Credit: Credit: NASA/NRL
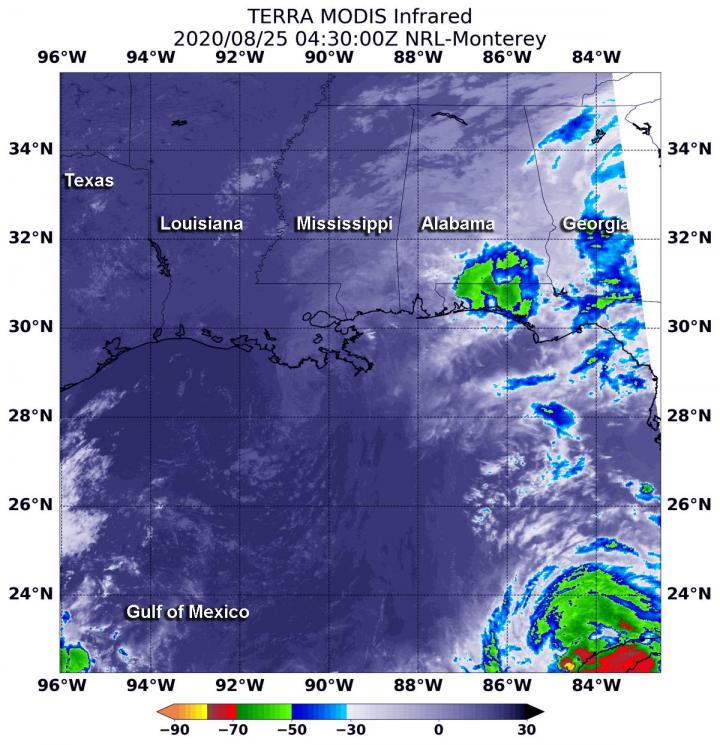
NASA’s Terra satellite passed over the Gulf of Mexico early on Aug. 25 and found a very small area of convection from post-tropical cyclone Marco, northeast of its center. All watches and warnings have been dropped as the storm continues to weaken toward dissipation.
Visible imagery and surface observations indicated that Marco made landfall around 7 p.m. EDT on Aug. 24 near the mouth of the Mississippi River. The center continued to move west and moved offshore and south of Louisiana by Aug. 25.
NASA’s Terra Satellite Reveals Effects of Wind Shear
NASA’s Terra satellite uses infrared light to analyze the strength of storms by providing temperature information about the system’s clouds. The strongest thunderstorms that reach high into the atmosphere have the coldest cloud top temperatures.
On Aug. 25 at 12:30 a.m. EDT (0430 UTC), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Terra satellite observed Marco in infrared light and found a small area of storms where cloud top temperatures as cold as minus 50 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 45.5 Celsius) over the western Florida Panhandle and coastal Alabama. Those storms were being pushed northeast of Marco’s center from southwesterly wind shear. Satellite imagery also shows the low-level circulation center was a swirl of clouds south of Louisiana, over the Gulf of Mexico.
In the Aug. 25, Marco discussion at 5 a.m. EDT, NHC Senior Hurricane Specialist Stacy Stewart noted, “Marco has been devoid of any significant convection for at least 12 hours. [NOAA’s Advanced Scatterometer] ASCAT scatterometer surface wind data around 0239Z (10:39 p.m. EDT on Aug. 24) suggested that Marco might have degenerated in a north-to-south elongated trough (elongated area of low pressure). Based on this information, Marco has been downgraded to post-tropical remnant low [pressure area].”
About Wind Shear
The shape of a tropical cyclone provides forecasters with an idea of its organization and strength. When outside winds batter a storm, it can change the storm’s shape and push much of the associated clouds and rain to one side of it. That is what wind shear does.
In general, wind shear is a measure of how the speed and direction of winds change with altitude. Tropical cyclones are like rotating cylinders of winds. Each level needs to be stacked on top each other vertically in order for the storm to maintain strength or intensify. Wind shear occurs when winds at different levels of the atmosphere push against the rotating cylinder of winds, weakening the rotation by pushing it apart at different levels.
Marco’s Final Status
At 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC) on Aug. 25, NOAA’s National Hurricane Center (NHC) reported the center of Post-Tropical Cyclone Marco was located near latitude 28.8 degrees north and longitude 91.2 degrees west. That is about 60 miles (100 km) south of Morgan City, La. and 110 miles (175 km) south-southeast of Lafayette, La. The post-tropical cyclone was moving toward the west near 10 mph (17 kph), and this general motion is expected to continue for the next day or so. Maximum sustained winds were near 30 mph (45 kph) with higher gusts. The estimated minimum central pressure was 1008.
Marco Nears its End
Brisk southwesterly vertical wind shear of 30 knots is forecast to increase to near 35 knots in 24 hours, which should prevent the redevelopment of deep convection near the center. On the forecast track, Marco should continue moving westward just offshore the coast of Louisiana until the system dissipates.
NASA Researches Tropical Cyclones
Hurricanes/tropical cyclones are the most powerful weather events on Earth. NASA’s expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
For more than five decades, NASA has used the vantage point of space to understand and explore our home planet, improve lives and safeguard our future. NASA brings together technology, science, and unique global Earth observations to provide societal benefits and strengthen our nation. Advancing knowledge of our home planet contributes directly to America’s leadership in space and scientific exploration.
###
For updated forecasts. visit: http://www.
By Rob Gutro
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
Rob Gutro
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




