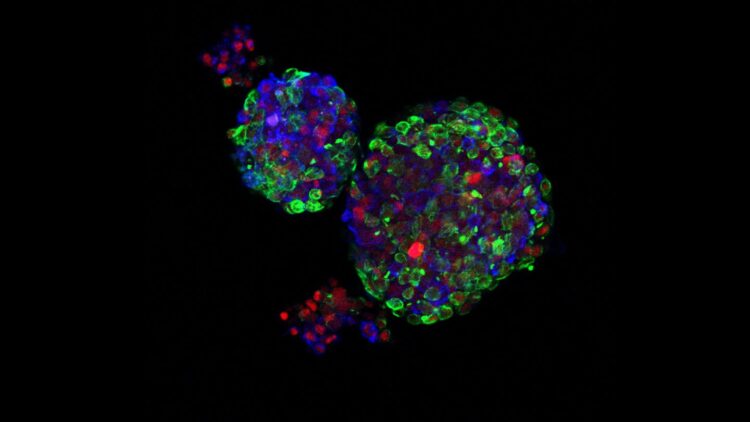
Credit: Chen Chen
An early age of pregnancy (25 years and younger) is known to reduce the overall risk of breast cancer by over 30%. CSHL Assistant Professor Camila dos Santos spent several years teasing out the molecular details behind the protective effects of pregnancy. She discovered that one way breast cells protect themselves from cancer after pregnancy in mice is to tuck away a particularly potent cancer gene, cMYC, where it cannot cause harm. Another trick is to keep breast cells suspended in a state of “pre-senescence,” a moment in the cell’s life cycle between dying, living, and potential cancer. These findings provide new insights into future cancer treatment and better ways to identify risk before a tumor develops.
Pregnancy blocks the deadly action of cMYC by rolling the gene away. Dos Santos suggests a familiar image:
“The event of pregnancy itself changes how regions of DNA are open or closed. Think of a yo-yo. The center of the yo-yo is what we call the nucleosome. It’s a bunch of proteins that protects the DNA. When you release a yo-yo, you have a string, which represents that part of the DNA became open. And because it’s open, now transcription factors can bind and either turn on or off genes. If you pull your yo-yo back, everything gets inside the yo-yo. That’s what we call closed chromatin, so transcription factors cannot bind there.”
Pregnancy turns off the cMYC gene and turns on another set of genes that promotes senescence. Cells repeat the pattern open and closed DNA in subsequent pregnancies.
Senescent cells “are in the gray zone, not growing or dying,” says dos Santos. Depending on how the cells are pushed, they can either stay senescent, die, or grow too much and turn into cancer cells. “It’s a very strong system, but you can mess up with it. And if you do mess up with it, that’s when cancer develops. It allows us now to work on how we can keep those senescent cells from being perturbed.”
Dos Santos says this is one of the few examples showing that a normal developmental process such as pregnancy can inhibit a cell from interacting with a cancer-promoting gene. She summarized her key findings this way: “You have cancer genes being shut down at the same time that genes leading this cell to a kind of a precipice, like they’re going to jump out and die, get turned on. We believe these signals are the key players for why these cells do not turn into cancer.”
Dos Santos and her team are currently working with human breast tissue organoids to see if human tissues act like those in mice. She’s also transplanting cells altered by pregnancy into mice that have never been pregnant, in order to ascertain whether the altered cells can affect a non-pregnant environment. Both experiments suggest new drug targets. “This has opened up doors for us to further explore questions that have not been explored before,” said dos Santos, such as whether puberty or aging can prevent cancer the way pregnancy does.
###
Media Contact
Sara Roncero-Menendez
[email protected]