Study advances science’s understanding of interferons, proteins that help combat viruses like SARS-CoV-2
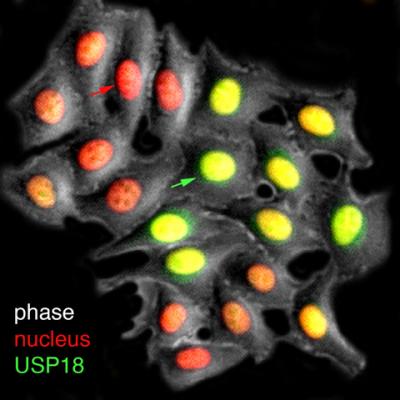
Credit: Hao Lab, UC San Diego
Science’s pursuits of unraveling how human cells fight viral infections kicked into high gear in 2020 with the devastating emergence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
A study published recently in eLife by University of California San Diego scientists describes fresh details about the mechanisms involved when individual human cells are attacked by viruses, with possible implications for COVID-19 clinical treatment. The research helps advance science’s understanding of interferons, a key group of immune response proteins released naturally by human cells when a virus is detected.
In response to a viral infection, human cells synthesize and secrete interferon-alpha, a chemical that triggers a series of biochemical reactions in cells, leading to the production of gene products that work to kill viruses or limit their spread. Interferon-alpha has been used clinically for more than 50 years in the treatments of diseases such as hepatitis B and C and HIV.
However such efforts have been limited because interferon-alpha, in addition to inducing antiviral effects, also triggers cell refractoriness–or insensitivity–to further treatments. This stalled effectiveness takes hold within hours after drug administration and lasts for several days, resulting in a low therapeutic response rate.
Looking into the details of these processes, Biological Sciences PhD student Anusorn Mudla, Associate Professor Nan Hao and their colleagues used a combination of experimental analyses and mathematical modeling to describe the intricate time-dependent regulatory mechanisms that human cells use to control the duration and strength of antiviral responses triggered by interferon. Their efforts resulted in the identification of a time delay in the production of USP18, an inhibitory factor that triggers cell refractoriness to prolonged interferon treatments.
“Based on these findings, repetitive administrations of interferon to cells, with the duration shorter than the delay time, are less able to induce this inhibitory factor. This could potentially suggest strategies leading to a higher therapeutic response rate than the routine chronic treatment of the drug,” said Hao, a researcher in the Section of Molecular Biology and the study’s senior author.
The findings are especially relevant given the urgent need for new defense tactics against the SARS-CoV-2 virus and the global COVID-19 pandemic. The new findings shed light on possible ways to enhance the effectiveness of interferon for future clinical use.
“Recent studies have shown that SARS-CoV-2 is especially sensitive to interferon-alpha, compared to other coronaviruses, making interferon treatment a potential strategy to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection,” said Hao.
Based on this finding, researchers could now design time-dependent administrations of interferon in an effort to minimize the production of this inhibitory factor and boost therapeutic responses.
###
The full author list includes: Anusorn Mudla, Yanfei Jiang, Kei-ichiro Arimoto, Bingxian Xu, Adarsh Rajesh, Andy Ryan, Wei Wang, Matthew Daugherty, Dong-Er Zhang and Nan Hao.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01 GM111458, R01 CA177305, R01 CA232147 and R35 GM133633), Pew Biomedical Research scholars, the DPST training scholarship from the Royal Thai government and the Cellular and Molecular Genetics training grant (T32 GM007240).
Media Contact
Mario Aguilera
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.



