Credit: Aalto University/Mikko Raskinen
For the first time ever, scientists have witnessed the interaction of a new phase of matter known as “time crystals”.
The discovery, published in Nature Materials, may lead to applications in quantum information processing because time crystals automatically remain intact – coherent – in varying conditions. Protecting coherence is the main difficulty hindering the development of powerful quantum computers.
Dr Samuli Autti, lead author from Lancaster University, said: “Controlling the interaction of two time crystals is a major achievement. Before this, nobody had observed two time crystals in the same system, let alone seen them interact.
“Controlled interactions are the number one item on the wish list of anyone looking to harness a time crystal for practical applications, such as quantum information processing.”
Time crystals are different from a standard crystal – like metals or rocks – which is composed of atoms arranged in a regularly repeating pattern in space.
First theorised in 2012 by Nobel Laureate Frank Wilczek and identified in 2016, time crystals exhibit the bizarre property of being in constant, repeating motion in time despite no external input. Their atoms are constantly oscillating, spinning, or moving first in one direction, and then the other.
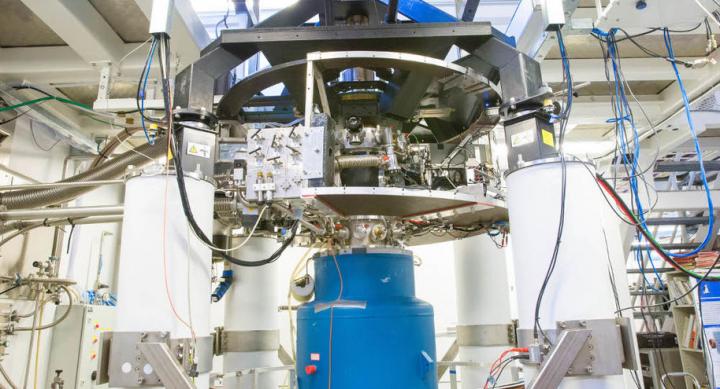
An international team of researchers from Lancaster, Yale, Royal Holloway London, and Aalto University in Helsinki observed time crystals by using Helium-3 which is a rare isotope of helium with one missing neutron. The experiment was carried out in Aalto University.
They cooled superfluid helium-3 to within one ten thousandth of a degree from absolute zero (0.0001K or -273.15°C). The researchers then created two time crystals inside the superfluid, and allowed them to touch.
The scientists observed the two time crystals interacting and exchanging constituent particles flowing from one time crystal to the other one, and back – a phenomenon known as the Josephson effect.
Time crystals have great potential for practical applications. They could be used to improve current atomic clock technology – complex timepieces that keep the most accurate time that we can possibly achieve. They could also improve technology such as gyroscopes, and systems that rely on atomic clocks, such as GPS.
###
Media Contact
Gillian.whitworth
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




