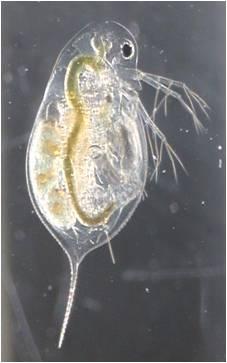
Credit: Eric von Elert
Water fleas – or Daphnia – ensure their survival by reacting to a signal substance of their predators (fish) with flight. The zoologist Meike Anika Hahn from Professor Dr Eric von Elert’s research group at the University of Cologne’s Institute of Zoology has identified this chemical messenger substance, which the fish releases into the water of lakes. When the water flea detects the substance ‘5α-cyprinol sulfate’ – a bile salt from the fish – it leaves the upper water layers and descends vertically into darker regions. The fish are unable to visually detect their prey there during daytime. This connection between the signal of the predator and the behaviour of its prey has now been published in the scientific journal eLife under the title ‘5α-cyprinol sulfate, a bile salt from fish, induces diel vertical migration in Daphnia’.
Eric von Elert explains how crucial this communication between fish and planktonic crustacean is to a healthy water environment: ‘The water flea is an important link in the lake’s ecosystem because it mainly feeds on the constantly growing microalgae. It is crucial for the lake that the Daphnia remain in their natural habitat – the surface of the water – and do not spend the day in the depths where they cannot find any algae. Therefore, it is important to know exactly which signal the water flea reacts to.’ Daphnia migrate up to 60 metres up and down the water column every day.
The bile salt in question is vital for the metabolism of fish, which is why, from an evolutionary perspective, they cannot stop releasing it into the water. Now that the substance has been identified, follow-up studies can be carried out to explore whether the fish are actually solely responsible for high concentrations of 5α-cyprinol sulphate. ‘It is possible that the substance also comes from contamination from wastewater facilities,’ says Professor von Elert.
In aquatic systems such as lakes, an enormous number of chemical reactions and interactions take place that the scientists need to understand the basics of. Especially if an intact system is disturbed from the outside, this can have serious consequences. ‘Ultimately, we want to find out how we might be able to restore the biological balance by adding specific natural ingredients’, von Elert concludes.
###
Media Contact
Eric von Elert
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




