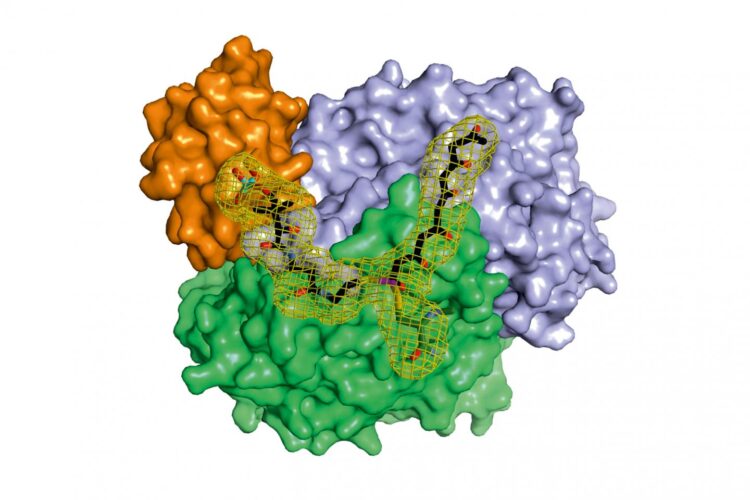
X-ray structure analysis gives detailed insights into molecular factory

Credit: Maximilian Schmalhofer and Prof. Dr. Michael Groll / TUM
The active agents of many drugs are natural products, so called because often only microorganisms are able to produce the complex structures. Similar to the production line in a factory, large enzyme complexes put these active agent molecules together. A team of the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Goethe University Frankfurt has now succeeded in investigating the basic mechanisms of one of these molecular factories.
Many important drugs such as antibiotics or active agents against cancer are natural products which are built up by microorganisms for example bacteria or fungi. In the laboratory, these natural products can often be not produced at all or only with great effort. The starting point of a large number of such compounds are polyketides, which are carbon chains where every second atom has a double bound to an oxygen atom.
In a microbial cell such as in the Photorhabdus luminescens bacterium, they are produced with the help of polyketide synthases (PKS). In order to build up the desired molecules step by step, in the first stage of PKS type II systems, four proteins work together in changing “teams”.
In a second stage, they are then modified to the desired natural product by further enzymes. Examples of bacterial natural products which are produced that way are, inter alia, the clinically used Tetracyclin antibiotics or Doxorubicin, an anti-cancer drug.
Interdisciplinary cooperation
While the modified steps of the second stage are well studied for many active agents, there have up to now hardly been any insights into the general functioning of the first stage of these molecular factories where the highly reactive polyketide intermediate product is bound to the enzyme complex and protected so that it cannot react spontaneously.
This gap is now closed by the results of the cooperation between the working groups of Michael Groll, professor of biochemistry at the Technical University of Munich, and Helge Bode, professor of molecular biotechnology at Goethe University Frankfurt, which are published in the renowned scientific journal Nature Chemistry.
Findings inspire to new syntheses of active agents
“In the context of this work, we were for the first time able to analyze complexes of the different partner proteins of type II polyketide synthase with the help of X-ray structure analysis and now understand the complete catalytic cycle in detail,” Michael Groll explains.
“Based on these findings, it will be possible in the future to manipulate the central biochemical processes in a targeted manner and thus change the basic structures instead of being restricted to the decorating enzymes,” Helge Bode adds.
Although it is a long way to develop improved antibiotics and other drugs, both groups are optimistic that now also the structure and the mechanism of the missing parts of the molecular factory can be explained. “We already have promising data of the further protein complexes,” says Maximilian Schmalhofer, who was involved in the study as a doctoral candidate in Munich.
###
The work was supported with funds of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) in the context of SPP 1617, SFB 1035 and the Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich (CIPSM) cluster of excellence and the LOEWE focus MegaSyn of the State of Hesse. X-ray structure data were measured at the Paul Scherrer Institute in Villigen (Switzerland). The Swedish National Infrastructure for Computing provided computing time for the theoretical modeling.
Publication:
Alois Braeuer, Qiuqin Zhou, Gina L.C. Grammbitter, Maximilian Schmalhofer, Michael Ruehl, Ville R.I. Kaila, Helge B. Bode und Michael Groll:
Structural snapshots of the minimal PKS system responsible for octaketide biosynthesis,
Nature Chemistry 06.07.2020 – DOI: 10.1038/s41557-020-0491-7
Media Contact
Andreas Battenberg
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.