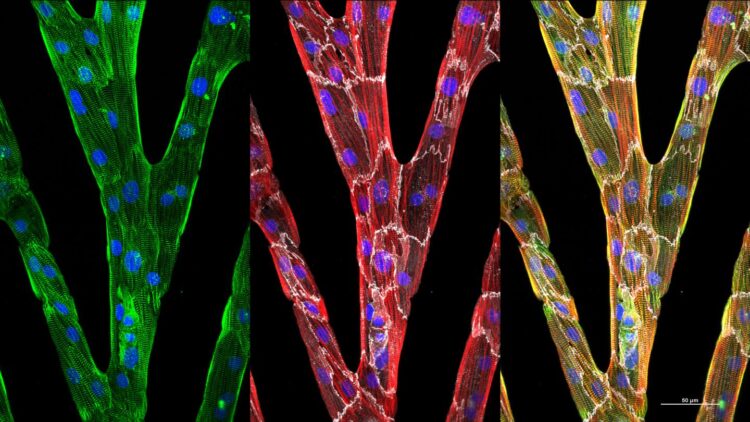
A new algorithm combines gradient methods with fast Fourier transforms to quantify the organization of cardiac myofibrils
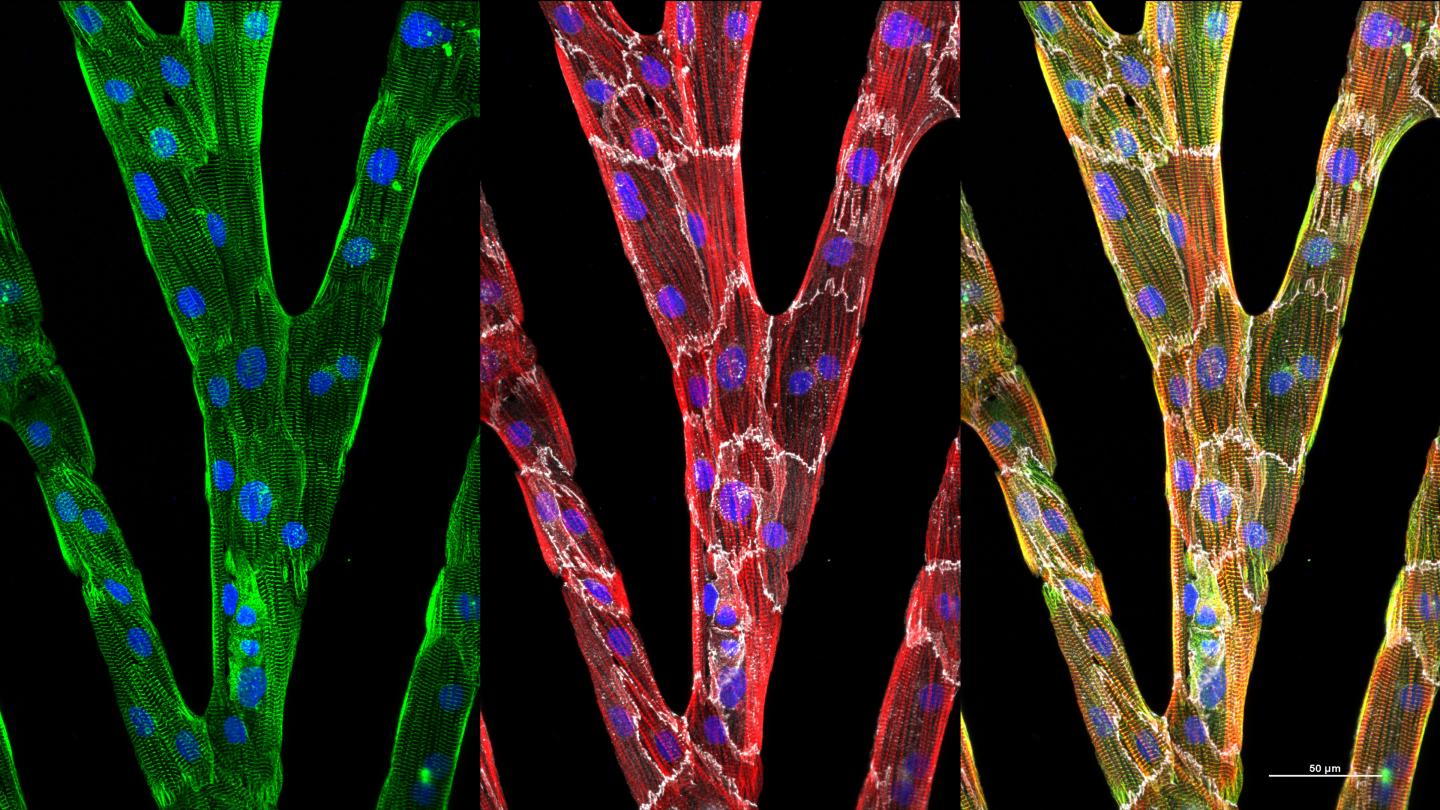
Credit: Brett N. Napiwocki
WASHINGTON, May 19, 2020 — Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States and other industrialized nations, and many patients face limited treatment options. Fortunately, stem cell biology has enabled researchers to produce large numbers of cardiomyocytes, the cells that make up the heart or cardiac muscle and have the potential to be used in advanced drug screens and cell-based therapies.
One of the pitfalls of these stem cell-generated cardiomyocytes is that they do not represent adult human cardiomyocytes but remain immature without further intervention. Additionally, current image analysis techniques do not allow researchers to analyze heterogeneous, multidirectional, striated myofibrils typical of immature cells to determine when new interventions are coaxing the cells to organize.
In the Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing, researchers showcase an algorithm that combines gradient methods with fast Fourier transforms, the scanning gradient Fourier transform or SGFT technique, to quantify myofibril structures in heart cells with considerable accuracy. Myofibrils are the elongated contractile unit of a muscle cell.
“If you look at adult human cardiac tissue, everything is not in perfect alignment. Everything is not stacked nicely and neatly like a bookshelf,” said Wendy Crone, an author of the paper. “The structures are more complicated. We wanted to be able to quantify the organization.”
This level of analysis, combined with new emerging studies of the effects of cell mutation, has the potential to produce new insights regarding the mechanisms underlying the generation of myofibrils and various cardiomyopathies, which make it harder for the heart muscle to pump blood to the rest of the body.
“There is myofibril disarray in certain diseases of the heart,” said Crone. “With our technique, we can quantify the disarray, which provides a better understanding of the severity of disease in heart cells.”
The heterogeneous, striated patterning that this new method can detect and quantify occurs in countless other instances in biology and elsewhere. For instance, the SGFT technique clearly detects the distribution of collagen organization and orientation in breast tissue biopsies, which is significant since breast tissue with cancer has more organized collagen structures. As prior studies have shown, the morphology of collagen fibers in breast cancer tissue is a strong prognostic indicator of the malignancy of the tumor.
The SGFT technique could also potentially be used to quantify striated patterns in early stage neurons derived from stems cells.
“Our code can quantify the organization of neural rosettes, too,” said Crone.
###
The article, “The scanning gradient Fourier transform (SGFT) method for assessing sarcomere organization and alignment,” is authored by Wendy C. Crone, Max R. Salick, Brett N. Napiwocki, Rachel A. Kruepke, Gavin T. Knight and Randolph Ashton. The article will appear in the Journal of Applied Physics on May 12, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/1.5129347). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
The Journal of Applied Physics is an influential international journal publishing significant new experimental and theoretical results in all areas of applied physics. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.