A new battery chemistry promises safer high-voltage lithium-ion batteries
Credit: © 2020 Yamada et al.
For the first time, researchers who explore the physical and chemical properties of electrical energy storage have found a new way to improve lithium-ion batteries. They successfully increased not only the voltage delivery of a lithium-ion battery but also its ability to suppress dangerous conditions that affect the current range of batteries. This improved lithium-ion battery could make longer journeys in electric vehicles possible and lead to the creation of a new generation of home energy storage, both with improved fire safety.
Let’s take a moment to think about batteries. They power pretty much every device that isn’t plugged into the wall, maybe even your car. However, despite their usefulness, most people only pay attention to them when they run out of power. But there are safety issues with current lithium-ion batteries that can damage equipment and have been known to start fires. Researchers at the Graduate School of Engineering and Graduate School of Science at the University of Tokyo came up with a way to improve safety and provide more charge.
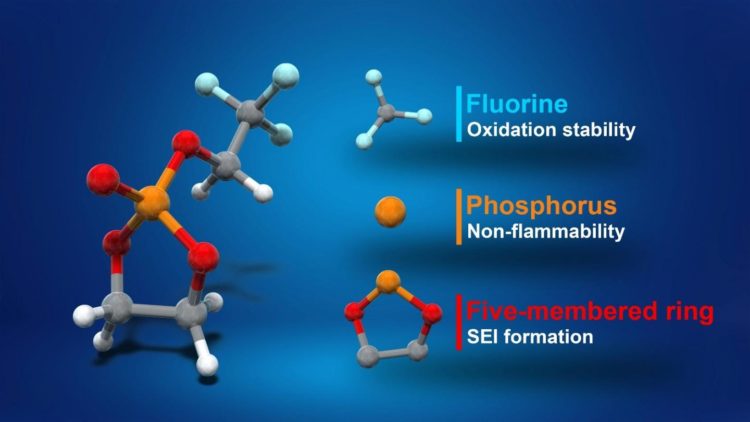
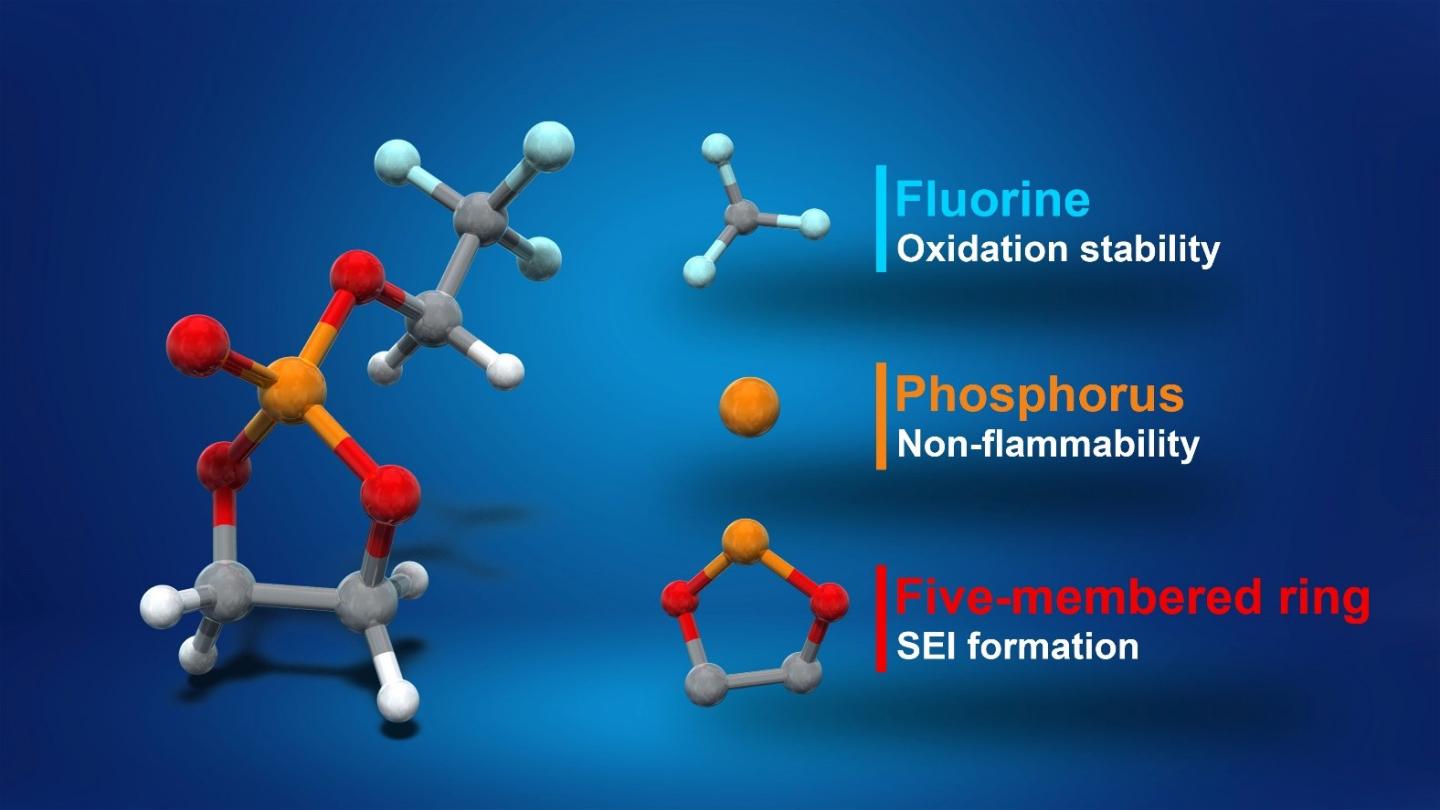
“A battery’s voltage is limited by its electrolyte material. The electrolyte solvent in lithium-ion batteries is the same now as it was when the batteries were commercialized in the early 1990s,” said Professor Atsuo Yamada. “We thought there was room for improvement, and we found it. Our new fluorinated cyclic phosphate solvent (TFEP) electrolyte greatly improves upon existing ethylene carbonate (EC), which is widely used in batteries today.”
EC is notoriously flammable and is unstable above 4.3 volts; TFEP, on the other hand, is nonflammable and can tolerate greater voltages of up to 4.9 volts. This extra voltage in an otherwise identically sized package can mean the batteries can last longer before they need another charge. As lithium ion-powered electric vehicles proliferate, this extra range and safety would no doubt prove extremely useful.
“We’re proud of this development and its effectiveness came as a bit of a surprise. This is because the way we came up with TFEP was novel in itself, thanks in part to our collaboration with organic chemist Professor Eiichi Nakamura,” continued Yamada. “Most research on electrolytes is a bit trial and error, with slight alterations to the basic chemistry rarely offering any advantage. Our approach came from a theoretical understanding of the underlying molecular structures. We predicted the safe, high-voltage properties before we experimentally verified them. So it was a very pleasant surprise indeed.”
###
Journal article
Qifeng Zheng, Yuki Yamada, Rui Shang, Seongjae Ko, Yun-Yang Lee, Kijae Kim, Eiichi Nakamura, Atsuo Yamada. A cyclic phosphate-based battery electrolyte for high voltage and safe operation. Nature Energy. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-020-0567-z
Supported by JSPS KAKENHI Specially Promoted Research (No. 15H05701 and 19H05459)
Related links
Meet researchers from the team in our recent short film “Building better batteries” http://www.
Yamada & Okubo Laboratory – http://yamada-lab.
Graduate School of Engineering – http://www.
Graduate School of Science – https:/
Research Contacts
Professor Atsuo Yamada
Department of Chemical System Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering,
The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656 JAPAN
Tel: +81-3-5841-7295
Email: [email protected]
Professor Eiichi Nakamura
Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science,
The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656 JAPAN
Tel: +81-3-5841-4356
Email: [email protected]
Press Contact
Mr. Rohan Mehra
Division for Strategic Public Relations, The University of Tokyo
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8654 JAPAN
Tel: +81-3-5841-0876
Email: [email protected]
About the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan’s leading university and one of the world’s top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world’s top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at https:/
Media Contact
Professor Atsuo Yamada
[email protected]
81-358-417-295
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.