Credit: Masaki Inada
An international collaboration led by scientists mainly at Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT) , Japan, has found that bone and muscle mass are regulated by the altered gravity. The experiments were done in space using Kibo, a ISS module developed by JAXA, and on the ground.
The researchers published their results on April 29th in the journal, Scientific Reports.
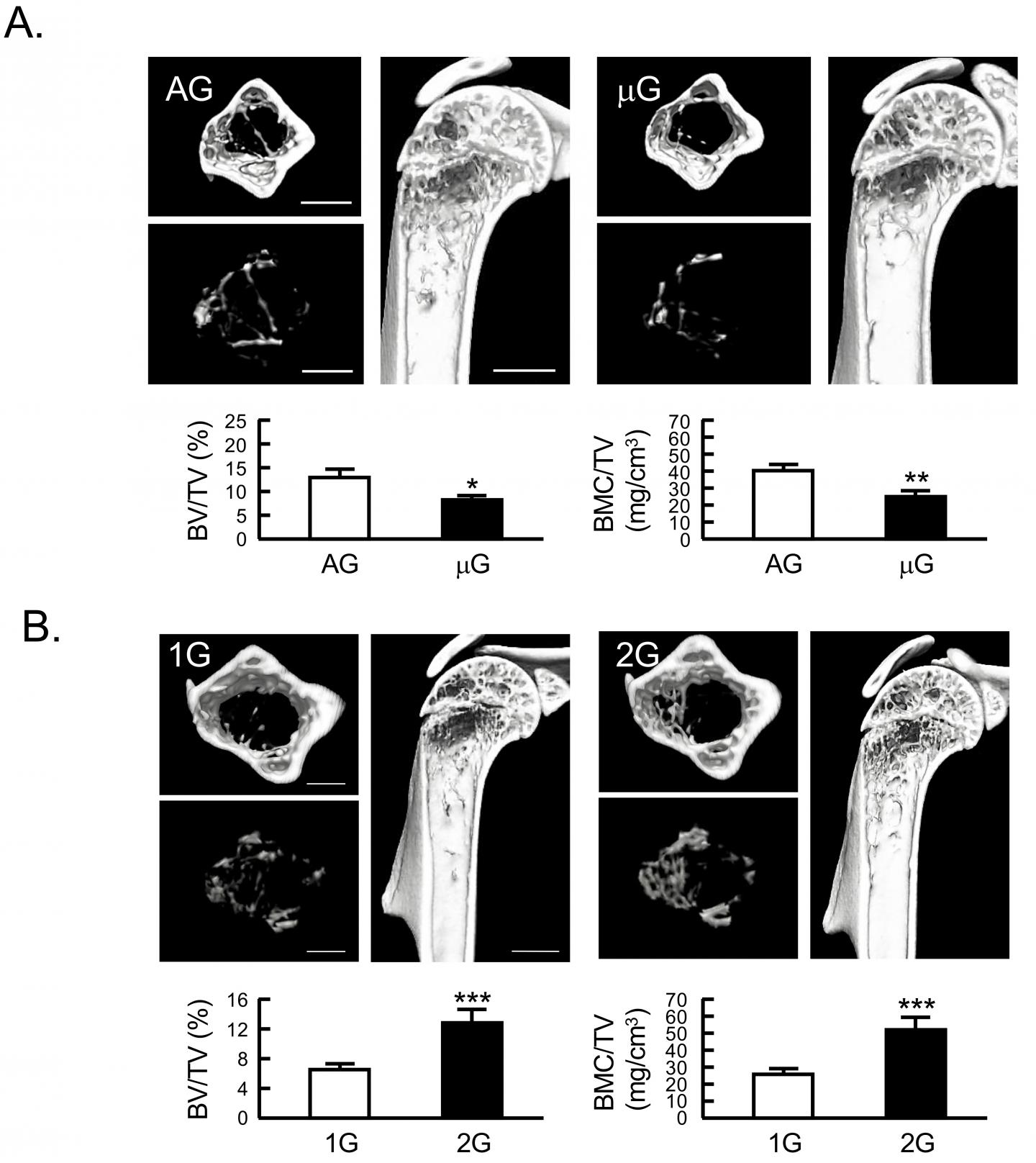
The research team explored the maintenance of the bone and muscle mass of mice among the opposite living circumstances of microgravity and hypergravity. “We examined the effects of 2G hypergravity on the ground and artificial 1G gravity in space for the effect of bone and muscle mass using newly developed centrifuge devices”, said Dr Masaki Inada, corresponding author on the paper and Associate Professor in the Department of Biotechnology and Life Science, Institute of Global Innovation Research at TUAT.
The team found that changing gravity with a physical load of own body weight altered the bone mass of forefoot (humerus) especially in fourth-foot walk animals (tetrapods) such as mice. For example, lower gravity, which was in space, showed loss in some bones such as the humerus and tibia. In addition, more gravity, which was in 2G on the ground artificially created by the centrifuge device, made more muscle such as the lower leg muscles (muscles from knee to ankle).
“Then we continuously examine to find the mechano-sensing factors regulated by mechanical stress in the mice for altered living circumstances of the gravity”, said Dr Inada. “To find forth dependent mechano-sensor results in controlling bone and muscle mass could be applied for novel drug development for the bone and muscle of skeletal diseases with disuse ability such as sarcopenia and osteoporosis.”
###
About Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT)
TUAT is a distinguished university in Japan dedicated to science and technology. TUAT focuses on agriculture and engineering that form the foundation of industry, and promotes education and research fields that incorporate them. Boasting a history of over 140 years since our founding in 1874, TUAT continues to boldly take on new challenges and steadily promote fields. With high ethics, TUAT fulfills social responsibility in the capacity of transmitting science and technology information towards the construction of a sustainable society where both human beings and nature can thrive in a symbiotic relationship. For more information, please visit http://www.
Original publication:
Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 29;9(1):6614. Hypergravity and microgravity exhibited reversal effects on the bone and muscle mass in mice. Tominari T, Ichimaru R, Taniguchi K, Yumoto A, Shirakawa M, Matsumoto C, Watanabe K, Hirata M, Itoh Y, Shiba D, Miyaura C, Inada M.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42829-z.
Contact:
Masaki Inada, DDSC., PhD,
Associate Professor,
Department of Biotechnology and Life Science, Institute of Global Innovation Research,
Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology.
Email: [email protected]
Media Contact
Yutaka Nibu, PhD
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




