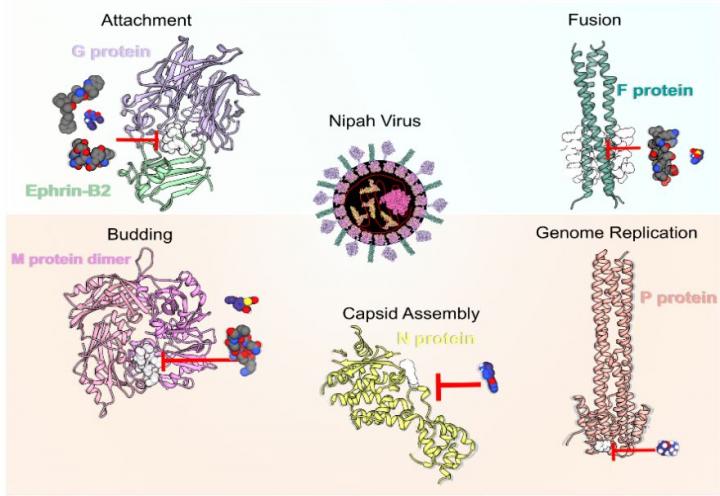
Credit: Mallur Madhusudhan, CC BY 4.0
Nipah virus, which is transmitted to humans from bats and pigs, has a high mortality rate and there are no licensed drugs against it. Now, researchers have used information on the structure of the Nipah virus to identified 150 possible inhibitors of the virus. The results are published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Nipah virus infections have killed 72-86% of infected individuals in Bangladesh and India. Although the disease was first identified in 1998, there are no approved drugs or vaccines against it. Though the overall number of fatalities linked with each individual outbreak has never been more than 105, the disease poses a deadly threat and could become pandemic.
In the new work, M.S. Madhusudhan and collagues at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Pune first made three-dimension models of the 9 Nipah virus proteins. Then, they used these models design inhibitory molecules to block the proteins’ activity. Finally, the team assessed how effective the proposed inhibitors would be against 15 different strains of the virus– 3 Bangladeshi, 7 Malaysian and 5 Indian strains.
The researchers computationally identified 4 putative peptides inhibitors and 146 small molecule inhibitors against Nipah virus proteins. 13 of their proposed inhibitors were short-listed as the most promising based on their binding strength, stability, and effectiveness against multiple strains of Nipah virus.
“We conclude that it is highly likely that the proposed inhibitors would be potent against all strains of the virus Nipah and other related zoonotic viruses that pose a serious epidemic threat,” the researchers say. “Computational approaches can help identify and design inhibitors that could be rapidly tested or even deployed.”
###
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper: http://journals.
Funding: MS Madhusudhan would like to acknowledge the Wellcome Trust-DBT India alliance for a senior fellowship. Neeladri Sen and Sanjana Nair would like to acknowledge CSIR-SPMF for funding. Kaustubh Amritkar would like to acknowledge INSIPRE-SHE fellowship. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Media Contact
Mallur Madhusudhan
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




