Credit: Physical Review Letters
Google is racing to develop quantum enhanced processors that utilize quantum mechanical effects to one day dramatically reduce the speed at which data can be processed.
In the near term, Google has devised new quantum enhanced algorithms that operate in the presence of realistic noise. The so called quantum approximate optimisation algorithm, or QAOA for short, is the cornerstone of a modern drive towards noise-tolerant quantum enhanced algorithm development.
The celebrated approach taken by Google in QAOA has sparked vast commercial interest and ignited a global research community to explore novel applications. Yet, little actually remains known about the ultimate performance limitations of Google’s QAOA algorithm.
A team of scientists, hailing from Skoltech’s Deep Quantum Laboratory, took up this contemporary challenge. The all-Skoltech team led by Prof. Jacob Biamonte discovered and quantified what appears to be a fundamental limitation in the wildly adopted approach initiated by Google.
Reporting in Physical Review Letters, the authors detail the discovery of so called reachability deficits – the authors show how these deficits place a fundamental limitation on the ability of QAOA to even approximate a solution to a problem instance.
The Skoltech team’s findings report a clear limitation of the variational QAOA quantum algorithm. QAOA and other variational quantum algorithms have proven extremely difficult to analyse using known mathematical techniques due to an internal quantum-to-classical feedback process. Namely, a given quantum computation can only run for a fixed amount of time. Inside this fixed time, a fixed number of quantum operations can be executed. QAOA seeks to iteratively utilize these quantum operations by forming a sequence of increasingly optimal approximations to minimize an objective function. The study places new limits on this process.
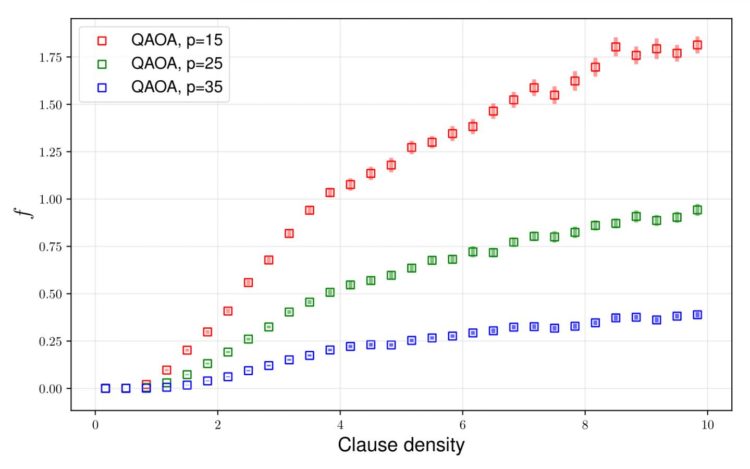
The authors discovered that QAOA’s ability to approximate optimal solutions for any fixed depth quantum circuit is fundamentally dependent on the problems “density.” In the case of the problem called MAX-SAT, the so called density can be defined as the ratio of the problems constraints to variable count. This is sometimes called clause density.
The authors discovered problem instances of high density whose optimal solutions cannot be approximated with guaranteed success, regardless of the algorithms’ run-time.
###
Media Contact
Alina Chernova
[email protected]
7-905-565-3633
Related Journal Article
http://dx.