Credit: Credit: NASA/NRL
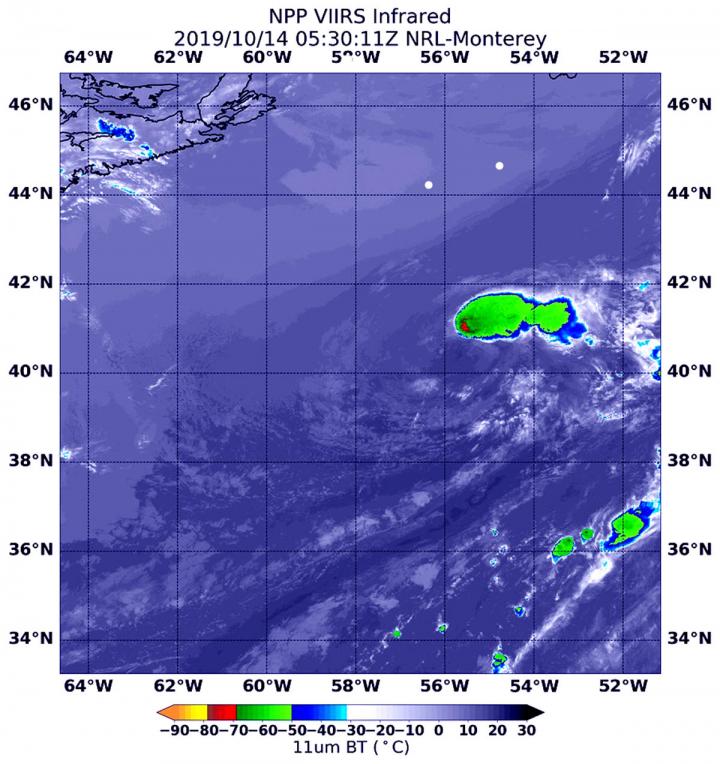
NASA’s Suomi NPP satellite passed over North Atlantic Ocean on Oct. 14 and provided forecasters with an infrared view of Tropical Storm Melissa that revealed wind shear was tearing the storm apart as it was becoming extra-tropical.
NASA’s Suomi NPP satellite used infrared light to analyze the strength of storms in Tropical Storm Melissa. Infrared data provides temperature information, and the strongest thunderstorms that reach high into the atmosphere have the coldest cloud top temperatures.
Melissa became an extra-tropical cyclone on Monday, Oct. 14. The only thunderstorms and precipitation associated with the circulation was displaced up to 100 miles east of the center in this infrared image from NASA-NOAA’s Suomi NPP satellite on Oct. 14, 2019 at 1:30 a.m. EDT (0530 UTC). That area had cloud top temperatures as cold as or colder than minus 70 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 56.6 Celsius). Cloud top temperatures that cold indicate strong storms with the potential to generate heavy rainfall.
That area of strong storms with coldest cloud tops were being pushed northeast by southwesterly wind shear. In general, wind shear is a measure of how the speed and direction of winds change with altitude. Tropical cyclones are like rotating cylinders of winds. Each level needs to be stacked on top each other vertically in order for the storm to maintain strength or intensify. Wind shear occurs when winds at different levels of the atmosphere push against the rotating cylinder of winds, weakening the rotation by pushing it apart at different levels.
The Suomi NPP satellite image also revealed that the inner-core consisted of a swirl of low clouds. NOAA’s National Hurricane Center (NHC) said the imagery also showed “a large amount of cool post-frontal stratocumulus wrapping into the northern and western portions of the circulation.”
What is Extra-tropical?
That means that a tropical cyclone has lost its “tropical” characteristics. The National Hurricane Center defines “extra-tropical” as a transition that implies both poleward displacement (meaning it moves toward the north or south pole) of the cyclone and the conversion of the cyclone’s primary energy source from the release of latent heat of condensation to baroclinic (the temperature contrast between warm and cold air masses) processes. It is important to note that cyclones can become extratropical and still retain winds of hurricane or tropical storm force.
Melissa’s Last Advisory
At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC), on Oct. 14, the NHC or National Hurricane Center issued the final advisory on the system. The center of Post-Tropical Cyclone Melissa was located near latitude 41.0 degrees north and longitude 51.4 degrees west. Melissa was moving toward the east near 23 mph (37 kph) and this general motion is expected to continue today through Tuesday. Maximum sustained winds were near 40 mph (65 kph) with higher gusts. NHC said, “Swells generated by Melissa are gradually subsiding along much of the U.S. east coast, portions of the Bahamas, Bermuda, and Atlantic Canada.”
The cyclone should gradually weaken before it dissipates today, Tuesday, Oct. 15.
Hurricanes are the most powerful weather event on Earth. NASA’s expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
###
Rob Gutro
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md
Media Contact
Rob Gutro
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




