Combining empirical knowledge and machine learning with a small experimental dataset
Credit: © Yuya Oaki
At JST Strategic Basic Research Programs, the research group led by associate professor Yuya Oaki and graduate student (at the time) Hiromichi Numazawa of Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University established a new design policy for organic materials for the anode of lithium-ion secondary cells in a joint work with research associate Yasuhiko Igarashi of Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo, through the use of Materials Informatics (MI)1). A high-capacity and high-stability material was successfully obtained via an extremely small number of experiments.
In order to conserve resources for batteries, organic materials without the use of metal is being researched worldwide. Traditionally, search for anode materials for lithium batteries and sodium-ion batteries had to rely on trial and error or experience and intuition of researchers.
MI generally performs machine learning for a large-scale data (big data), and is a technique that reduces involvement of researchers’ experience and intuition. One of the challenges was how experimental researchers use their own small-scale data and empirical knowledge.
The research group examined a method, “experiment-oriented MI”, which fuses small-scale but relatively accurate experimental data with experience and intuition of experimental researchers?, and has achieved improved yield of nanosheet materials and so on.
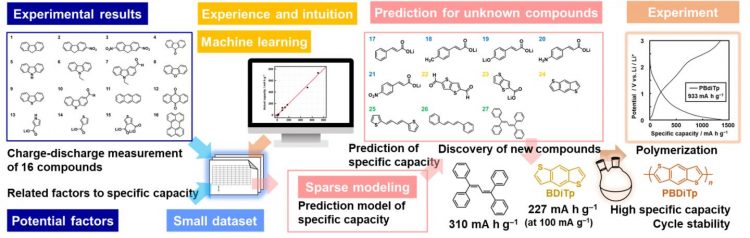
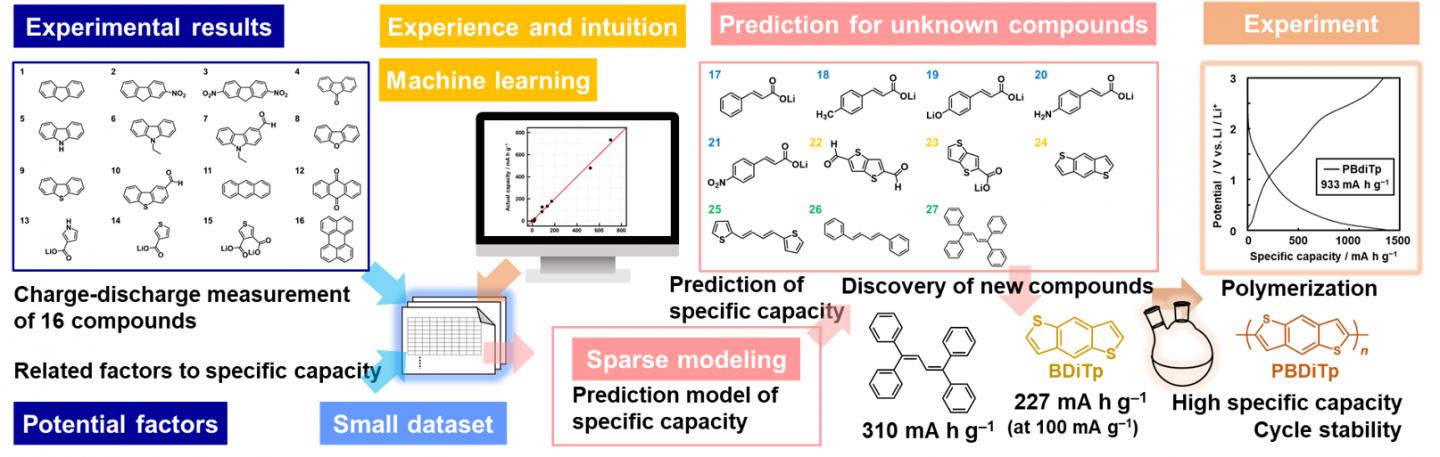
In this study, the capacity of 16 organic compounds as an anode was measured; further, a small number of factors that can determine the capacity using sparse modelingn2), which is a data science technique, was identified. Based on this result, a capacity prediction formula was developed by considering the identified factors as variables (prediction model). Next, 11 commercially available compounds, with expectation for a certain capacity as an anode, were selected partially based on the experience and intuition of researchers, and the predicted capacity value was calculated prior to the experiment. Further, the capacity of three compounds with the highest predicted value was measured, and two compounds were observed to exhibit high capacity. Subsequently, one of these compounds, the thiophene compound, was polymerized and a polymer anode material with improved capacity, durability, and quick charge-discharge property was obtained.
The design policy for the organic anode material established in the present study is important for further improvement in performance. Combining a small experimental dataset, experience and intuition of researchers, and machine learning led to a successful discovery of a high-performance material. It also showed the effectiveness of combining experimental science and MI in improving the efficiency of material search.
###
Note 1) Materials informatics (MI)
An academic field that incorporates computer informatics into material science. Compared to the conventional method of repeating experiments with various combinations of materials, it is able to efficiently search new materials or alternative materials.
Note 2) Sparse modeling
Based on an assumption that factors that explain a phenomenon are small in number (sparse), this method identifies the major factors included in data according to an appropriate specification. The overall image can be captured from limited information, and it is used in a wide range of fields such as clarifying MRI images. In the present study, we assumed that in search of organic material for battery anodes, important factors that determine capacity of anode would be small in number, and applied sparse modeling to identify important factors in predicting capacity.
Media Contact
Yuya Oaki
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.