Credit: Rohan Shirwaiker, NC State University
North Carolina State University researchers have developed a technique to improve the characteristics of engineered tissues by using ultrasound to align living cells during the biofabrication process.
“We’ve reached the point where we are able to create medical products, such as knee implants, by printing living cells,” says Rohan Shirwaiker, corresponding author of a paper on the work and an associate professor in NC State’s Edward P. Fitts Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering. “But one challenge has been organizing the cells that are being printed, so that the engineered tissue more closely mimics natural tissues.
“We’ve now developed a technique, called ultrasound-assisted biofabrication (UAB), which allows us to align cells in a three-dimensional matrix during the bioprinting process. This allows us to create a knee meniscus, for example, that is more similar to a patient’s original meniscus. To date, we’ve been able to align cells for a range of engineered musculoskeletal tissues.”
To align the cells, the researchers built an ultrasound chamber that allows ultrasonic waves to travel across the area where a bioprinter prints living cells. These ultrasonic waves travel in one direction and are then reflected back to their source, creating a “standing ultrasound wave.” The soundwaves effectively herd the cells into rows, which align with areas where the ultrasound waves and the reflected waves cross each other.
“We can control the alignment characteristics of the cells by controlling the parameters of the ultrasound, such as frequency and amplitude,” Shirwaiker says.
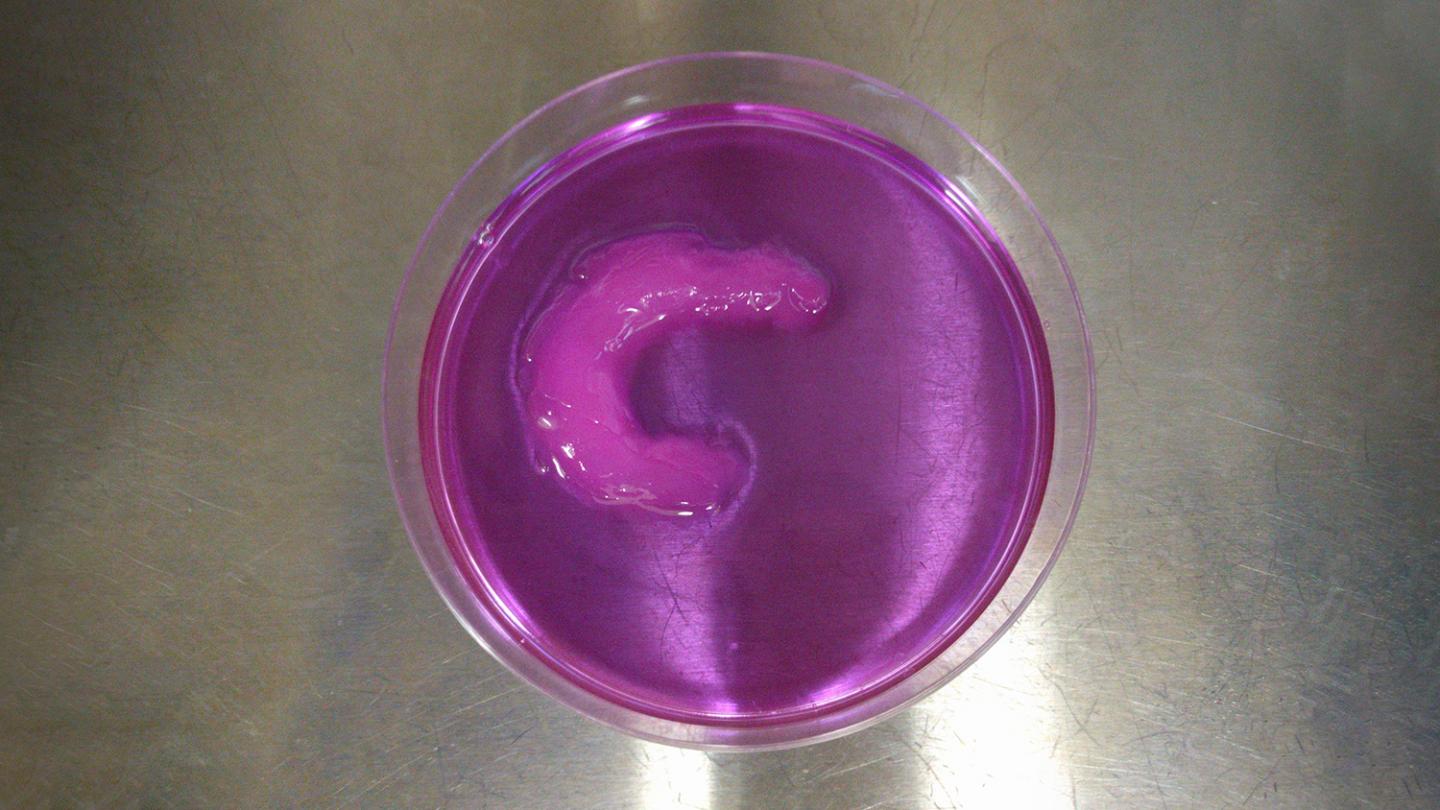
To demonstrate the viability of the UAB technique, the researchers created a knee meniscus, with the cells aligned in a semilunar arc – just as they are in a natural meniscus.
“We were able to control the alignment of the cells as they were printed, layer by layer, throughout the tissue,” Shirwaiker says. “We’ve also shown the ability to align cells in ways that are particularly important for other orthopedic soft tissues, such as ligaments and tendons.”
The researchers also found that some combinations of ultrasound parameters led to cell death.
“This is important, because it gives us a clear understanding of both what we can do to improve tissue performance and what we need to avoid in order to preserve living cells,” Shirwaiker says.
To that end, the researchers have created computational models that allow users to predict the performance of any given set of parameters before beginning the biofabrication process.
One other benefit of the UAB technique is that it is relatively inexpensive.
“There’s a one-time cost for setting up the ultrasound equipment – which can use off-the-shelf technology” Shirwaiker says. “After that, the operating costs for the ultrasound components are negligible. And the UAB technique can be used in conjunction with most existing bioprinting technologies.
“We have a patent pending on the UAB technique, and are now looking for industry partners to help us explore commercialization,” Shirwaiker says.
###
The paper, “Ultrasound-assisted biofabrication and bioprinting of preferentially aligned three-dimensional cellular constructs,” is published in the journal Biofabrication. First author of the paper is Parth Chansoria, a Ph.D. student and Provost Doctoral Fellow at NC State. The paper was co-authored by Lokesh Karthik Narayanan and Karl Schuchard, who are Ph.D. students at NC State.
The work was done with support from the National Science Foundation’s Faculty Early Career Development Program, under grant number 1652489.
Media Contact
Matt Shipman
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




