Credit: Illustration: Robert Grosse/Ulrike Endesfelder
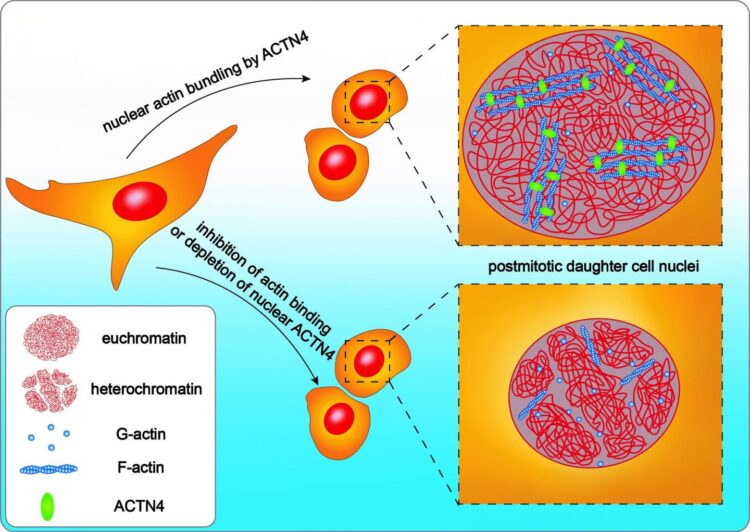
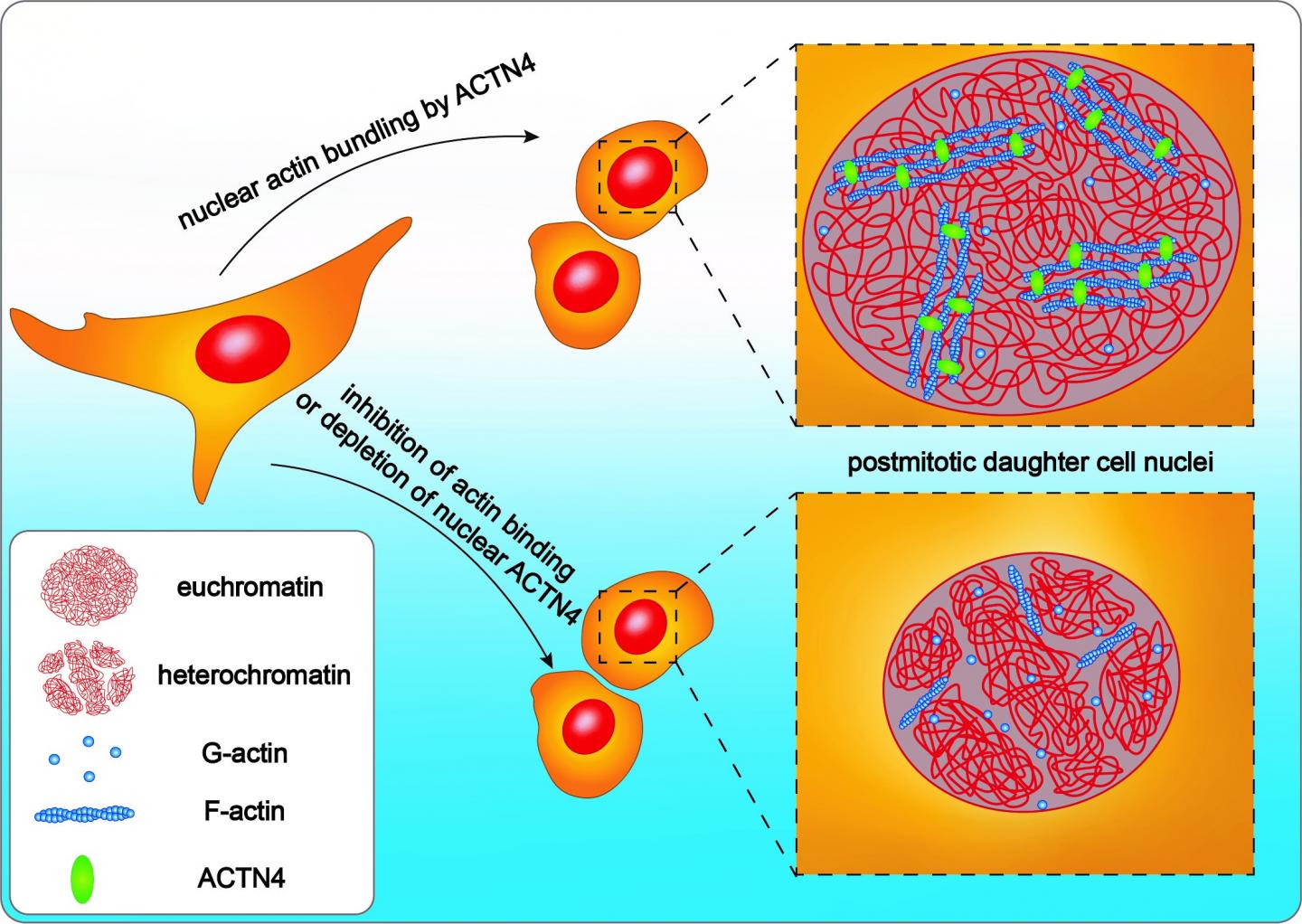
By far the most important process in cell development is how cells divide and then enlarge in order to multiply. A research team headed by Freiburg medical scientist Prof. Dr. Robert Grosse has now discovered that bundled fibers of actin within a cell nucleus play an important part in how they enlarge after division. Fibers of the structural protein actin stabilize the outer form of the cell and transport substances into a cell. The mechanisms that influence the growth of the cell nucleus after division were less well known by scientists. The researchers have published their results in the journal ‘EMBO reports’.
After dividing, cell nuclei have to grow in order to reorganize and unpack the genetic information in chromatin, the basic genetic material, and so process and read it. With this work the scientists show that bundled fibers of actin – which are normally responsible for exercising force – work within the cell to expand the nucleus. Using a video microscope the researchers have measured in living cells how cell nuclei enlarge immediately after division. In order to observe the fibers of actin and skeletal structures in the cell nucleus, they also used a high-resolution super-resolution microscope.
In the future Grosse and his team want to clarify whether mechanical forces work within the cell nucleus to re-organize them to sort the genetic information. If so, this process could for example be disrupted or changed in tumor cells or play a part in stem cells.
###
Freiburg medical scientist Robert Grosse is a professor of Pharmacology and Toxicology and director of Division I at the Institute of Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology, as well as a member of the Cluster of Excellence CIBSS – Centre for Integrative Biological Signalling Studies at the University of Freiburg. His team is working with a group headed by Dr. Ulrike Endesfelder from the Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology in Marburg, which is contributing expertise in super-resolution microscopy.
Original publication: Krippner, S., Winkelmeier, J., Knerr, J., Brandt, D. T., Virant, D., Schwan, C., Endesfelder, U. & Grosse, R. (2020). Post-mitotic expansion of cell nuclei requires nuclear actin filament bundling by a-actinin 4. In EMBO Reports, DOI: 10.15252/embr.202050758
Contact: Institute of Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Freiburg
Media Contact
Robert Grosse
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.