The global search for a group Strep A vaccine has narrowed after researchers identified a common gene signature in almost all global Strep A strains by sequencing thousands of genomes in a project spanning 10 years and more than 20 countries
Credit: The Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity
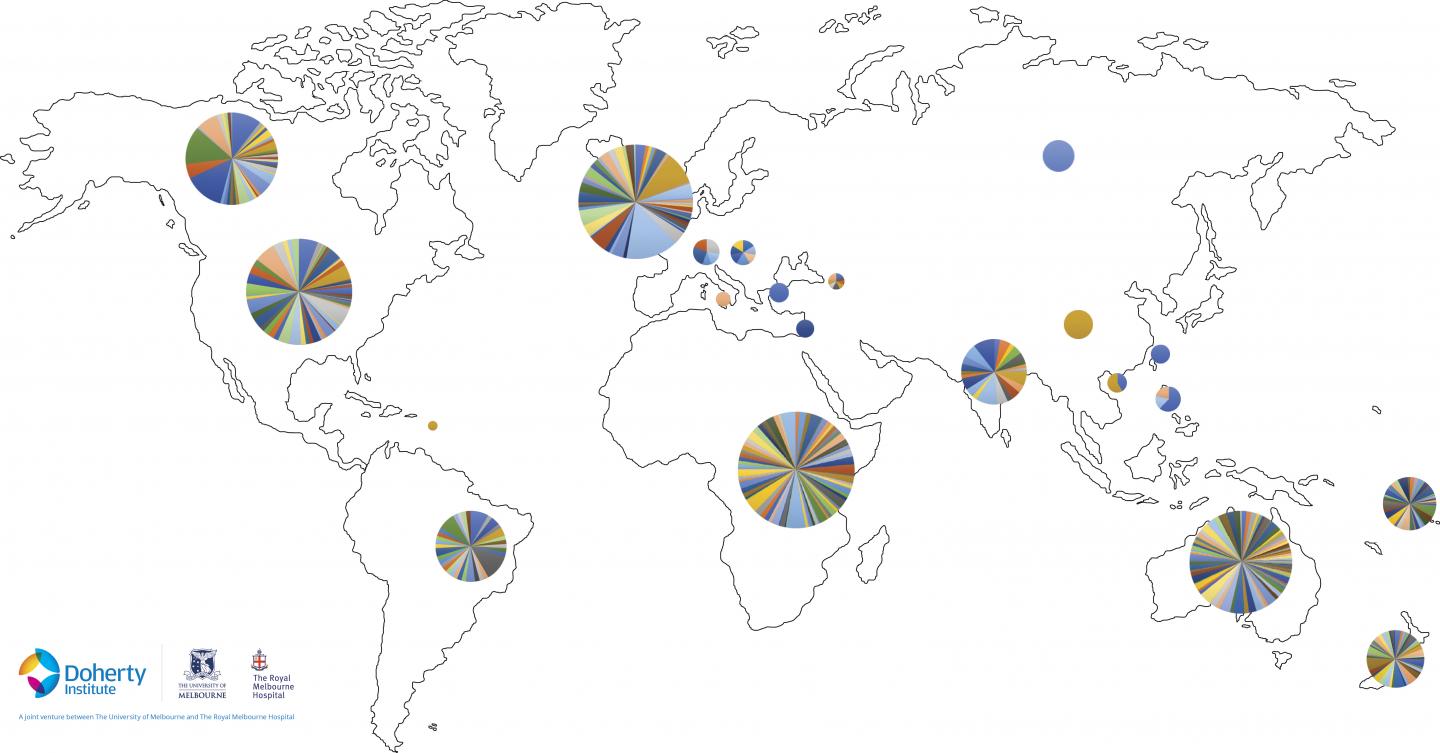
The global search for a group A streptococcal (Strep A) vaccine has narrowed after researchers identified a common gene signature in almost all global Strep A strains by sequencing thousands of genomes in a project spanning 10 years and more than 20 countries.
Strep A, is a bacterial pathogen that in some regions of the world is a very common cause of skin sores
and sore throats. In these endemic regions, a large proportion of the population is constantly exposed
to Strep A – left untreated can lead to rheumatic heart disease. Aboriginal Australians experience one of the highest incidences of rheumatic heart disease in the world.
Globally, Strep A is estimated to cause more than half a million deaths per year due to invasive and immune-mediated diseases1.
Published today in Nature Genetics, a research project by the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute), the Wellcome Sanger Institute in the UK and the University of Queensland, collated Strep A isolates from endemic areas around the world.
Lead author, University of Melbourne Dr Mark Davies, Doherty-Sanger Fellow at the Doherty Institute and the Wellcome Sanger Institute, said there is a knowledge gap of Strep A in endemic settings with most of the information on the bacterial pathogen coming from high-income settings in Australia, the
UK and the US.
“We have little knowledge of the bugs that live and drive disease in endemic areas. So for the past 10 years we have been collating isolates from all over the world – Africa, the Pacific, New Zealand and Australian Aboriginal communities – to determine the specifics of the pathogen, how it causes disease and why it is different in the endemic regions to high-income regions,” Dr Davies explained.
“Using large-scale genomic sequencing, we identified the existence of more than 290 genetically different lineages of clinically important Strep A, highlighting the challenges of designing an effective global vaccine.”
The project found that current leading Strep A vaccine candidates would have limited coverage in the areas where the vaccine is most needed, in streptococcal endemic settings.
“However, using all the data we collected, we narrowed down common gene signatures in almost all strains of Strep A globally, which is a tremendous step forward in identifying what may work as a global vaccine candidate,” Dr Davies said.
Professor Gordon Dougan, an author from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and University of Cambridge, said millions of people around the world are affected by Strep A.
“It can cause a range of conditions, from sore throats and outbreaks of scarlet fever in the UK, to infections leading to rheumatic heart diseases in populations such as the Australian Aboriginal population,” Professor Dougan said.
“In addition to aiding research into a vaccine, genomic data from our study will help researchers understand how Strep A causes disease and why it is different in high-income areas to endemic
regions.”
In February this year, the Australian Medical Research Future Fund announced an injection of $35 million to advance the development of a Strep A vaccine.
Australian Infectious Diseases Research Centre Director, Professor Mark Walker of the University of Queensland, said this research has the potential to fast track a Strep A vaccine.
“Vaccine developers and the wider scientific community can now use the database that we have created to identify the most common genes to aid in the development of what could be an effective group A strep vaccine,” Professor Walker said.
“I believe a global vaccine is possible – renewed momentum through our and other research findings, in addition to increased funding commitments, will enhance the drive for a global vaccine.”
###
Media Contact
Catherine Sommerville
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




