Credit: Dr. Börge Göbel/MLU
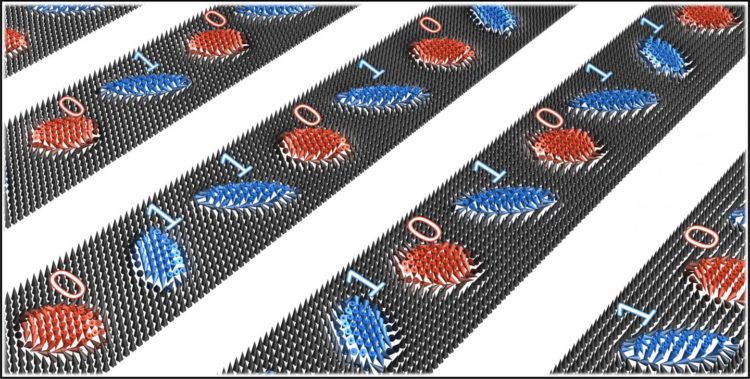
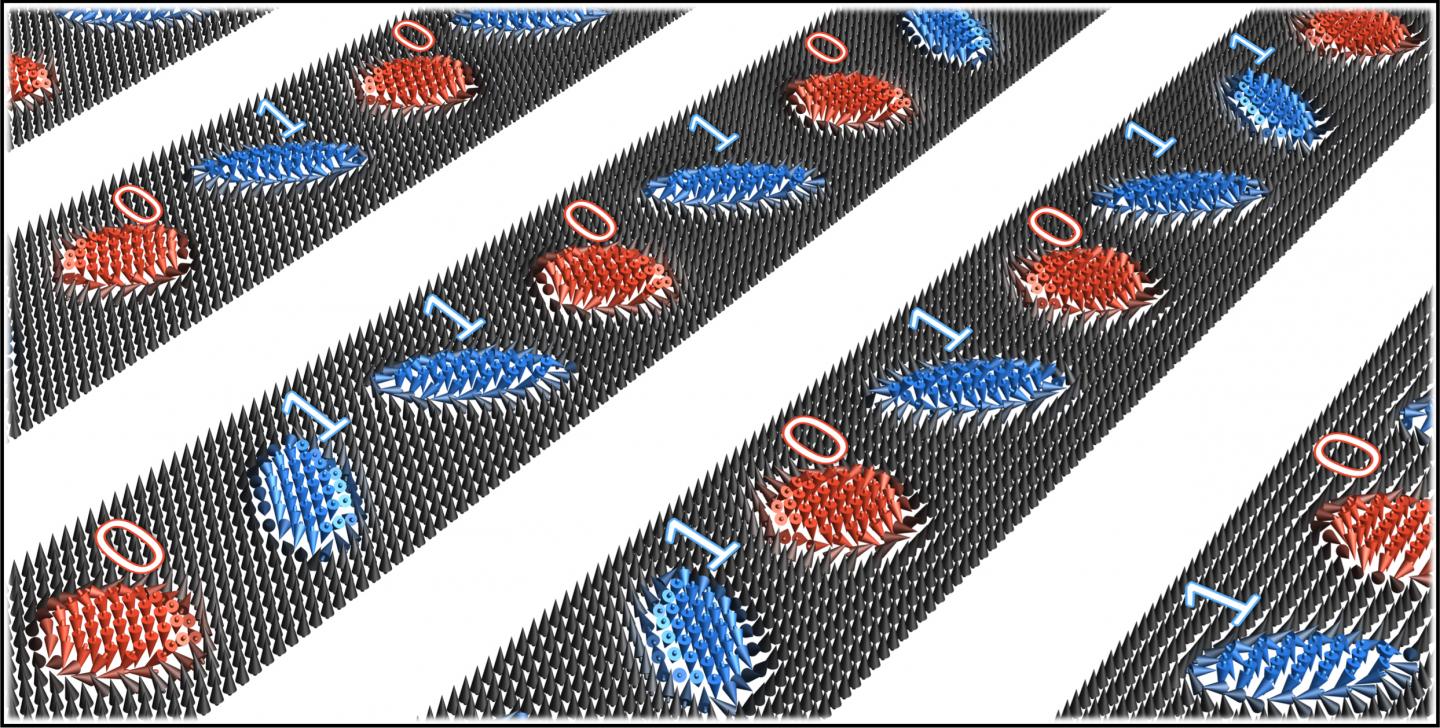
Magnetic (anti)skyrmions are microscopically small whirls that are found in special classes of magnetic materials. These nano-objects could be used to host digital data by their presence or absence in a sequence along a magnetic stripe. A team of scientists from the Max Planck institutes (MPI) of Microstructure Physics in Halle and for Chemical Physics of Solids in Dresden and the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) has now made the observation that skyrmions and antiskyrmions can coexist bringing about the possibility to expand their capabilities in storage devices. The results were published in the scientific journal “Nature Communications“.
With the ever-increasing volumes of digital data from the growing numbers of devices, the demand for data storage capacity has been enhanced dramatically over the past few years. Conventional storage technologies are struggling to keep up. At the same time, the ever-increasing energy consumption of these devices – hard disk drives (HDD) and random-access memories (RAM) – is at odds with a “green” energy landscape. Required are entirely new devices that have greater performance at a drastically reduced energy consumption.
A promising proposal is the magnetic racetrack memory-storage device. It consists of nanoscopic magnetic stripes (the racetracks) in which data is encoded in magnetic nano-objects, typically by their presence or absence at specified positions. One possible nano-object is a magnetic (anti)skyrmion: this is an extremely stable whirl of magnetization with a size that can be varied from micrometers to nanometers. These objects can be written and deleted, read and, most importantly, moved by currents, therefore allowing the racetrack to be operated without any moving parts. “By stacking several racetracks, one on top of each other, to create an innately three-dimensional memory-storage device, the storage capacity can be drastically increased compared to solid state drives and even hard disk drives. Moreover, such a racetrack memory device would operate at a fraction of the energy consumption of conventional storage devices. It would be much faster, and would be much more compact and reliable”, explains Prof Stuart Parkin, director of the MPI of Microstructure Physics in Halle and Alexander von Humboldt Professor at the MLU.
“Skyrmions and antiskyrmions are ‘opposite’ magnetic whirls. However, until recently, it was believed that these two distinct objects can only exist in different classes of materials.” explains Prof Ingrid Mertig from the institute of physics at MLU. The research team from Max Planck institutes in Halle and Dresden and the MLU has now discovered that antiskyrmions and skyrmions can coexist under certain conditions in the same material. Dr Börge Göbel, a member of Mertig’s research group, provided the theoretical explanation for the unexpected experimental observations that were carried out by Jagannath Jena in Parkin’s group. The measured single crystal materials, Heusler compounds, were prepared by Dr Vivek Kumar in the group of Prof Claudia Felser at the MPI in Dresden.
Skyrmions and antiskyrmions are stabilized in different materials by a magnetic interaction that is directly tied to the structure of the host material. In some materials only skyrmions can form, while in other materials, antiskyrmions are energetically preferred by this interaction. However, what was previously overlooked is that the individual magnets in each material (the “magnetic dipoles”) also significantly interact with each other via their dipole-dipole interaction. This interaction always prefers skyrmions. For this reason, even “antiskyrmion materials” can exhibit skyrmions (but not vice versa). This happens preferably as the temperature is lowered. At a critical transition temperature, the two distinct objects coexist.
Besides its fundamental relevance, this finding allows for an advanced version of the racetrack memory data storage, where a bit sequence could, for example, be encoded by a sequence of skyrmions (‘1’ bit) and antiskyrmions (‘0’ bit). This concept would be more reliable than conventional racetracks.
###
Media Contact
Ronja Münch
[email protected]
49-345-552-1438
Related Journal Article
http://dx.