One-of-a-kind video shows how bacterium annihilates the body’s immune cells.
Credit: NTNU Centre for Molecular Inflammation Research (CEMIR)
The tuberculosis bacterium has been around as long as mankind has.
To fight the bacterium, we need to know how it attacks the body’s immune system.
Researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) have taken the next step toward that goal by filming the process.
It’s thought that every fourth person harbors tuberculosis bacteria in their body, although only five to ten percent of the infected population actually get sick.
People who contract the illness need to take antibiotics for up to two years.
Antibiotic resistance in some patients means they never recover. Those who have had the disease and survive do not become immune.
One person who lives close to the tuberculosis bacterium is Professor Trude Helen Flo at NTNU’s Centre of Molecular Inflammation Research (CEMIR).
Now she and nanotechnologists Kai and Marianne Sandvold Beckwith at NTNU and EMBL Heidelberg have managed to film in detail how the death process unfolds inside a cell.
This is rare fare, even among researchers, which is why the world premiere was recently published in the journal Nature Communications.
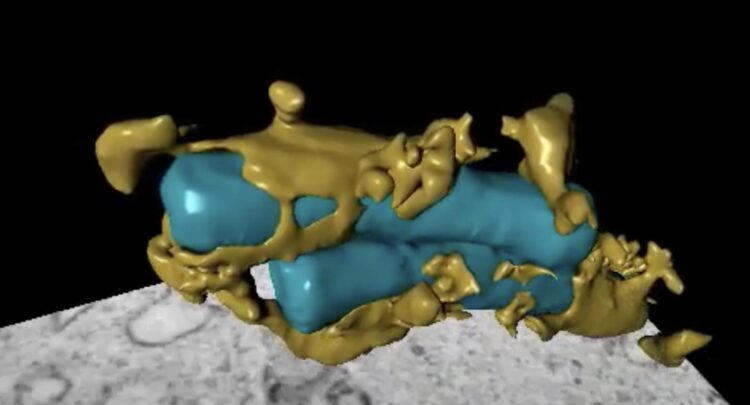
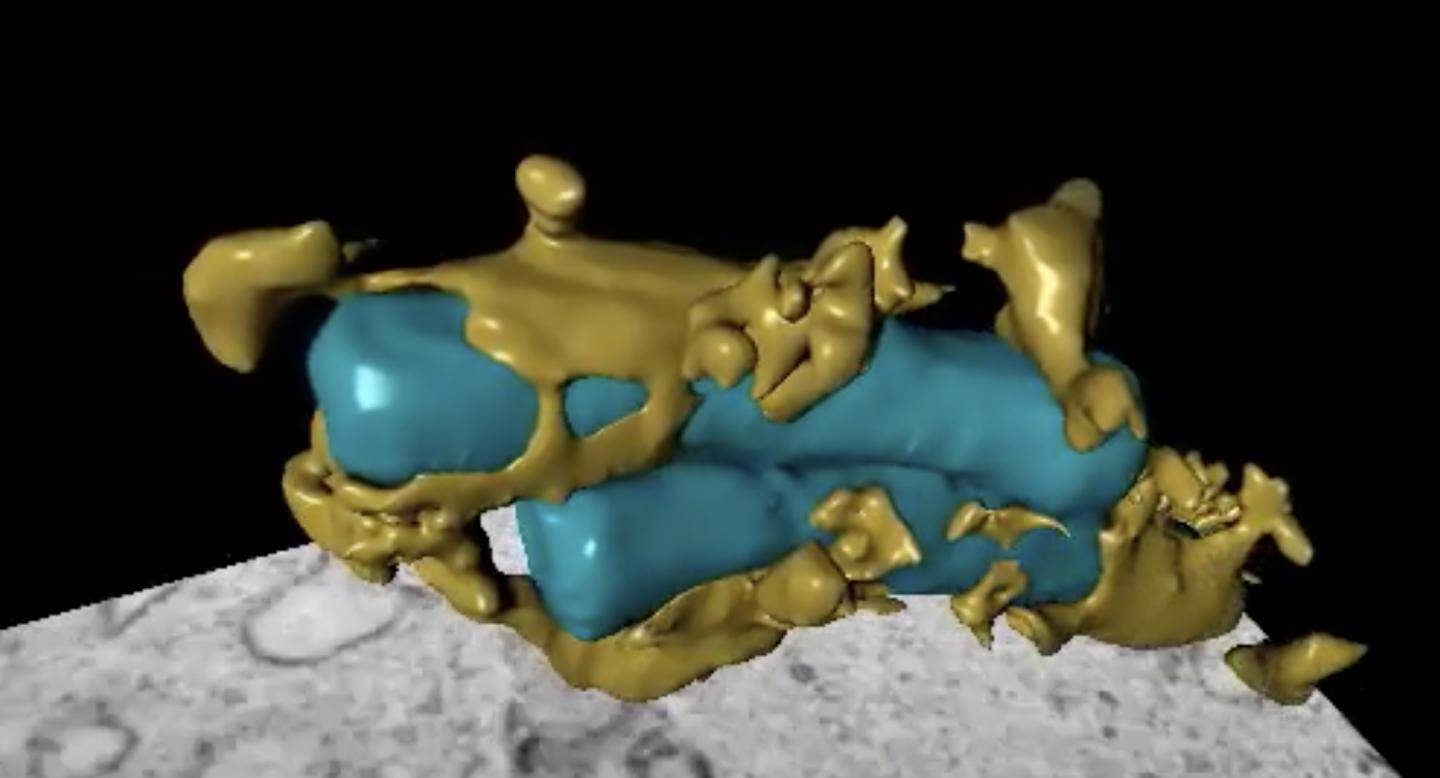
“We observed the tuberculosis bacterium and some of the proteins we study with fluorescent colours like blue, red and green in the cells. We used advanced fluorescence microscopy to film them before studying them with a 3D electron microscope that has nanometre resolution,” says Flo.
The most harmful bacteria are the best at fooling the body’s immune system.
The TB bacterium hides in the very cells that are supposed to kill it.
“The tuberculosis bacterium lives in macrophages that are the guards, waste removers and caretakers of the immune system,” says Flo.
The main role of macrophages in the immune system is to eat and destroy microbes, while alerting the rest of the immune system. TB bacteria have found ways to hide inside the macrophage and avoid being killed.
“The tuberculosis bacterium lives in the world’s best hiding place,” says Flo.
The research team filmed the infection in multiple 24-hour time-lapse sequences.
When the tuberculosis bacterium makes a person sick, it is because cells full of bacteria rupture and spread the contents to other cells in the lungs, creating an inflammation that damages the lung tissue. The person begins to cough, and the bacteria spreads.
For the first time, NTNU researchers have managed to show exactly how this happens inside the cell and in what order.
The only way for the tuberculosis bacterium to spread is to first get out of the cell it lives in. The bacteria begin to reproduce and at some point kill the cell they live in in order to spread further.
“The TB bacterium does this by punching holes in the membrane that encloses the macrophages. This triggers an explosive immune response in which the cell they live in dies, allowing the bacteria to spread to other cells. The bacteria operate in two modes: one where they divide and multiply while hidden inside the cell they live in, and one where they break out and infect healthy tissue,” says Flo.
Filming allowed the researchers to study this process much more precisely.
The researchers can apply this understanding in their work to treat the disease.
“Antibiotics work against the bacteria, but we envision developing a treatment that could control the cell death and tissue damage caused by the tuberculosis bacterium. Combined with antibiotics, this might provide more effective treatment, but we aren’t there yet,” says Flo.
###
Citation: Beckwith, K.S., Beckwith, M.S., Ullmann, S. et al. Plasma membrane damage causes NLRP3 activation and pyroptosis during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Nat Commun 11, 2270 (2020). https:/
Media Contact
Trude Helen Flo
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.