron Research Chair in Alzheimer’s Disease). https:/
About INRS
INRS is a university dedicated exclusively to graduate level research and training. Since its creation in 1969, INRS has played an active role in Quebec’s economic, social, and cultural development and is ranked first for research intensity in Quebec and second in Canada. INRS is made up of four interdisciplinary research and training centres in Quebec City, Montreal, Laval, and Varennes, with expertise in strategic sectors: Eau Terre Environnement, Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications, Urbanisation Culture Société, and Armand-Frappier Santé Biotechnologie. The INRS community includes more than 1,400 students, postdoctoral fellows, faculty members, and staff.
Source
Audrey-Maude Vézina
Service des communications de l’INRS
418 254-2156
[email protected]
Media Contact
Audrey-Maude Vezina
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.