Rice team’s SEMseg method makes nanoparticle analysis quicker and more affordable
Credit: Landes Research Group/Rice University
HOUSTON – (June 8, 2020) – Rice University scientists have developed an easy and affordable tool to count and characterize nanoparticles.
The Rice labs of chemists Christy Landes and Stephan Link created an open-source program called SEMseg to acquire data about nanoparticles, objects smaller than 100 nanometers, from scanning electron microscope (SEM) images that are otherwise difficult if not impossible to analyze.
The size and shape of the particles influences how well they work in optoelectronic devices, catalysts and sensing applications like surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy.
SEMseg is described in a study led by Landes and Rice graduate student Rashad Baiyasi in the American Chemical Society’s Journal of Physical Chemistry A.
The program is available for download from GitHub at https:/
SEMseg — for SEM segmentation — springs from the team’s study in Science last year that showed how proteins can be used to push nanorods into chiral assemblies. “This work was one result of that,” Landes said. “We realized there was no good way to quantitatively analyze SEM images.”
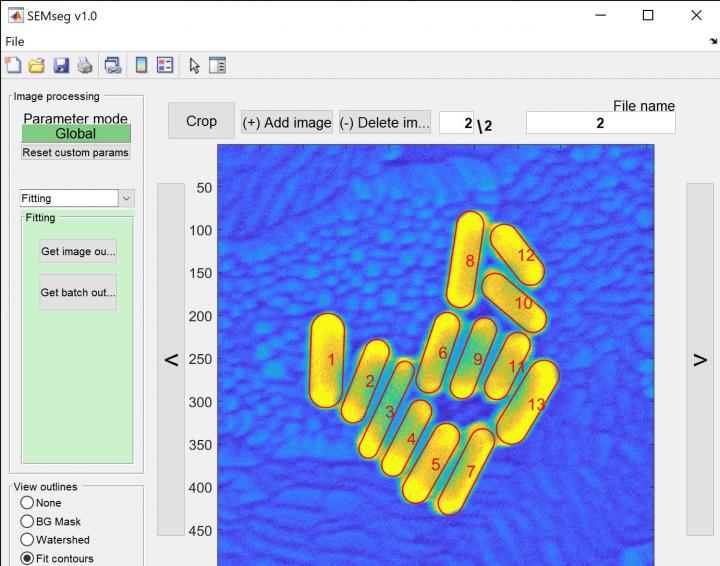
Counting and characterizing individual or aggregate nanorods is usually done with complex and expensive transmission electron microscopes (TEM), manual measurement that is prone to human bias or programs that fail to distinguish between particles unless they’re far apart. SEMseg extracts pixel-level data from low-contrast, low-resolution SEM images and recombines it into sharp images.
SEMseg can quickly distinguish individual nanorods in closely packed assemblies and aggregates to determine the size and orientation of each particle and the size of gaps between them. That allows for a more efficient statistical analysis of aggregates.
“In a matter of minutes, SEMseg can characterize nanoparticles in large datasets that would take hours to measure manually,” Baiyasi said.
Segmenting nanoparticles, he said, refers to isolating and characterizing each constituent particle in an aggregate. Isolating the constituent nanoparticles lets researchers analyze and characterize the heterogenous structure of aggregates.
Baiyasi said SEMseg can be adapted for such other imaging techniques as atomic force microscopy and could be extended for other nanoparticle shapes, like cubes or triangles.
###
Co-authors are Rice postdoctoral researchers Miranda Gallagher and Qingfeng Zhang and graduate students Lauren McCarthy and Emily Searles. Link is a professor of chemistry and of electrical and computer engineering. Landes is a professor of chemistry, of electrical and computer engineering and of chemical and biomolecular engineering.
The Army Research Office, the National Science Foundation and the Robert A. Welch Foundation supported the research.
Read the abstract at https:/
Download the program at https:/
This news release can be found online at https:/
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
Related materials:
Chemists clarify a chiral conundrum: http://news.
Landes Research Group: https:/
Link Research Group: https:/
Rice Department of Chemistry: https:/
Wiess School of Natural Sciences: https:/
Image for download:
https:/
Rice University scientists have created an open-source algorithm, SEMseg, that simplifies nanoparticle analysis using scanning electron microscope images. (Credit: Landes Research Group/Rice University)
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,962 undergraduates and 3,027 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 4 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Media Contact
Jeff Falk
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




