Credit: Courtesy of Adrian Mellage
Under changing, increasingly dynamic climatic conditions, temperate soils are forecast to experience a high degree of variability in moisture conditions due to periods of drought and/or flood. These periodic shifts between well-drained and waterlogged conditions have the potential to enhance carbon cycling by microbes and influence soil quality and land-derived greenhouse gas emissions.
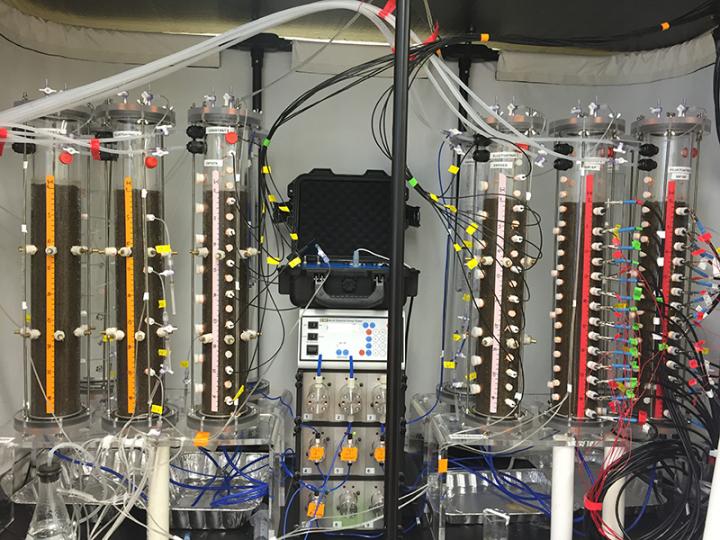
In a recently published study in Vadose Zone Journal, researchers subjected a soil column to controlled periods of waterlogging versus drainage. The team showed that dynamic water saturation led to pronounced pulses of carbon dioxide emissions and higher depletion of soil organic carbon at the depth exposed to fluctuating water saturation. The research was carried out in a novel experimental setup, in which the water saturation conditions experienced by the soil column were manipulated while monitoring oxygen content, redox potential and porewater composition.
Remarkably, the depth region of the soil columns exposed to dynamic waterlogging developed lower microbial biomass relative to static conditions, but these remaining microbes exhibited a higher activity. In contrast to expected results, dynamic waterlogging conditions did not result in a higher diversity of the microbial community.
The ability to understand the factors controlling the cycling of nutrients and carbon under dynamic environmental conditions can be achieved by applying novel experimental techniques such as these. The findings suggest that the enhanced carbon cycling under dynamic waterlogging is driven by a more active, and not a more abundant or compositionally more diverse, microbial community. Ultimately, these effects of dynamic waterlogging can be incorporated into global scale predictive models to improve our predictive capabilities of the biosphere’s response to environmental change.
###
Adapted from Pronk, GJ, Mellage, A, Milojevic, T, et al. Carbon turnover and microbial activity in an artificial soil under imposed cyclic drainage and imbibition. Vadose Zone J. 2020; 19:e20021
Media Contact
Rachel Schutte
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




