New updated Wilderness Medical Society guidelines on management of exercise-related hyponatremia published in Wilderness & Environmental Medicine highlight the importance of avoiding overhydration
Credit: Wilderness & Environmental Medicine
Philadelphia, March 18, 2020 – Hyponatremia is a condition of low sodium concentration in the blood. Prolonged overhydration during exercise is the primary cause of all forms of exercise-associated hyponatremia (EAH) and should be avoided. The updated EAH clinical practice guidelines issued by the Wilderness Medical Society stress that individuals engaged in physical and endurance activities should drink to satisfy their thirst (known as “drink to thirst”) to avoid overhydration. The guidelines appear in Wilderness & Environmental Medicine, published by Elsevier.
Review articles and international consensus statements have mainly focused on the incidence of EAH in organized endurance events that are conducted in the frontcountry, where medical tents and local emergency medical services are typically available on site and transport to a local hospital is readily available. However, many prolonged individual exertional activities such as backpacking, ultramarathons, and multiple-day endurance events take place in the backcountry with limited or no medical support and expectations of delayed medical evacuation.
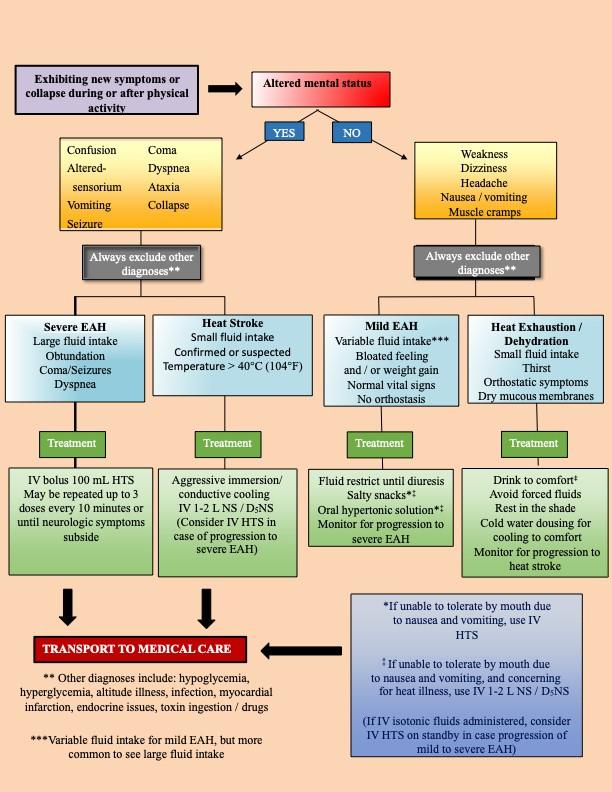
Appropriated management of EAH depends first on correctly diagnosing the condition. The guidelines address the assessment of patients with overlapping or nonspecific signs that can make differential diagnosis challenging, for example, with heat exhaustion or exertional heat stroke.
“Even after 40 years of worldwide documentation of EAH in both frontcountry and backcountry physical activities there is still an ongoing need for education of the public, event directors, EMS personal, and clinicians for prevention strategies and medical management caused by overhydration of fluids that can result in rare, but life threatening medical outcomes,” explained lead author Brad L. Bennett, PhD, Adjunct Professor, Military & Emergency Medicine Department, F. Edward Hébert School of Medicine, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, MD, USA. “The typical field response for heat-related illness or when someone is dehydrated is to encourage oral hypotonic fluid intake or administer rapid isotonic IV fluids to endurance activity participants. However, such universal treatment may result in increased morbidity and mortality in the EAH patient.”
The guidelines recommend that:
- Appropriate education and coordination among participants, event directors, support crews, park rangers, first responders, and EMS transport personnel are essential in both prevention and management of EAH.
- Prolonged overhydration during exercise, which is the primary risk factor in the development of all forms of EAH, should be avoided.
- Sodium and/or salty snacks should be freely available for consumption along with the appropriate fluids, particularly in long, hot events in non-heat acclimatized persons.
- Participants should drink enough to satisfy their thirst but avoid overdrinking.
- Point-of-care testing should be done on at-risk, symptomatic patients, when available.
- Oral fluids should be restricted if EAH from fluid overload is associated with mild symptoms.
- Hypotonic fluids are contraindicated with suspected EAH.
- The use of oral salt or hypertonic fluids may be effective in reversing moderate to severe symptoms of EAH when no IV hypertonic saline (3 percent) is available.
- Patients should be observed for at least 60 minutes after exercise to ensure no decompensation from delayed symptomatic EAH.
- Receiving caregivers should be alerted to the potential diagnosis of EAH and fluid management restrictions when transferring care.
“It is important to note that no single recommendation for fluid hydration will work in the range of physical activities in different humidity and ambient temperatures with varied sweat rate, body mass, exercise intensity, and duration. However, for the majority of individuals, drinking according to thirst can help prevent EAH and the potential for life threatening outcomes,” commented Dr Bennett.
EAH is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe EAH being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms may include nausea and vomiting, headache, short-term memory loss, confusion, and lethargy, altered mental status, coma, seizures, and/or respiratory distress, some of which can be confused with other medical conditions.
###
Media Contact
Theresa Monturano
[email protected]
215-239-3711
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




