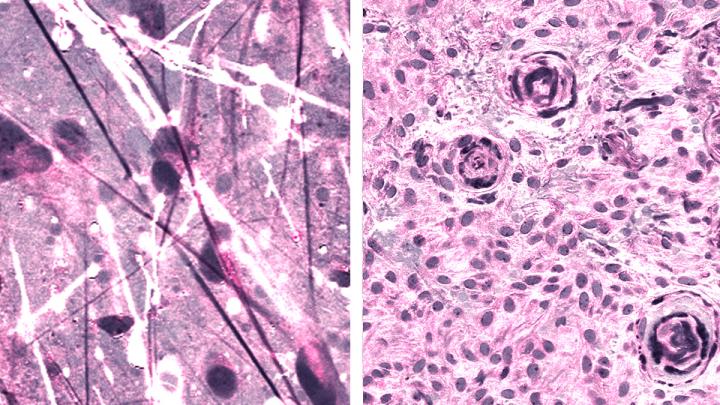
Credit: Daniel Orringer, NYU Langone Health
A novel method of combining advanced optical imaging with an artificial intelligence algorithm produces accurate, real-time intraoperative diagnosis of brain tumors, a new study finds.
Published in Nature Medicine on January 6, the study examined the diagnostic accuracy of brain tumor image classification through machine learning, compared with the accuracy of pathologist interpretation of conventional histologic images. The results for both methods were comparable: the AI-based diagnosis was 94.6% accurate, compared with 93.9% for the pathologist-based interpretation.
The imaging technique, stimulated Raman histology (SRH), reveals tumor infiltration in human tissue by collecting scattered laser light, illuminating essential features not typically seen in standard histologic images.
The microscopic images are then processed and analyzed with artificial intelligence, and in under two and a half minutes, surgeons are able to see a predicted brain tumor diagnosis. Using the same technology, after the resection, they are able to accurately detect and remove otherwise undetectable tumor.
“As surgeons, we’re limited to acting on what we can see; this technology allows us to see what would otherwise be invisible, to improve speed and accuracy in the OR, and reduce the risk of misdiagnosis,” says senior author Daniel A. Orringer, MD, associate professor of Neurosurgery at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, who helped develop SRH and co-led the study with colleagues at the University of Michigan. “With this imaging technology, cancer operations are safer and more effective than ever before.”
How the Study Was Conducted
To build the artificial intelligence tool used in the study, researchers trained a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) with more than 2.5 million samples from 415 patients to classify tissue into 13 histologic categories that represent the most common brain tumors, including malignant glioma, lymphoma, metastatic tumors, and meningioma.
In order to validate the CNN, researchers enrolled 278 patients undergoing brain tumor resection or epilepsy surgery at three university medical centers in the prospective clinical trial. Brain tumor specimens were biopsied from patients, split intraoperatively into sister specimens, and randomly assigned to the control or experimental arm.
Specimens routed through the control arm–the current standard practice–were transported to a pathology laboratory and went through specimen processing, slide preparation by technicians, and interpretation by pathologists, a process which takes 20-30 minutes. The experimental arm was performed intraoperatively, from image acquisition and processing to diagnostic prediction via CNN.
Notably, the diagnostic errors in the experimental group were unique from the errors in the control group, suggesting that a pathologist using the novel technique could achieve close to 100% accuracy. The system’s precise diagnostic capacity could also be beneficial to centers that lack access to expert neuropathologists.
“SRH will revolutionize the field of neuropathology by improving decision-making during surgery and providing expert-level assessment in the hospitals where trained neuropathologists are not available,” says Matija Snuderl, MD, associate professor in the Department of Pathology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and a co-author of the study.
NYU Langone’s Brain and Spine Tumor Center Offers Cutting-Edge Treatment
Dr. Orringer joined NYU Langone in August 2019, bringing with him the SRH technology he helped to develop. NYU Langone’s Brain and Spine Tumor Center is the first to offer this technique, using Invenio’s NIO Laser Imaging System, in the Northeast.
The newest addition to the center’s comprehensive suite of neurosurgical imaging technologies, SRH works in concert with intraoperative MRI and fluorescence-guided surgery to provide high-resolution precision guidance for NYU Langone’s world-class neurosurgeons.
“NYU Langone’s Department of Neurosurgery has long been a leader in bringing the most advanced treatment options to our patients,” says John G. Golfinos, MD, Joseph P. Ransohoff Professor of neurology and chair of the Department of Neurosurgery. “With the addition of Dr. Orringer’s expertise and this game-changing technology, we’re now even better equipped to provide safe surgeries and quality outcomes for the most complex brain tumor cases.”
The implementation of this new system is the most recent of NYU Langone’s efforts to integrate artificial intelligence in clinical practice to improve diagnostics of cancer. Researchers and clinicians at NYU Langone’s Perlmutter Cancer Center have made recent strides in lung cancer, breast cancer, and brain tumor.
###
Media Contact
Annie Harris
[email protected]
212-404-3588
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




