Credit: Associate Professor Sirje Rüütel Boudinot
An article entitled “Human Peripheral Blood Eosinophils Express High Levels of the Purinergic Receptor P2X4” written by an international immunology research group was recently published in the scientific journal Frontiers in Immunology.
This is a collaborative work of scientists from the Immunology Laboratory of Tallinn University of Technology, from research institutes of Sweden, France and Taiwan (Karolinska Institutet, Université Paris-Saclay, INRA, National Tsing-Hua University); it also involved medical doctors from the North Estonia Medical Centre.
A member of the research group, Associate Professor at TalTech’s Division of Gene Technology Sirje Rüütel Boudinot says, “Our seven-year research focused primarily on the study of a pain receptor and its involvement in the potential development of inflammatory and cancerous lesions”.
The analysis was linked to previous studies of these laboratories targeting mechanisms of multiple sclerosis (MS). Multiple sclerosis is still an incurable but widespread disease of the central nervous system, which disrupts the smooth flow of nerve impulses. It causes an inflammatory autoimmune disorder – the body’s natural defences attack its own nervous tissue.
Dr Rüütel Boudinot says, “The role of the receptor P2X4 in the development of multiple diseases has been little explored so far. The receptor mediates interactions between a cell and the external environment, leading to its activation, i.e. to modification of its biology and metabolism. Our studies help to understand cells’ inflammatory response and involvement in pain.”
Since MS is an autoimmune disorder leading to brain lesions, the researchers explored possible mechanisms controlling immune cell activation, and their interactions with neurons and other cells of the brain.
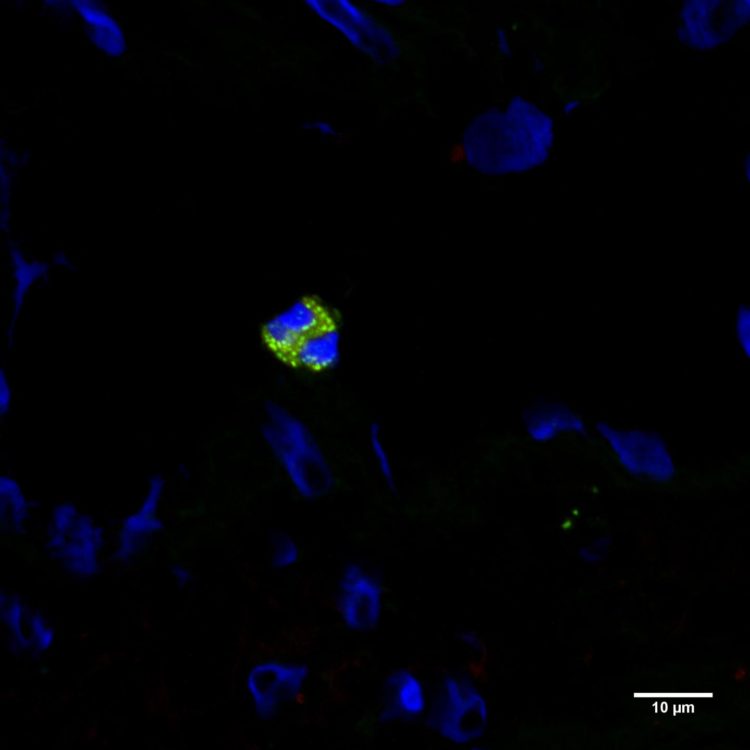
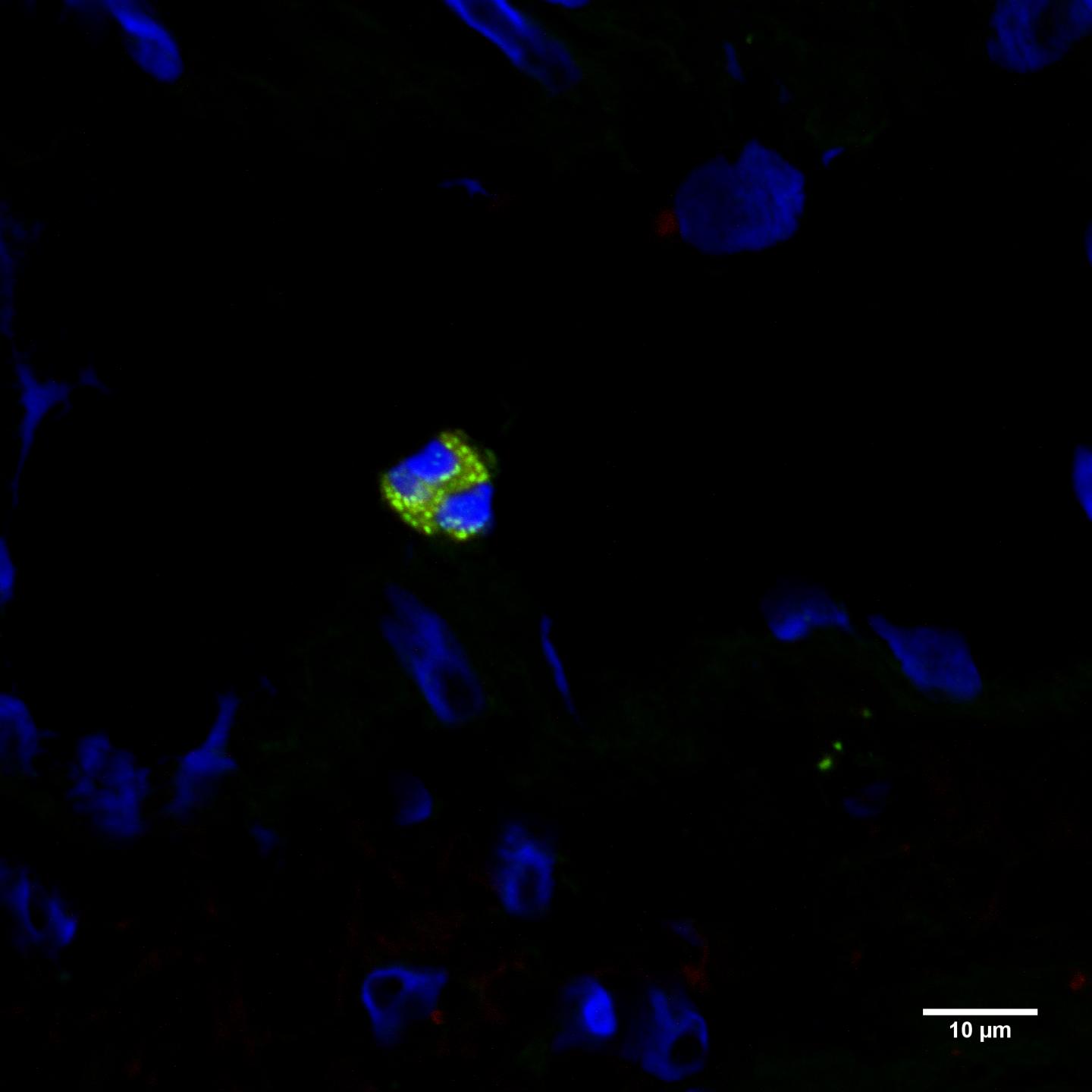
“In the course of the research, we used antibodies (specific markers) we produced, that are directed against the P2X4 receptor. P2X4 is an important receptor expressed by nerve cells. It plays a key role in pain hypersensitivity. So far, the expression and function of the P2X4 receptor has been mostly studied in the nervous system. This receptor, however, is engaged in a communication between the immune system and the nervous system.
The researchers demonstrated by using their marker that human eosinophils (a type of immune cells, subtype of leucocytes) express high levels of P2X4. This in turn means that the marker produced can be used for the study of allergies, as well as inflammatory and cancerous lesions in which these cells are involved. The analyses indicate that eosinophils could rapidly mediate signals from the nervous system.
“Our findings pave the way for future studies of the role of P2X4 receptors in eosinophil activation. They support the hypothesis that eosinophils play an important role in our immune system in addition to pain and other known functions. P2X4 receptors bind the neurotransmitter (ATP) adenosine triphosphate that can be associated with tumors; the expression level of P2X4 is also high in several tumors. In the future, we will explore the potential role of P2X4 in the control of eosinophil responses against cancerous lesions,” Dr Rüütel Boudinot says.
###
Additional information: Dr Sirje Rüütel Boudinot, [email protected]
Source: Frontiers in Immunology https:/
Kersti Vähi, TalTech Research Administration Office
Media Contact
Sirje Rüütel Boudinot
[email protected]
372-620-4430
Related Journal Article
http://dx.