Credit: Koji Nishiguchi, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
Mice born blind have shown significant improvement in vision after undergoing a new gene therapy developed by a team of Japanese scientists.
The results were published on January 24th in Nature Communications.
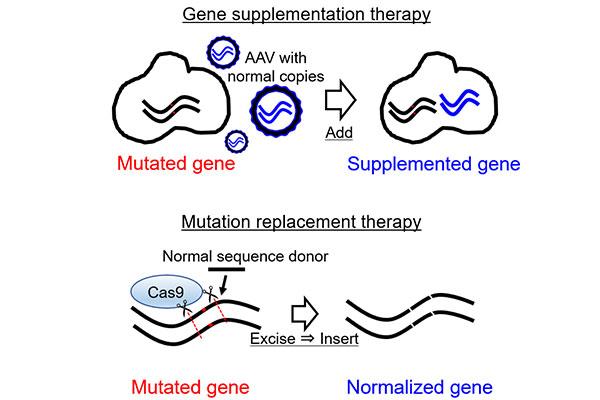
This new method is an alternative strategy of gene supplementation, which involves supplementing the defective gene, such as the ones that can lead to inherited retinal degeneration, with a healthy one. The healthy gene is delivered via the adeno-associated virus (AAV). However, the virus can only hold only a small healthy gene, and the vast majority of patients with defects in a larger gene cannot be treated with this method.
“To overcome this problem, we developed a single AAV gene therapy platform that allows local replacement of a mutated sequence with its healthy counterpart that can treat almost any mutation,” said Koji Nishiguchi, co-first author on the paper and associate professor in the Department of Advanced Ophthalmic Medicine at Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine.
The single AAV gene therapy platform combines CRISPR-Cas9 technology with micro-homology-mediated end joining. These two thing act essentially as genetic scissors and genetic glue respectively. Researchers can target a specific defective gene, cut it out and glue in a healthy replacement.
In blind mice, this approach rescued approximately 10% of photoreceptors, resulting in improved light sensitivity and an increase in visual activity. The improvement in vision was about the same result gene supplementation can produce.
“By treating mice blinded by inherited retinal degeneration with the new treatment, we show that a robust visual restoration can be achieved at a level similar to that mediated by conventional gene supplementation, assuring its potential for clinical application,” Nishiguchi said. “The platform paves the way for treating patients with mutations in larger genes, which comprise the vast majority of those with inherited retinal degeneration. Furthermore, a similar approach can be applied to treat almost any ocular and non-ocular inherited conditions.”
Now, the researchers are applying the new genome editing platform to develop a therapy for human patients with retinitis pigmentosa, a group of rare conditions that can cause loss of peripheral vision and difficulty seeing at night. They will target common mutations among patients that remain untreatable by conventional gene therapy. Nishiguchi’s team plans to have therapy in a clinical trial by as early as 2025.
###
Media Contact
Koji Nishiguchi
[email protected]
81-227-177-294
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




