Coronavirus could be transmitted through a long-lasting cloud of virus-containing aerosol droplets ejected from a flushing toilet.
Credit: J.-X. Wang
WASHINGTON, June 16, 2020 — Researchers used a computer simulation to show how a flushing toilet can create a cloud of virus-containing aerosol droplets that is large and widespread and lasts long enough that the droplets could be breathed in by others.
With recent studies showing the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19 can survive in the human digestive tract and show up in feces of the infected, this raises the possibility the disease could be transmitted with the use of toilets.
Toilet flushing creates a great deal of turbulence, and qualitative evidence suggests this can spread both bacteria and viruses. The public, however, remains largely unaware of this infection pathway, since few quantitative studies have been carried out to investigate this possible mechanism.
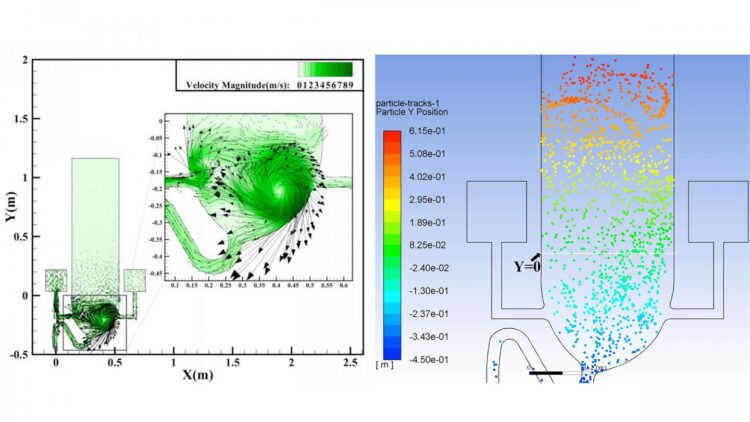
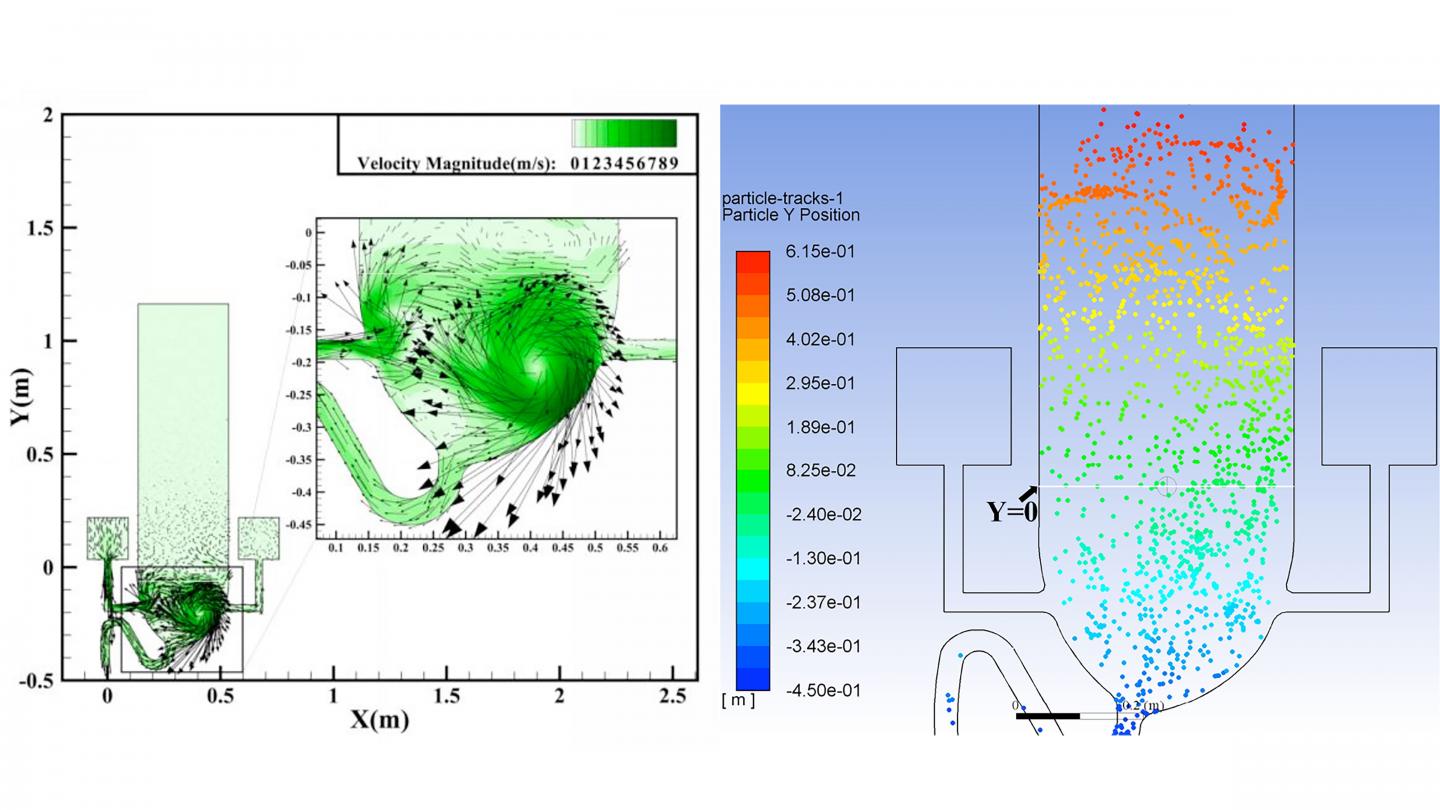
In the journal Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, precise computer models were used to simulate water and air flows in a flushing toilet and the resulting droplet cloud. The investigators used a standard set of fluid dynamic formulas, known as the Navier-Stokes equations, to simulate flushing in two types of toilet — one with a single inlet for flushing water, and another with two inlets to create a rotating flow.
The investigators also used a discrete phase model to simulate movement of the numerous tiny droplets likely to be ejected from the toilet bowl into the air. A similar model was used recently to simulate the movement of aerosol droplets ejected during a human cough. (See https:/
The results of the simulations were striking.
As water pours into the toilet bowl from one side, it strikes the opposite side, creating vortices. These vortices continue upward into the air above the bowl, carrying droplets to a height of nearly 3 feet, where they might be inhaled or settle onto surfaces. These droplets are so small they float in the air for over a minute. A toilet with two inlet ports for water generates an even greater velocity of upward flowing aerosol particles.
“One can foresee that the velocity will be even higher when a toilet is used frequently, such as in the case of a family toilet during a busy time or a public toilet serving a densely populated area,” said co-author Ji-Xiang Wang, of Yangzhou University.
The simulations show that nearly 60% of the ejected particles rise high above the seat for a toilet with two inlet ports. A solution to this deadly problem is to simply close the lid before flushing, since this should decrease aerosol spread.
However, in many countries, including the United States, toilets in public restrooms are often without lids. This poses a serious hazard. The investigators also suggest a better toilet design would include a lid that closes automatically before flushing.
###
The article, “Can a toilet promote virus transmission? From a fluid dynamics perspective,” is authored by Yun-Yun Li, Ji-Xiang Wang and Xi Chen. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on June 16, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0013318). Thereafter, it can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.