Credit: University of Southampton
A new infection test, made up of sheets of paper patterned by lasers, has been developed by University of Southampton researchers to allow diagnosis at the point of care – helping doctors give patients the right treatment, faster.
Laboratory tests to identify the cause of common infections like urinary tract infections (UTIs) can take up to four days, with doctors having to use broad-action antibiotics as a first line of treatment.
This may not only be less effective than using drugs specific to the infection, but also contributes to an increase in antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Now new research, led by Dr Collin Sones from the University of Southampton and published in Biosensors and Bioelectronics, shows a paper-based device made using lasers could allow doctors to find out which antibiotic, if any, they should give.
‘Cheap and easy to use’
Using similar methods to existing pregnancy tests and urine dipsticks, the new technology has the potential to be cheap to produce, easy to use and could be done by a doctor or nurse on the ward – slashing diagnosis times.
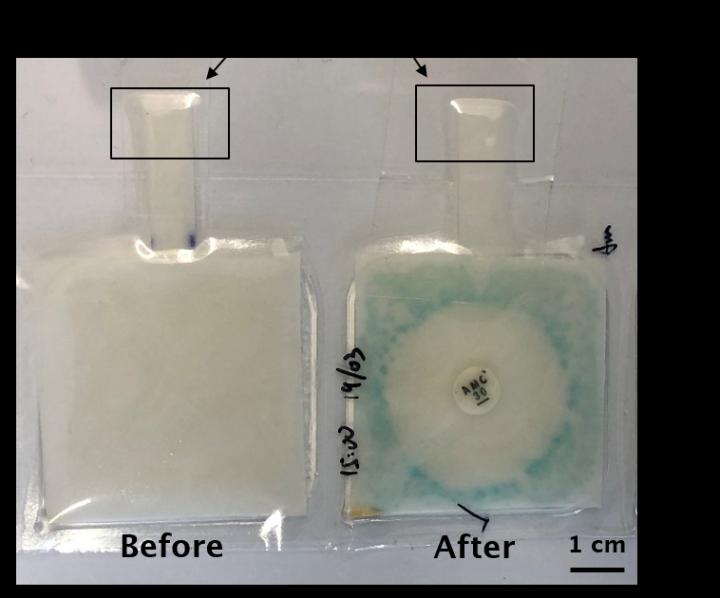
Made using lasers, the test paper has three layers – a top layer containing four common antibiotics in confined rectangular areas, an absorbent paper in the middle and an agar gel-containing base layer, all sealed in a plastic casing.
The liquid sample (e.g. urine) is added to a small paper tab, which is then covered with tape to prevent drying out or contamination.
The sample then spreads across the middle paper layer, coming into contact with the four rectangles containing the test antibiotics (amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin and nitrofurantoin).
If bacteria are present the paper will turn blue and if the infection can be treated with one of the antibiotics there will be a clear patch around the corresponding rectangle.
As well as giving doctors an early identification of bacterial infection, the test also directs which one of the four common antibiotics will work best – or if it is a strain untreatable with any of them.
When compared against standard lab tests done in petri dishes with agar gel, using artificial urine spiked with the bacteria E.coli, the team got comparable results.
‘Fighting antibiotic resistance’
A serious threat, which opens the prospect of routine procedures and infections to small cuts once again becoming potentially life threatening, antibiotic resistant infections rose by 9% in England between 2017 and 2018, with about 61,000 cases.
It occurs when bacteria evolve defences against antibiotics, usually through being exposed to the drug for too long or at too low a dose – allowing the strongest, most drug resistant, to survive and replicate.
Cutting overuse of antibiotics, particularly broad-action drugs, is critical for preventing more resistant strains emerging, keeping the drugs effective and reducing the threat to patients.
“By enabling doctors to quickly determine if an infection is caused by bacteria, and if the bacteria are resistant to four common antibiotics, this device could cut down on unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions and help fight the growing threat of antibiotic resistance,” said Dr Sones.
Dr Sones and his team will present their research, as part of the University of Southampton’s Network on Antimicrobial Resistance and Infection Prevention (NAMRIP), on 25th February at a Superbugs event at the UK Parliament.
###
Notes to Editors
For further information and interview requests, please contact Steve Bates, Media Relations Officer, University of Southampton. [email protected]; 02380 593212
The University of Southampton drives original thinking, turns knowledge into action and impact, and creates solutions to the world’s challenges. We are among the top 100 institutions globally (QS World University Rankings 2019). Our academics are leaders in their fields, forging links with high-profile international businesses and organisations, and inspiring a 24,000-strong community of exceptional students, from over 135 countries worldwide. Through our high-quality education, the University helps students on a journey of discovery to realise their potential and join our global network of over 200,000 alumni. http://www.
Media Contact
Steve Bates
[email protected]
0238-059-3212
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




