A detailed new model of a bacterial secretion system provides directions for developing precisely targeted antibiotics
Credit: Caltech
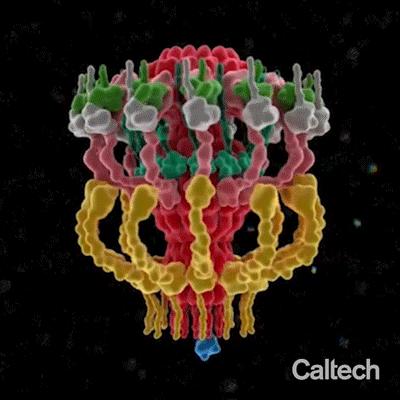
Gastric cancer, Q fever, Legionnaires’ disease, whooping cough–though the infectious bacteria that cause these dangerous diseases are each different, they all utilize the same molecular machinery to infect human cells. Bacteria use this machinery, called a Type IV secretion system (T4SS), to inject toxic molecules into cells and also to spread genes for antibiotic resistance to fellow bacteria. Now, researchers at Caltech have revealed the 3D molecular architecture of the T4SS from the human pathogen Legionella pneumophila with unprecedented details. This could in the future enable the development of precisely targeted antibiotics for the aforementioned diseases.
The work was done in the laboratory of Grant Jensen, professor of biophysics and biology and Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator, in collaboration with the laboratory of Joseph Vogel at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis (WUSTL). A paper describing the research appeared online on April 22 in the journal Nature Microbiology.
There are nine different types of bacterial secretion systems, Type IV being the most elaborate and versatile. A T4SS can ferry a wide variety of toxic molecules–up to 300 at once–from a bacterium into its cellular victim, hijacking cellular functions and overwhelming the cell’s defenses.
In 2017, Caltech postdoctoral scholar Debnath Ghosal and his collaborators used a technique called electron cryotomography to reveal, for the first time, the overall low-resolution architecture of the T4SS in Legionella, the bacteria that causes Legionnaires’ disease, a severe and often lethal form of pneumonia.
Ghosal, along with Kwangcheol Jeong of WUSTL and their colleagues, have now made a detailed structural model of this dynamic multi-component machine. The team also made precise perturbations to the bacterium’s genes to study mutant versions of the T4SS, revealing how this complex machine organizes and assembles.
The model revealed that the secretion system is composed of a distinct chamber and a long channel, like the chamber and barrel of a gun. Characterizing these and other components of the T4SS could enable the development of precisely targeted antibiotics.
Current antibiotics act broadly and wipe out bacteria throughout the body, including the beneficial microorganisms that live in our gut. In the future, antibiotics could be designed to block only the toxin delivery systems (such as the T4SS) of harmful pathogens, rendering the bacteria inert and harmless without perturbing the body’s so-called “good bacteria.”
###
The paper is titled “Molecular architecture, polar targeting and biogenesis of the Legionella Dot/Icm T4SS.” Ghosal and Jeong are co-first authors. In addition to Jensen and Vogel, other co-authors are former Caltech postdoctoral scholar Yi-Wei Chang, now of the University of Pennsylvania; Jacob Gyore of WUSTL; Lin Teng of the University of Florida; and Adam Gardner of the Scripps Research Institute. The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Media Contact
Lori Dajose
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




