Credit: Jingnan Yang, Chenjiang Qian, Xin Xie, Kai Peng, Shiyao Wu, Feilong Song, Sibai Sun, Jianchen Dang, by Yang Yu, Shushu Shi, Jiongji He, Matthew J. Steer, Iain G. Thayne, Bei-Bei…
DPs originate from parameter-dependent degeneracies of a system’s energy lev-els. Due to the topological Berry phase, DPs play a fundamental role in physical and chemical dynamics, such as peculiar photonics in 2D materials or condensed matter systems which provide topological quantum processing. Meanwhile, active emitters in photonic structures are essential for the coherent electron-photon interface in the quantum photonic network. Therefore, realizing DPs in active photonic structures can greatly benefit the implementing of quantum information processing and scaling up in the quantum network. However, multiple quantum emitters in active cavities are usu-ally randomly positioned, thus result in symmetric and uncontrollable backscattering which forbids a degeneracy with only trivial eigenstates. As a result, the coherent in-terface between electrons and photons at DPs is hard to achieve.
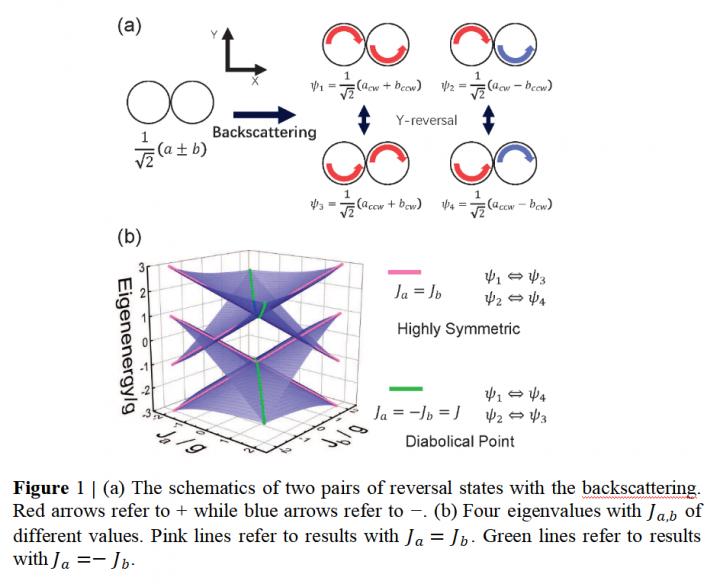
In a paper newly published in Light Science & Application, scientists from Insti-tute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and co-workers demonstrate DPs in two strongly coupled microdisks with embedded quantum dots (QDs). Due to that the individual control of each QD is impossible, a macroscopical control of backscat-tering was proposed based on the competition between two types of scatterers (QDs and defects), which solves the problem of low controllability. Through optimization, a balanced competition was successfully achieved with backscattering coupling strength from negative to positive in single microdisks, clearly demonstrated by the experi-mental statistics. Furthermore, compared to single microdisks with two-dimensional Hamiltonians, two strongly coupled microdisks have supermodes with four-dimensional Hamiltonians. The spectra are affected by not only the absolute backscat-tering coupling strengths but also their signs. Thus, coupled cavities are a good plat-form to study the fundamental physics of backscattering and make DP possible. Her-mitian degeneracies at DPs were observed when the backscattering coupling strengths in two microdisks have the same absolute value but in the opposite signs.
At DP of two coupled cavities, the system has eigenspaces in which the phases of two microdisks have a nonlinear correlation, indicating a controllable phase shift between them. Therefore, the two coupled cavities are potential in directional laser and quantum phase control. Moreover, when the interaction between emitters and cavities is improved in future, this system can be predicted with an important role in studying quantum DP behaviors and integrating photons at DPs into quantum net-works.
“The randomly positioned quantum dots and defects are very hard to control and can result in symmetric backscattering. We introduced the macroscopical control based on the competition between different types of scatterers and achieved backscat-tering coupling strength with both negative or positive values.”
“We experimentally demonstrated one pair of DPs in the spectra with two strongly coupled microdisks, which are different from the ordinary DP without backscattering or in a single perfect microcavity. DPs here can produce nonlinear cor-relation with a phase shift between two microdisks, with potential application in opti-cal quantum information processing, topological optics and fundamental physics at DPs using photonic structures.” The scientists said.
###
Media Contact
Xiulai Xu
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




