Credit: Elizabeth Flores-Gomez Murray/ Penn State
The possibility of achieving room temperature superconductivity took a tiny step forward with a recent discovery by a team of Penn State physicists and materials scientists.
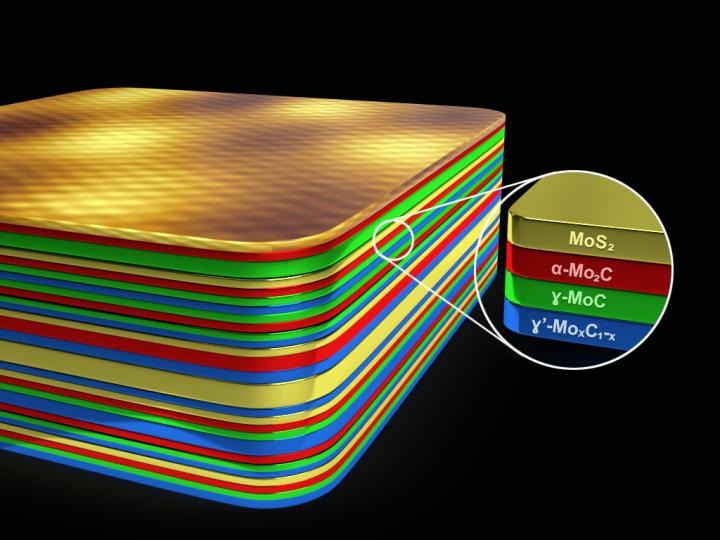
The surprising discovery involved layering a two-dimensional material called molybdenum sulfide with another material called molybdenum carbide. Molybdenum carbide is a known superconductor — electrons can flow through the material without any resistance. Even the best of metals, such as silver or copper, lose energy through heat. This loss makes long-distance transmission of electricity more costly.
“Superconductivity occurs at very low temperatures, close to absolute zero or 0 Kelvin,” said Mauricio Terrones, corresponding author on a paper in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences published this week. “The alpha phase of Moly carbide is superconducting at 4 Kelvin.”
When layering metastable phases of molybdenum carbide with molybdenum sulfide, superconductivity occurs at 6 Kelvin, a 50% increase. Although this is not remarkable in itself — other materials have been shown to be superconductive at temperatures as high as 150 Kelvin — it was still an unexpected phenomenon that portends a new method to increase superconductivity at higher temperatures in other superconducting materials.
The team used modeling techniques to understand how the effect occurred experimentally.
“Calculations using quantum mechanics as implemented within density functional theory assisted in the interpretation of experimental measurements to determine the structure of the buried molybdenum carbide/molybdenum sulfide interfaces,” said Susan Sinnott, professor of materials science and engineering and head of the department. “This work is a nice example of the way in which materials synthesis, characterization and modeling can come together to advance the discovery of new material systems with unique properties.”
According to Terrones, “It’s a fundamental discovery, but not one anyone believed would work. We are observing a phenomenon that to the best of our knowledge has never been observed before.”
The team will continue experimenting with superconductive materials with the goal of someday finding materials combinations that can carry energy through the grid with zero resistance.
###
In addition to Terrones and Sinnott, authors on the PNAS paper, titled “Superconductivity enhancement in phase-engineered molybdenum carbide/sulfide vertical heterostructures,” are doctoral students or graduated doctorate recipients Fu Zhang, Yanfu Lu, Lavish Pabbi, Anna Binion, Tomotaroh Granzier-Nakajima, Tiany Zhang and Zhong Lin; and postdoctoral scholars Kazunori Fujisawa And Yu Lei, Professor Eric Hudson and former Research Assistant Professor Laura Elias, all of Penn State, and Wenkai Zhang and Luis Balcas of Florida State.
The Department of Energy, funded this research which was recently renewed to continue their research.
Media Contact
A’ndrea Elyse Messer
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




