Credit: NIAID
WHAT:
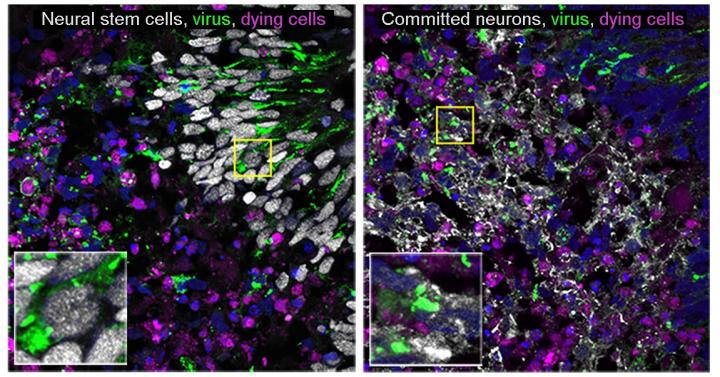
Scientists have determined that La Crosse virus (LACV), which can cause inflammation of the brain, or encephalitis, in children, affects brain cells differently depending on their developmental stage. Neurons–the primary brain cells of the central nervous system–evolve from neural stem cells and during development “commit” to becoming neurons. A new National Institutes of Health study shows that uncommitted neural stems cells generally survive LACV infection, while LACV often kills neurons. The study also shows that neurons infected by LACV can be rescued by interferon, a powerful antiviral protein. The study results appear in the Journal of Neuroinflammation.
LACV is spread by mosquitoes and was first identified in the early 1960s. Most infections in people are mild but the virus sometimes–particularly in children–enters the brain, infects neurons and causes disease ranging from learning and memory difficulties to paralysis, seizures and death. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention receives reports of an average of 68 LACV encephalitis cases each year in the United States, nearly all east of the Mississippi River.
The NIH scientists, from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, used cerebral organoids to model how LACV infects the human brain. Cerebral organoids are small spheres of human brain cells ranging in size from that of a poppy seed to a small pea. Importantly, cerebral organoids contain different neuronal cell types, which allowed the investigators to assess the sensitivity of neural stem cells and neurons to LACV infection.
After infecting cerebral organoids with LACV, the researchers observed that the virus was more likely to kill neurons, and they also found that the immune response to the virus was weaker in those cells than in neural stem cells. The largest observed difference was in genes activated by interferon, which are important in protecting cells from viruses.
The investigators then repeated the experiment, but this time treated the cerebral organoids with interferon 24 hours after infecting them. The therapy successfully protected neurons from virus-induced death. The scientists plan to continue developing their cerebral organoid model and studying the feasibility of using interferon to treat LACV infection and other viral diseases of the brain.
###
ARTICLE:
C Winkler et al. Neuronal maturation reduces the type I IFN response to orthobunyavirus infection and leads to increased apoptosis of human neurons. Journal of Neuroinflammation DOI: 10.1186/s12974-019-1614-1 (2019).
WHO:
Karin E. Peterson, Ph.D., and Clayton Winkler, Ph.D., neuroimmunology investigators in NIAID’s Laboratory of Persistent Viral Diseases, are available to comment on this study.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact Ken Pekoc, (301) 402-1663, [email protected].
NIAID conducts and supports research–at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide–to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
Media Contact
Ken Pekoc
[email protected]
301-402-1663
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




