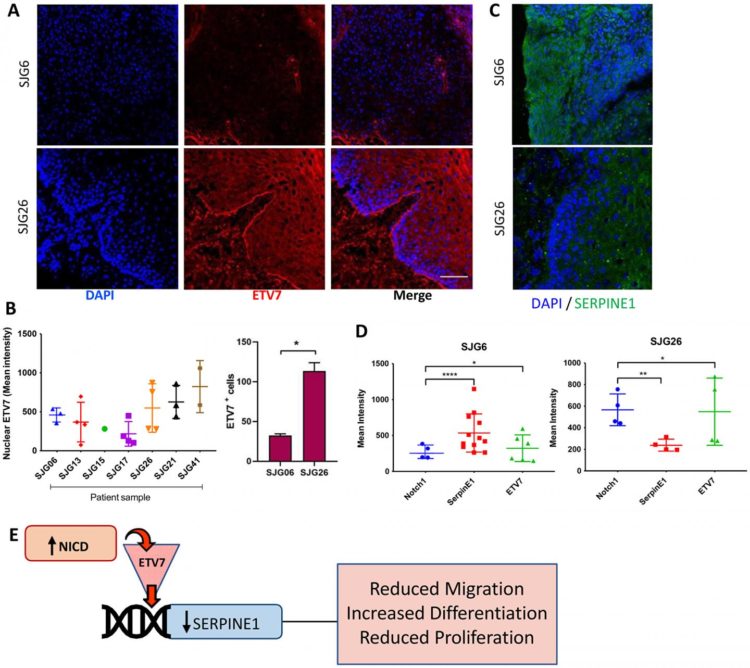
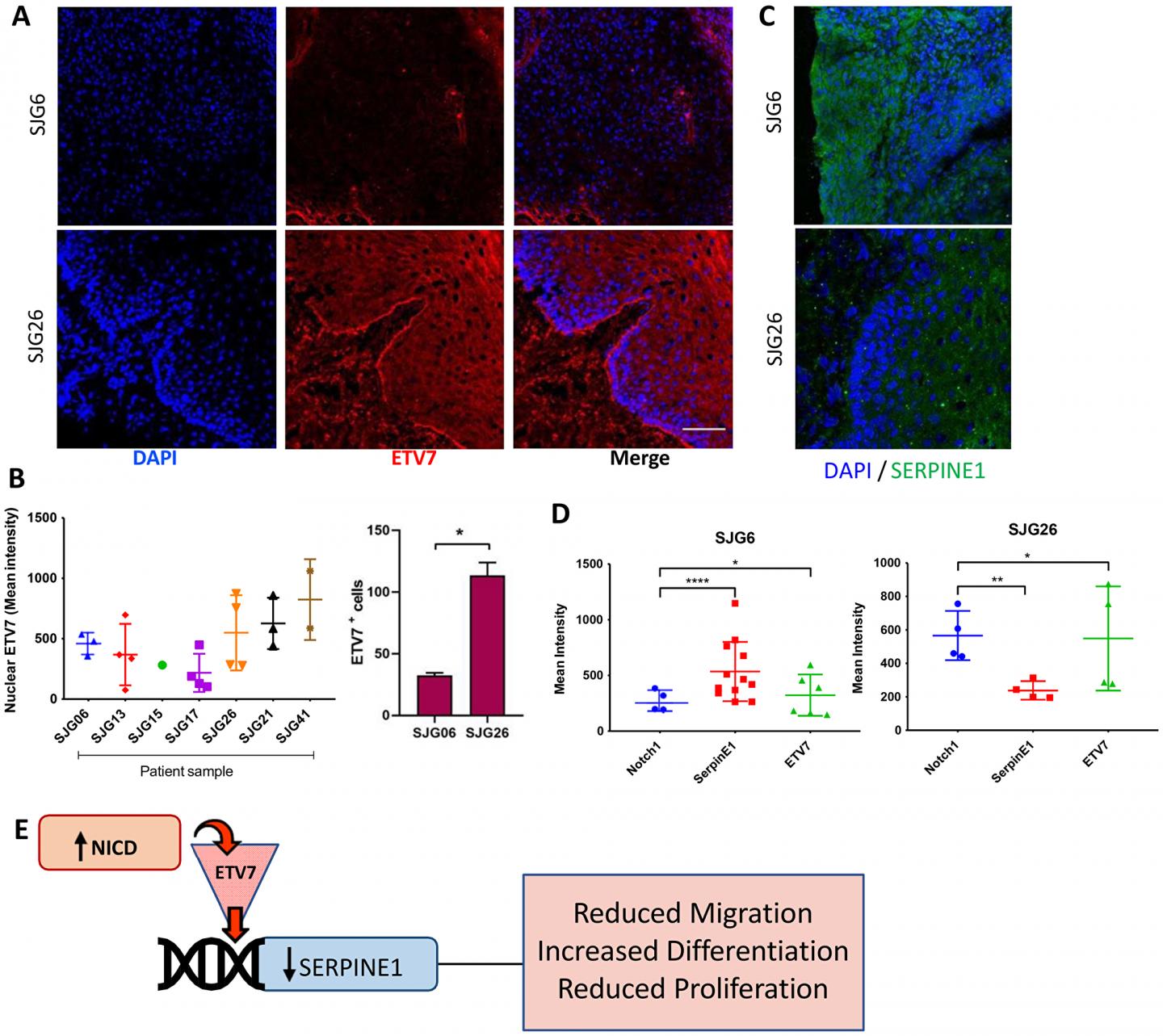
The cover for issue 63 of Oncotarget features Figure 6, “Inverse relationship between ETV7 and SERPINE1 in OSCC,” by Salameti, et al.
Credit: Correspondence to – Fiona M. Watt – [email protected]
The cover for issue 63 of Oncotarget features Figure 6, “Inverse relationship between ETV7 and SERPINE1 in OSCC,” by Salameti, et al.
In this study, the research team investigated NOTCH1 mutations in keratinocyte lines derived from OSCC biopsies that had been subjected to whole exome sequencing.
One line, SJG6, was found to have truncating mutations in both NOTCH1 alleles, resulting in loss of NOTCH1 expression.
Overexpression of the NOTCH1 intracellular domain in SJG6 cells promoted cell adhesion and differentiation, while suppressing proliferation, migration and clonal growth, consistent with the previously reported tumour suppressive function of NOTCH1 in OSCC.
Dr. Fiona M. Watt from the Centre for Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine, King’s College London, Tower Wing, Guy’s Hospital, London, UK said “Notch1 is a heterodimeric and multifunctional transmembrane receptor that regulates key cellular processes, including cell fate determination, maintenance of stem cells, cell survival, proliferation and apoptosis.”
Notch1 is a heterodimeric and multifunctional transmembrane receptor that regulates key cellular processes, including cell fate determination, maintenance of stem cells, cell survival, proliferation and apoptosis.
The majority of NOTCH1 mutations occur in the EGF-like ligand binding domain of the NECD, and prevent ligand binding and downstream signaling.
The detection of NOTCH1 mutations in dysplastic regions, and reduced expression of NOTCH1 in pre-neoplastic and cancerous skin lesions, suggests its potential gate-keeper properties.
Some studies have implicated Notch1 signaling in angiogenesis and therapy resistance in HNSCC, while in vitro studies have pointed to the role of NOTCH1 in promoting keratinocyte differentiation.
The Watt Research Team concluded that their study indicates that the tumour suppressive role of NOTCH1 in OSCC is manifested, at least in part, by ETV7-mediated suppression of SERPINE1.
###
Full text – http://www.
Correspondence to – Fiona M. Watt – [email protected]
Keywords – oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), NOTCH1, SERPINE1, ETV7/TEL2, cell adhesion
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a weekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit http://www.
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit http://www.
Media Contact
18009220957×105
[email protected]
Media Contact
Ryan James Jessup
[email protected]
202-638-9720
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.