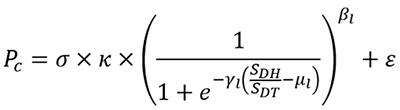
Credit: Kobe University
A research team at Kobe University Hospital have further illuminated the likelihood of cancer drug side effects that can occur due to genetic mutations in the drug-metabolizing enzyme. The team led by Dr. TAKAOKA Yutaka also developed a mathematical model by using the results of molecular simulation analyses to predict the possibility of side effects.
It is hoped that this research will pave the way for effective predictions of cancer drug side effects and treatment results.
These research findings were first published in the American Scientific Journal ‘PLOS ONE‘ on November 15 2019.
Research Background
Predictions regarding cancer treatment effectiveness and side effects can be made relating to 1. Drug metabolism and 2. Drug effectiveness on administration. However, how well drugs will be metabolized, their effectiveness and the likelihood of side-effects depends on individual differences. For example, before a patient with colon cancer is treated with the anti-cancer drug Irinotecan, a genetic analysis of their UGT1A1 must be performed. UGT1A1 is an enzyme found mainly in the liver which is responsible for processing many chemical substances, including Irinotecan. It is known that the patient with mutations in the UGT1A1 gene (in particular the mutations UGT1A1*6 and UGT1A1*28) have difficulty metabolizing this cancer drug, making severe side effects.
In recent years, genetic analysis technology has been advancing and new mutations in UGT1A1 are being discovered. To date, around 70 different mutations have been found. The ability of each of these newly discovered mutations to metabolize drugs is unknown, therefore it is difficult to accurately determine the likelihood of adverse reactions to anti-cancer agents.
Research Methodology
Professor Takaoka et al. used the results from molecular computer simulation analyses and wet laboratory experiments (using cells) to develop the following mathematical model for drug metabolism by the UGT1A1 (Figure 1).
They succeeded in using this mathematical model to predict the ability of UGT1A1 mutants to metabolize the anti-cancer agent with high accuracy- as shown in the bar graph (Figure 2). The predictions using the mathematical equation (gray bars) are very similar to the actual results (black bars).
Based on these results, this method was able to predict the drug metabolizing ability of UGT1A1 mutations. It is hoped that this methodology could be used to predict the possibility of cancer drug side-effects before they are prescribed- even for newly discovered mutations of UGT1A1.
Further Research
It is expected that further research using a similar methodology could be utilized to predict cancer drug effectiveness. Professor Takaoka et al. have already used RIKEN’s K-computer to perform a basic analysis and they are currently working towards being able to predict the effectiveness of drugs utilized in lung cancer treatment.
###
Media Contact
Verity Townsend
[email protected]
81-788-035-282
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




