Credit: NASA Worldview
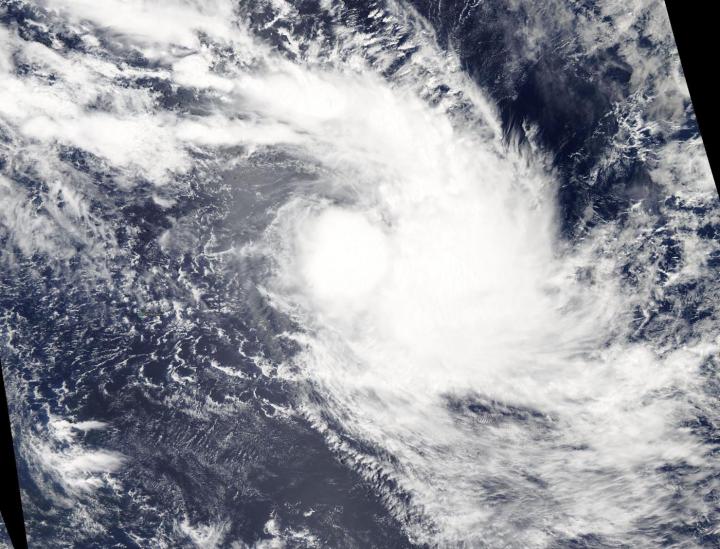
Shortly after Tropical Cyclone Francisco formed on Feb. 5 in the Southern Indian Ocean, NASA’s Aqua satellite provided a visible image of the storm.
On Feb. 5, 2020, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite provided a visible image of Francisco that showed powerful thunderstorms around the low-level center. Satellite imagery showed shallow thunderstorm banding wrapping into the center of the low-level center and strong convective bands of thunderstorms over the eastern semicircle.
On Feb. 5 at 4 a.m. EST (0900 UTC), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) noted that Tropical Cyclone Francisco was located near latitude 17.3 degrees south and longitude 68.5 degrees east, about 647 nautical miles east-southeast of Mauritius. Maximum sustained winds 40 knots (46 mph/74 kph). This storm is moving to the southeastward.
Francisco is forecast to slightly intensify today, Feb. 5. The JTWC expects Francisco will continue to track southeast to south over the next day and a half and turn to the west-southwest after which time it is expected to begin weakening.
###
NASA’s Aqua satellite is one in a fleet of NASA satellites that provide data for hurricane research.
Tropical cyclones/hurricanes are the most powerful weather events on Earth. NASA’s expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
By Rob Gutro
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
Rob Gutro
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




