Presented in a study by Mariana Nogueira and Mathieu De Craene, within the framework of the CardioFunxion project, led by Bart Bijnens (ICREA) and Gemma Piella, members of the Physense and SiMBioSys research groups at BCN MedTech
Credit: © 2019 Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.101594
Echocardiography is a test that uses ultrasound techniques to produce images of the heart in real time. Stress echocardiography uses this technique to evaluate the heart rate response while performing an activity in which the heart has to work (stress). Stress echocardiography can reveal traces of cardiovascular disease in its early stages, before it manifests, and so this technique becomes a valuable screening tool.
A protocol of stress echocardiography that has proved to have advantages in the clinical practice is obtained while performing handgrip exercises. However, the maximal exercise levels are not easily quantified and regulated, requiring the analysis of the complete data sequences (thousands of images), which poses a challenge for the clinician.
An analytical framework is proposed that explicitly addresses the practical challenges posed by analysing thousands of complete data and illustrates the potential of their study on a specific group of heart patients
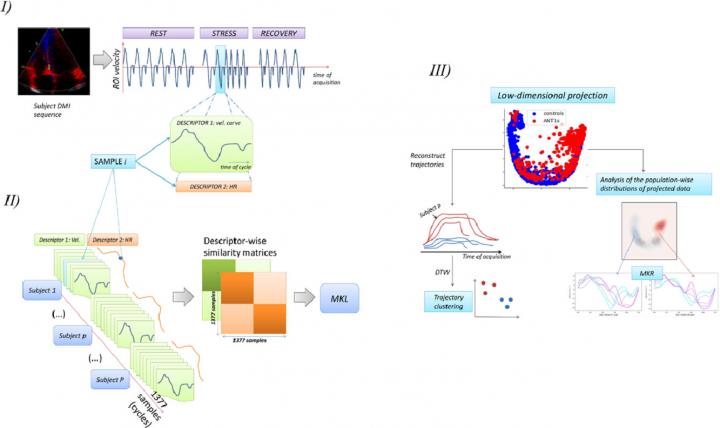
A study published in the journal Medical Image Analysis, proposes an operational framework for the analysis of this complex dataset. The article has just been published, on 6 November, in the advanced online edition. In this study, the physiological data of heart function are obtained by echocardiography while subjects performed a series of handgrip exercises. The data were integrated by Multiple Kernel Learning (MKL).
The study was coordinated by Bart Bijnens (ICREA-UPF) and Gemma Piella, researchers of the Physense and SiMBioSys research groups, respectively, which belong to the BCN MedTech research unit at the Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC) at UPF who work in the field of Machine Learning for clinical decision-making. Mariana Nogueira and Mathieu De Craene are the first authors of the article and researchers at Medisys Philips Research in Paris (France) within the framework of the CardioFunXion project. Sergio Sánchez Martínez is co-author and a member of SiMBioSys; Devyani Chowdhury, co-author of the study and a researcher at the University of Pennsylvania (USA).
An analytical framework based on machine learning
The authors propose an analytical framework that explicitly addresses the practical challenges posed by analysing thousands of complete data and illustrates the potential of their study on a specific group of heart patients. The article presents the results of image acquisitions obtained from 15 patients, 10 healthy and 5 with the ANT1 (Adenine Nucleotide Translocator-1) mutation, which affects cardiac cycles. For the study, the researchers analysed a total of 1,377 cardiac cycles.
“Our framework uses Multiple Kernel Learning (MKL) to project heterogeneous data retrieved during each cardiac cycle during the stress test in a low-dimensional space where the main data variations are encoded. Here, the stress response of each subject can be seen as a trajectory, and from the similarity between trajectories, the subjects can be allocated to groups that reflect different response patterns”, Bijnens and Piella explain.
MKL provides a simplified representation that is explored to discriminate groups of response and understand the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms
Then, the authors explain, the physiological interpretation of the results is decoded allowing reconstructing the input signals along any trajectory through the low-dimension output space. This simplified representation is explored to discriminate groups of response and understand the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms.
The authors have proposed a framework for analysing nonstandardized stress echocardiography sequences. Using unsupervised MKL, they combined the information on the myocardial velocity and heart rate to obtain a lower-dimensional representation of the data. The proposed framework is illustrated in the sequences of handgrip exercises acquired in a control group of healthy subjects and patients with the ANT1 mutation.
The results show that the methodology proposed by these experts in machine learning is able to discriminate between different responses and provide information about the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms, demonstrating its ability to analyse such complex datasets showing the potential of nonstandardized protocols, such as handgrip exercises to unmask differential cardiac response mechanisms. Indeed, the results confirm that the proposed framework is able, for each study subject, to distinguish healthy or pathological responses and record pathology-specific patterns.
###
Media Contact
UPF
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




