Credit: Credit: NASA JPL/Heidar Thrastarson
NASA analyzed the cloud top temperatures in Typhoon Kalmaegi using infrared light to determine the strength of the storm. Kalmaegi is known locally as Ramon in the Philippines where warnings are in effect.
Kalmaegi has triggered warnings in the Philippines. Philippines tropical cyclone wind signals include Signal #2 for the Luzon provinces of Cagayan (including Babuyan Islands), northern portion of Isabela (Sta Maria), San Pablo, Maconacon, Cabagan, Sto Tomas, Quezon, Delfin Albano, Tumauini and Divilacan, Apayao, Kalinga and Ilocos Norte. In addition, Signal #1 is in effect for the Luzon provinces of Batanes, Ilocos Sur, Abra, Mountain Province, Benguet, Ifugao, La Union, Northern Aurora (Dilasag), Casiguran and Dinalungan and the rest of Isabela.
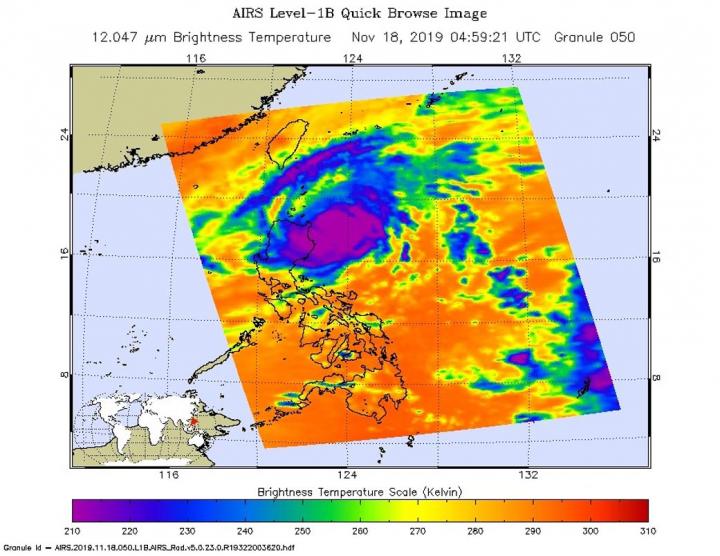
One of the ways NASA researches tropical cyclones is using infrared data that provides temperature information. Cloud top temperatures identify where the strongest storms are located. The stronger the storms, the higher they extend into the troposphere, and the colder the cloud temperatures.
On Nov. 19 at 4:59 UTC (Nov. 18 at 11:59 p.m. EST) NASA’s Aqua satellite analyzed the storm using the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument. The AIRS imagery showed the strongest storms circling the center of circulation, and over the northeastern side of Luzon, northern Philippines. In those areas, AIRS found coldest cloud top temperatures as cold as or colder 210 Kelvin minus 81 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 63.1 degrees Celsius). NASA research has shown that cloud top temperatures that cold indicate strong storms that have the capability to create heavy rain.
Tropical cyclones do not always have uniform strength, and some sides have stronger sides than others, so knowing where the strongest sides of the storms are located helps forecasters. NASA then provides data to tropical cyclone meteorologists so they can incorporate it in their forecasts.
At 10 a.m. EST (1500 UTC) on Nov. 19, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center or JTWC noted that the center of Kalmaegi was located near latitude 18.9 degrees north and longitude 123.0 degrees east. That puts the center about 282 nautical miles north-northeast of Manila, Philippines. Maximum sustained winds were near 75 knots (86 mph/139 kph).
Kalmaegi is turning into a westerly then southwesterly course, rounding the northern areas of Luzon. The storm will start to weaken as it moves southwest into the South China Sea.
Typhoons and hurricanes are the most powerful weather event on Earth. NASA’s expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
The AIRS instrument is one of six instruments flying on board NASA’s Aqua satellite which launched on May 4, 2002.
###
By Rob Gutro
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
Rob Gutro
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/



