Credit: Professor Inkyu Park, KAIST
KAIST researchers have developed a novel wearable strain sensor based on the modulation of optical transmittance of a carbon nanotube (CNT)-embedded elastomer. The sensor is capable of sensitive, stable, and continuous measurement of physical signals. This technology, featured in the March 4th issue of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces as a front cover article, shows great potential for the detection of subtle human motions and the real-time monitoring of body postures for healthcare applications.
A wearable strain sensor must have high sensitivity, flexibility, and stretchability, as well as low cost. Those used especially for health monitoring should also be tied to long-term solid performance, and be environmentally stable. Various stretchable strain sensors based on piezo-resistive and capacitive principles have been developed to meet all these requirements.
Conventional piezo-resistive strain sensors using functional nanomaterials, including CNTs as the most common example, have shown high sensitivity and great sensing performance. However, they suffer from poor long-term stability and linearity, as well as considerable signal hysteresis. As an alternative, piezo-capacitive strain sensors with better stability, lower hysteresis, and higher stretchability have been suggested. But due to the fact that piezo-capacitive strain sensors exhibit limited sensitivity and strong electromagnetic interference caused by the conductive objects in the surrounding environment, these conventional stretchable strain sensors are still facing limitations that are yet to be resolved.
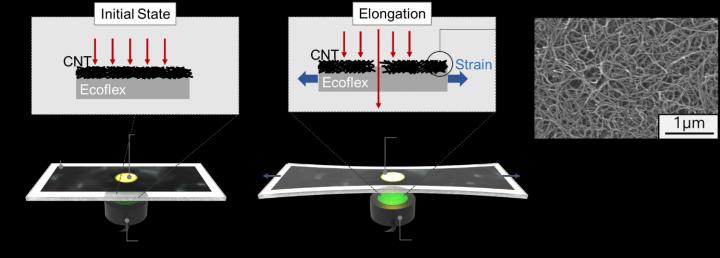
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering suggested that an optical-type stretchable strain sensor can be a good alternative to resolve the limitations of conventional piezo-resistive and piezo-capacitive strain sensors, because they have high stability and are less affected by environmental disturbances. The team then introduced an optical wearable strain sensor based on the light transmittance changes of a CNT-embedded elastomer, which further addresses the low sensitivity problem of conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
In order to achieve a large dynamic range for the sensor, Professor Park and his researchers chose Ecoflex as an elastomeric substrate with good mechanical durability, flexibility, and attachability on human skin, and the new optical wearable strain sensor developed by the research group actually shows a wide dynamic range of 0 to 400%.
In addition, the researchers propagated the microcracks under tensile strain within the film of multi-walled CNTs embedded in the Ecoflex substrate, changing the optical transmittance of the film. By doing so, it was possible for them to develop a wearable strain sensor having a sensitivity 10 times higher than conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
The proposed sensor has also passed the durability test with excellent results. The sensor’s response after 13,000 sets of cyclic loading was stable without any noticeable drift. This suggests that the sensor response can be used without degradation, even if the sensor is repeatedly used for a long time and in various environmental conditions.
Using the developed sensor, the research team could measure the finger bending motion and used it for robot control. They also developed a three-axes sensor array for body posture monitoring. The sensor was able to monitor human motions with small strains such as a pulse near the carotid artery and muscle movement around the mouth during pronunciation.
Professor Park said, “In this study, our group developed a new wearable strain sensor platform that overcomes many limitations of previously developed resistive, capacitive, and optical-type stretchable strain sensors. Our sensor could be widely used in a variety of fields including soft robotics, wearable electronics, electric skin, healthcare, and even entertainment.”
###
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Media Contact
Younghye Cho
[email protected]
82-423-502-294
Original Source
http://news.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




