New types of cathodes, suitable for advanced energy storage, can be developed using beyond-lithium ion batteries
Credit: Supplied by University of Technology Sydney
The rapid development of renewable energy resources has triggered tremendous demands in large-scale, cost-efficient and high-energy-density stationary energy storage systems.
Lithium ion batteries (LIBs) have many advantages but there are much more abundant metallic elements available such as sodium, potassium, zinc and aluminum.
These elements have similar chemistries to lithium and have recently been extensively investigated, including sodium-ion batteries (SIBs), potassium-ion batteries (PIBs), zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs), and aluminium-ion batteries (AIBs). Despite promising aspects relating to redox potential and energy density the development of these beyond-LIBs has been impeded by the lack of suitable electrode materials
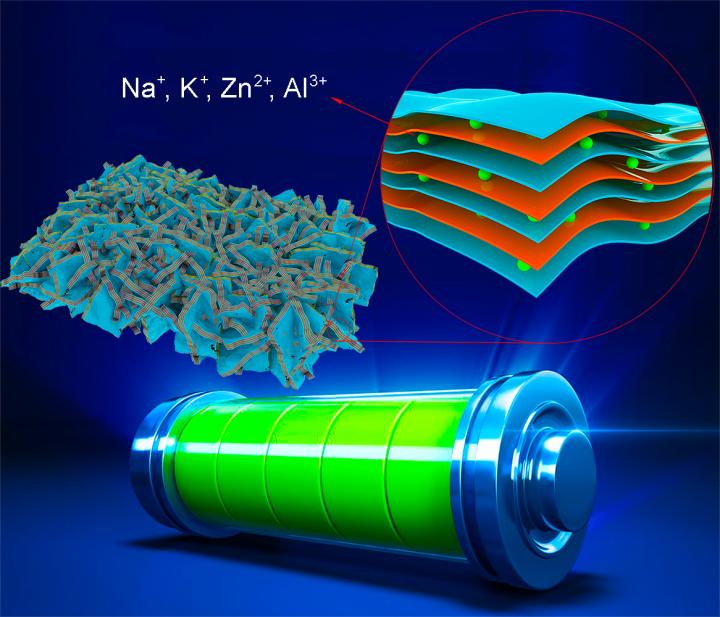
New research led by Professor Guoxiu Wang from the University of Technology Sydney, and published in Nature Communications, describes a strategy using interface strain engineering in a 2D graphene nanomaterial to produce a new type of cathode. Strain engineering is the process of tuning a material’s properties by altering its mechanical or structural attributes.
“Beyond-lithium-ion batteries are promising candidates for high-energy-density, low-cost and large-scale energy storage applications. However, the main challenge lies in the development of suitable electrode materials,” ” Professor Wang, Director of the UTS Centre for Clean Energy Technology, said.
“This research demonstrates a new type of zero-strain cathodes for reversible intercalation of beyond-Li+ ions (Na+, K+, Zn2+, Al3+) through interface strain engineering of a 2D multilayered VOPO4-graphene heterostructure.
When applied as cathodes in K+-ion batteries, we achieved a high specific capacity of 160 mA h g-1 and a large energy density of ~570 W h kg?1, presenting the best reported performance to date. Moreover, the as-prepared 2D multilayered heterostructure can also be extended as cathodes for high-performance Na+, Zn2+, and Al3+-ion batteries.
The researchers say this work heralds a promising strategy to utilize strain engineering of 2D materials for advanced energy storage applications.
“The strategy of strain engineering could be extended to many other nanomaterials for rational design of electrode materials towards high energy storage applications beyond lithium-ion chemistry,” Professor Wang said.
###
The research was a collaboration with Professor Takayoshi Sasaki from National Institute for Materials Science, Japan.
Media Contact
Marea Martlew
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




