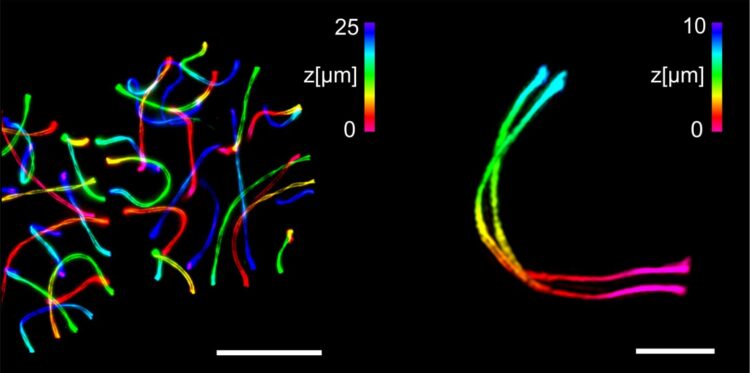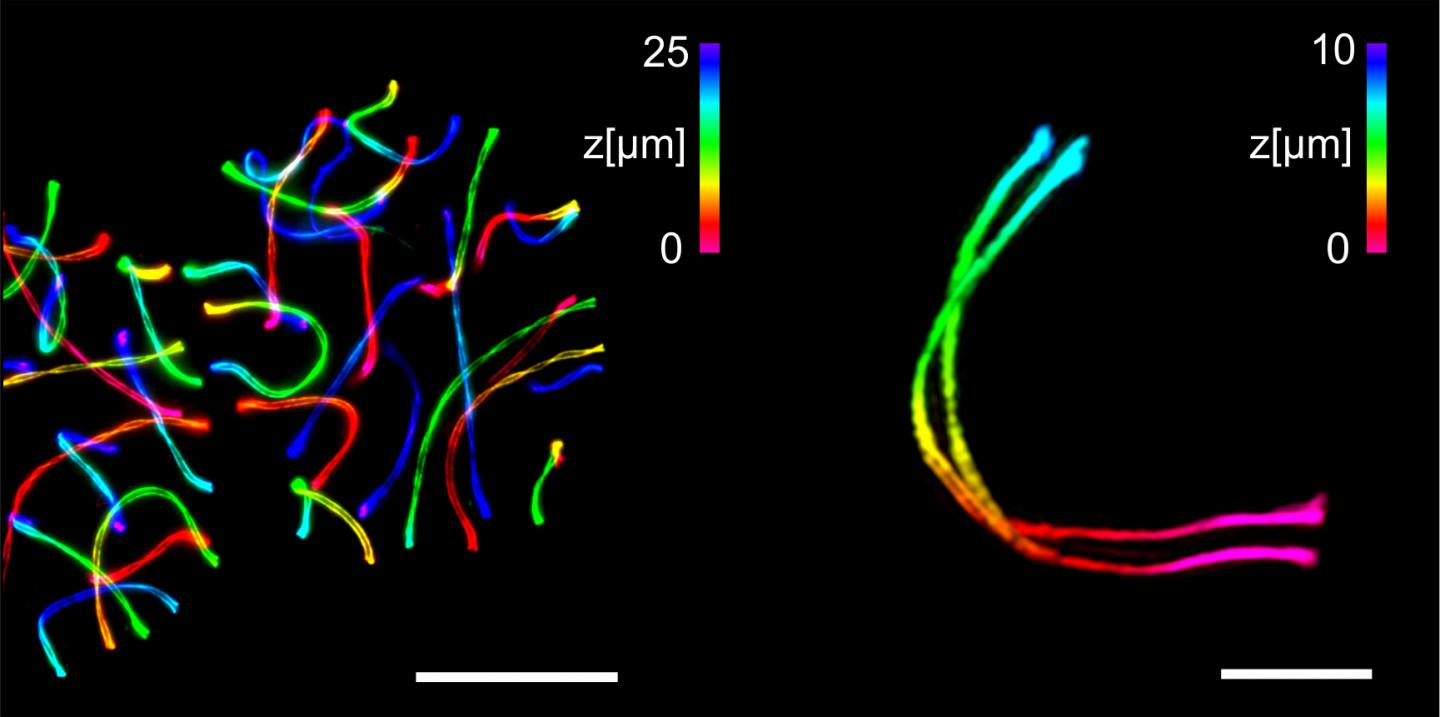
Credit: (Picture: Working groups Benavente and Sauer / University of Wuerzburg)
The synaptonemal complex is a ladder-like cell structure that plays a major role in the development of egg and sperm cells in humans and other mammals. “The structure of this complex has hardly been changed in evolution, but its protein components vary greatly from organism to organism,” says Professor Ricardo Benavente, cell and developmental biologist at the Biocenter of Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany.
This points to the fact that the structure is crucial for the undisturbed function of the complex. Benavente is investigating the synaptonemal complex together with Markus Sauer, Professor of Biotechnology and Biophysics at the JMU Biocenter. The latest findings of the two research groups have been published in the journal Nature Communications.
The data indicate, among other things, that the synaptonemal complex in the case of the mouse is not, as previously assumed, double-layered, but far more complex.
Sophisticated combination of microscopy techniques
“In our study, we combined structured illumination microscopy SIM with various methods of expansion microscopy ExM,” explains Sauer, who is an expert in high-resolution microscopy. The ExM enables greater resolution by embedding the target structures into a swellable polymer which can be physically ~ 4fold expanded.
ExM in combination with SIM enabled the researchers for the first time to visualize the three-dimensional ultrastructure of the synaptonemal complex by multicolour imaging with a spatial resolution of 20 to 30 nanometres.
“If immunolabeling is performed after expansion of the complex, the antibody accessibility can be improved compared to other high-resolution methods. This has enabled us to decipher details of the molecular organisation that were previously hidden,” said Benavente and Sauer. In addition, the images can now be taken with almost molecular resolution on a standard light microscope.
With the combination of ExM-SIM, the JMU teams are now looking to discover further details of the synaptonemal complex and other multi-protein complexes.
Info box: Synaptonemal complex
The synaptonemal complex is ultimately responsible for the individuality of the human being. It occurs exclusively in the cells from which the egg and sperm cells of humans and other mammals develop. The complex ensures that the chromosomes exchange genetic material with each other. Thus, a subsequent cell division results in the formation of individual egg or sperm cells.
###
Media Contact
Markus Sauer
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.