Credit: Adapted from ACS Materials Letters 2019, DOI:
10.1021/acsmaterialslett.9b00376.
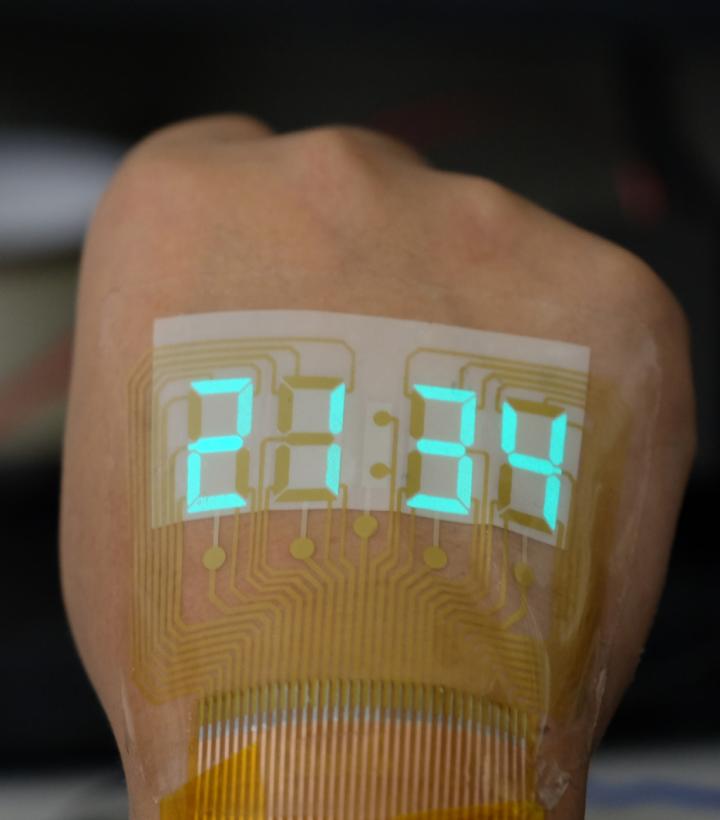
Imagine a runner who doesn’t need to carry a stopwatch or cell phone to check her time: She could just gaze at the glowing stopwatch display on the back of her hand. Such human-machine interfaces are no longer science fiction, but they still have a way to go before becoming mainstream. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Materials Letters have developed a stretchable light-emitting device that operates at low voltages and is safe for human skin.
Recently, scientists have developed stretchable light-emitting devices called alternating-current electroluminescent (ACEL) displays that can be stuck on skin or other surfaces like a temporary tattoo. However, the displays require relatively high voltages to achieve sufficient brightness, which could create safety concerns. So, Desheng Kong and colleagues wanted to develop an ACEL that could operate at lower voltages and thus be safer for human skin.
To make their device, the researchers sandwiched an electroluminescent layer, made of light-emitting microparticles dispersed in a stretchable dielectric material, between two flexible silver nanowire electrodes. The device contained a new type of dielectric material, in the form of ceramic nanoparticles embedded in a rubbery polymer, that increased the brightness compared with existing ACEL displays. They used this material to make a four-digit stopwatch display, which they mounted onto a volunteer’s hand. At low voltages, the stretchable display was sufficiently bright to be seen under indoor lighting. The bright stretchable display could find a broad range of applications in smart wearables, soft robotics and human-machine interfaces, the researchers say.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from National Key Research and Development Program of China, National Natural Science Foundation of China and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
The abstract that accompanies this study is available here.
The American Chemical Society, the world’s largest scientific society, is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us on Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]
301-775-8455
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




