UVA IDs natural process tumors co-opt to feed their growth, spread
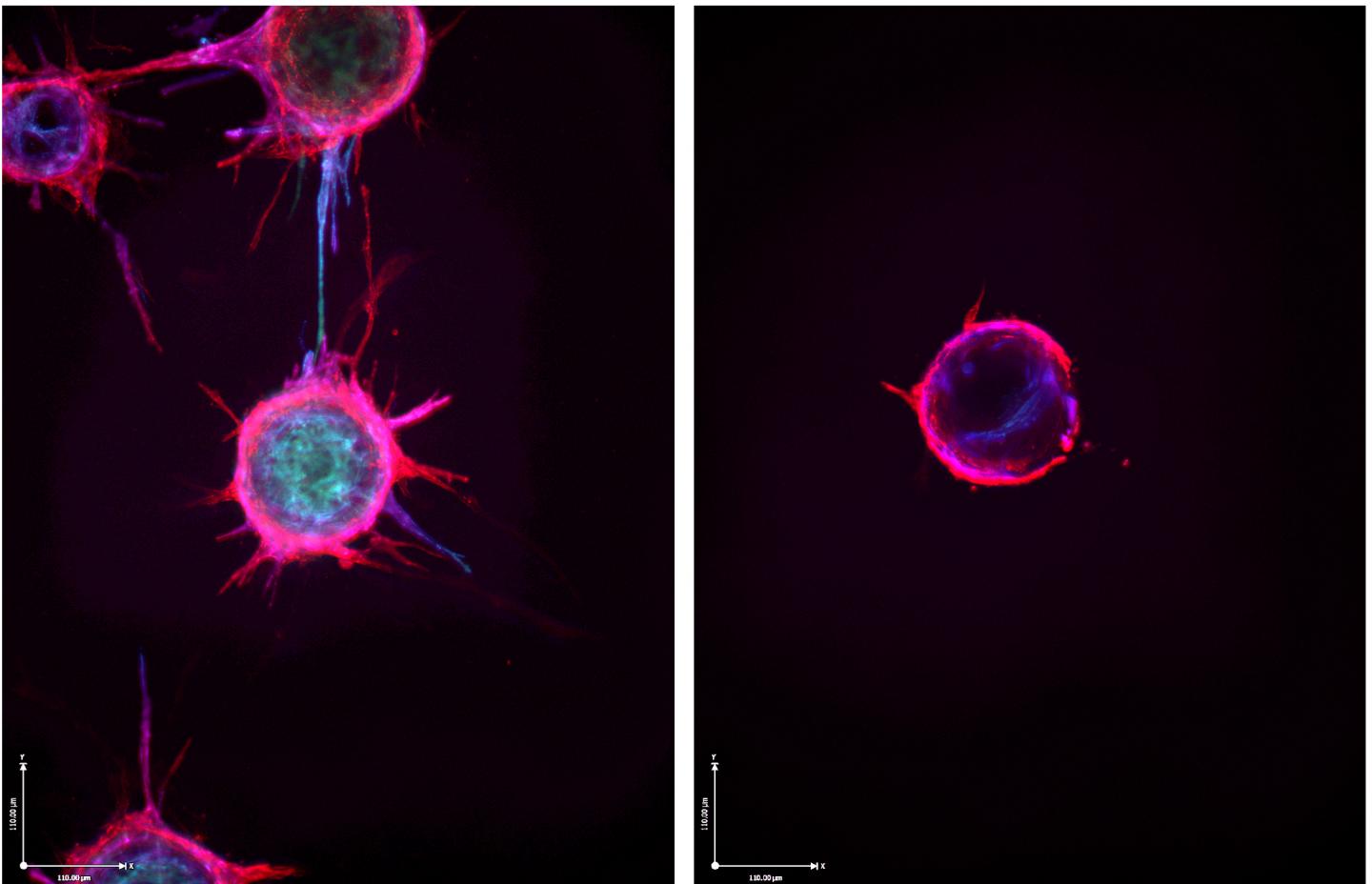
Credit: Courtesy Dudley Lab, UVA School of Medicine
Researchers at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have shed light on how cancers hijack the body’s natural wound-healing response to grow and spread.
The researchers have identified specific processes within endothelial cells – the cells that line blood vessels – that tumors use to build out their own blood supply. These processes are normally used by the body to repair tissue, heal injuries and grow new blood vessels, but tumors co-opt them to create blood vessels that will nourish them and feed their growth.
“A tumor is not just a ball of malignant cancer cells, right? It’s almost like a little miniature organ that creates or co-opts its own blood supply,” explained Andrew C. Dudley, PhD, of UVA’s Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Cancer Biology. “A tumor steals as it’s growing and developing. It steals physiological processes that help it along. And one of those processes is wound healing. And that’s what we’ve been studying – how the tumor subverts this process of wound healing.”
Unexpected Diversity
Intriguingly, the research suggests that endothelial cells have a previously unknown degree of specialization that varies among individual cells. Some appear to have a better ability to form new blood vessels than others.
PhD student James V. McCann was able, using some cutting-edge methodologies, to stratify various endothelial cells based on what he called their “functional diversity.” This was based partly on the amount of a particular type of microRNA, and the gene it targets, inside the cells. MicroRNAs are tiny molecules responsible for controlling the expression of genes, a process that goes haywire in cancer.
Endothelial cells that were rich in this particular microRNA struggled to sprout new blood vessels, he found, while those with less were better at it. The amount varied even among individual endothelial cells within a developing tumor.
Looking at breast cancer samples, the researchers were able to determine that patients with the best outcomes were those with the highest levels of the microRNA. Further, delivering the microRNA to the endothelial cells of a developing tumor in mice significantly reduced the number of blood vessels and slowed overall tumor growth, McCann found.
The researchers caution that there are obstacles that prevent their work from being immediately applicable in people. Treating breast cancer won’t be as simple as giving patients more of this specific microRNA. However, the scientists are excited to have shed light on a vascular-directed process that cancer exploits to create its own blood supply, and to have given scientists new leads in the battle against the disease.
“Cancer as an un-healing wound is an old hypothesis” McCann said. “But we have identified a new way tumors subvert the wound healing process for growth and development.”
###
The researchers have published their findings in the Journal of Clinical Investigation and was featured on the cover. The research team consisted of McCann, Lin Xiao, Dae Joong Kim, Omar F. Khan, Piotr S. Kowalski, Daniel G. Anderson, Chad V. Pecot, Salma H. Azam, Joel S. Parker, Yihsuan S. Tsai, Alisa S. Wolberg, Stephen D. Turner, Kohei Tatsumi, Nigel Mackman and Dudley. Anderson disclosed that he has a patent related to the work.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, including grants RO1-CA177874 and P30-CA14051; the American Cancer Society, grant 129755-RSG-16-176-01-DDC; and an AACR-Bayer Innovation and Discovery Grant, 17-80-44-DUDL. In addition, the work was partially supported by the U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command’s Armed Forces Institute of Regenerative Medicine, grant W81XWH-08-2-0034.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog at http://makingofmedicine.
Media Contact
Josh Barney
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




